All MCAT Biology Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #21 : Cellular Processes And Functions
Which answer choice incorrectly matches the type of chromatin with the phase of mitosis?
Heterochromatin—interphase
Euchromatin—telophase
Heterochromatin—prophase
Euchromatin—interphase
Heterochromatin—metaphase
Euchromatin—telophase
DNA is stored in loosely wound euchromatin before mitosis. During mitosis, the DNA condenses into chromosomes, which are made of heterochromatin. It becomes more dense during prophase, and stays that way until the end of mitosis. Euchromatin is more lightly packed than heterochromatin.
Mitosis follows the following sequence: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis. Interphase refers to the time period between mitotic divisions. During interphase, most DNA is euchromatin, but some regions remain as heterochromatin to prevent unwanted transcription; thus DNA exists as both types of chromatin during interphase, but only as heterochromatin during mitosis. Matching euchromatin to telophase is the answer, as this is a false statement.
Example Question #11 : Mitosis And Meiosis
Something goes wrong during meiosis in a male and the four daughter sperm cells that are produced all have the wrong amount of chromosomes. Two of the sperm have one extra chromosome and the other two have one missing chromosome. At what step did the problem most likely occur, and what was it?
Telophase I—deletion
Metaphase I—nondisjunction
Telophase II—translocation
Prophase I—trisomy
Anaphase I—inversion
Metaphase I—nondisjunction
If nondisjunction occurs in Metaphase I, then one extra chromosome composed of two tetrads would go into one of the cells starting metaphase II while the other would have one less. This extra chromosome would then undergo the rest of meiosis normally, leaving an extra chromosome, composed of one tetrad in two of the daughter sperm. These are the two that are missing from the other daughter sperm.
Example Question #1352 : Biology
When does genetic crossover occur during meiosis?
Telophase II
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Prophase I
This is a simple memorization problem. Crossover occurs when the nucleus decondenses. The chromosomes are able to crossover during prophase I when chromosome pairs are aligned next to one another. Crossover cannot occur later in meiosis, as the chromosomes have already been separated.
Example Question #1353 : Biology
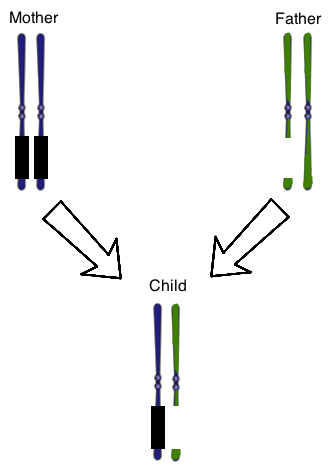
The concept of genomic imprinting is important in human genetics. In genomic imprinting, a certain region of DNA is only expressed by one of the two chromosomes that make up a typical homologous pair. In healthy individuals, genomic imprinting results in the silencing of genes in a certain section of the maternal chromosome 15. The DNA in this part of the chromosome is "turned off" by the addition of methyl groups to the DNA molecule. Healthy people will thus only have expression of this section of chromosome 15 from paternally-derived DNA.
The two classic human diseases that illustrate defects in genomic imprinting are Prader-Willi and Angelman Syndromes. In Prader-Willi Syndrome, the section of paternal chromosome 15 that is usually expressed is disrupted, such as by a chromosomal deletion. In Angelman Syndrome, maternal genes in this section are deleted, while paternal genes are silenced. Prader-Willi Syndrome is thus closely linked to paternal inheritance, while Angelman Syndrome is linked to maternal inheritance.
Figure 1 shows the chromosome 15 homologous pair for a child with Prader-Willi Syndrome. The parental chromosomes are also shown. The genes on the mother’s chromosomes are silenced normally, as represented by the black boxes. At once, there is also a chromosomal deletion on one of the paternal chromosomes. The result is that the child does not have any genes expressed that are normally found on that region of this chromosome.
A scientist is investigating a cell undergoing division, and notes that chromosome 15 is aligned with the other chromosomes in the center of the cell, as if along a line. Each of the 23 pairs of chromosomes is arranged as a tetrad along this plate. Which phase of cell division is this cell most likely undergoing?
Metaphase of mitosis
Metaphase I
Anaphase of mitosis
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Metaphase I
Metaphase I is the best answer. Because the chromosomes are arranged as tetrads, we know that it is in meiosis I. Only in meiosis I do we separate homologous chromosome pairs, rather than sister chromatids.
Additionally, because the chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell, metaphase is the most likely phase of meiosis. Anaphase involves the separation of chromosomes, and telophase is the terminal phase after full separation is accomplished.
Example Question #22 : Cellular Processes And Functions
Which of the following processes occur in meiosis but do not occur in mitosis?
I. Spindle formation
II. Separation of homologous chromosomes
III. Separation of sister chromatids
IV. Recombination
II only
II and IV
I, II, and III
I, II, III, and IV
II and IV
Mitosis and meiosis are similar processes that yield very different results. One of the major differences is that meiosis separates homologous chromosomes prior to separating sister chromatids. This is what leads to the reduction of ploidy. Both processes involve spindle formation (the microtubule apparatus that pulls the chromosomes/chromatids apart). Recombination is a phenomenon unique to meiosis that results in increasing genetic diversity.
Example Question #1355 : Biology
Cellular division is an essential part of the cell cycle. When a cell divides it passes genetic information to daughter cells. The amount of genetic information passed on to daughter cells depends on whether the cell undergoes mitosis or meiosis. Mitosis is the most common form of cell division. All somatic cells undergo mitosis, whereas only germ cells undergo meiosis. Meiosis is very important because it produces gametes (sperm and eggs) that are required for sexual reproduction. Human germ cells have 46 chromosomes (2n = 46) and undergo meiosis to produce four haploid daughter cells (gametes).
Meiosis is a form of __________ reproduction and mitosis is a form of __________ reproduction.
asexual . . . asexual
sexual . . . asexual
sexual . . . sexual
asexual . . . sexual
sexual . . . asexual
The key difference between sexual and asexual reproduction is recombination. If a process involves shuffling of genetic material between chromosomes (recombination), then it is sexual reproduction. Recall that crossing over, a type of genetic recombination, occurs during prophase I of meiosis. This leads to the production of daughter cells that are distinct from the parents; therefore, meiosis is a form of sexual reproduction.
In mitosis there is no genetic recombination and the daughter cells are identical to the parent cells; therefore, mitosis is a form of asexual reproduction.
Example Question #1356 : Biology
Cellular division is an essential part of the cell cycle. When a cell divides it passes genetic information to daughter cells. The amount of genetic information passed on to daughter cells depends on whether the cell undergoes mitosis or meiosis. Mitosis is the most common form of cell division. All somatic cells undergo mitosis, whereas only germ cells undergo meiosis. Meiosis is very important because it produces gametes (sperm and eggs) that are required for sexual reproduction. Human germ cells have 46 chromosomes (2n = 46) and undergo meiosis to produce four haploid daughter cells (gametes).
Which of the following is not a characteristic of meiosis?
It produces four haploid daughter cells
It functions to grow and repair the human body
It produces egg and sperm cells with no homologous chromosomes
It is preceded by the G2 phase
It functions to grow and repair the human body
Meiosis is the process by which a diploid cell divides into four haploid daughter cells. The daughter cells produced are called gametes (sperm in males and egg in females). By definition, a haploid cell contains only one set of chromosomes; therefore, the egg and sperm cells will not contain any homologous chromosomes.
Recall that mitosis is part of the cell cycle and that it is preceded by three phases: G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase. Meiosis is immediately followed by the G2 phase. The main function of meiosis is to produce haploid gametes that can be used for sexual reproduction. Growth and repair of tissues in the human body is accomplished by mitosis, not meiosis.
Example Question #11 : Mitosis And Meiosis
Which of the following occurs in mitosis, but does not occur in meiosis?
Separation of sister chromatids
Nuclear envelope breakdown
Separation of homologous chromosomes
None of these answers
None of these answers
The main differences between meiosis and mitosis are that, during meiosis I, there is recombination between homologous chromosomes and the separation of homologous chromosomes. During mitosis, homologous chromosomes are not separated, only the sister chromatids. Both processes involve the breakdown of the nuclear envelope, allowing DNA to enter the cytoplasm and align at the equatorial plate and both processes involve separation of sister chromatids.
Only meiosis involves separation of homologous chromosomes. Since the question asks for an event exclusive to mitosis, none of these answers are suitable.
Example Question #32 : Cellular Processes And Functions
Cellular division is an essential part of the cell cycle. When a cell divides it passes genetic information to daughter cells. The amount of genetic information passed on to daughter cells depends on whether the cell undergoes mitosis or meiosis. Mitosis is the most common form of cell division. All somatic cells undergo mitosis, whereas only germ cells undergo meiosis. Meiosis is very important because it produces gametes (sperm and eggs) that are required for sexual reproduction. Human germ cells have 46 chromosomes (2n = 46) and undergo meiosis to produce four haploid daughter cells (gametes).
Which of the following is true regarding mitosis and meiosis?
I. Meiosis I produces twice as many daughter cells as mitosis
II. Crossing over only occurs during prophase I of meiosis
III. The daughter cells of meiosis I have the same amount of DNA as the daughter cells of mitosis
I only
II and III
I and II
II only
II and III
Meiosis contains two different cellular divisions: meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis I produces two haploid daughter cells with chromosomes composed of two sister chromatids, whereas meiosis II produces four haploid daughter cells with singular sister chromatids (single-chromatid chromosomes). Mitosis only has one cellular division and produces two diploid daughter cells.
Statement I is false because meiosis I and mitosis produce the same number of daughter cells. Both divisions result in two daughter cells. Meiosis II divisions will result in four daughter cells.
Crossing over is a type of genetic recombination that exclusively occurs during prophase I of meiosis; therefore, statement II is true. This occurs because crossing over requires the formation of tetrads of homologous chromosomes.
The daughter cells of mitosis contain one sister chromatid from each homologous chromosome and the daughter cells of meiosis I contain one homologous chromosome from each pair. Although their types of chromosomes are different, both daughter cells from each division contain the same amount of DNA. The only difference is that the daughter cells of mitosis contain DNA in the form of sister chromatids, whereas daughter cells of meiosis I contain DNA in the form of the homologous chromosome. Statement III is true. The best answer is II and III. Remember that sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes code for the same genes, but contain different alleles.
Example Question #35 : Cellular Processes And Functions
Meiosis is a form of cell division that occurs in special types of cells called germ cells. It is different from mitosis because it takes a diploid cell and splits it into four, nonidentical haploid cells. In males, these haploid cells are called sperm and in females they are called eggs or ova. Meiosis has two steps: meiosis I and meiosis II. Both steps have their corresponding prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Meiosis I phases are similar to mitotic phases, with a few key differences. Meiosis II phases are exactly identical to the mitotic phases.
A student is observing a set of cells under the microscope. He takes notes but forgets to write the mitotic phase for each slide. His notes are as follows.
Cell A: Site of ribosome synthesis disappears
Cell B: The nuclear content spills out into the cytoplasm
Cell C: No sister chromatids are visible
What is the mitotic phase of each cell?
Cell A: Prophase
Cell B: Anaphase
Cell C: Telophase
Cell A: Prophase
Cell B: Prophase
Cell C: Telophase
Cell A: Metaphase
Cell B: Prophase
Cell C: Metaphase
Cell A: Anaphase
Cell B: Anaphase
Cell C: Metaphase
Cell A: Prophase
Cell B: Prophase
Cell C: Telophase
There are four main phases in mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Prophase involves nuclear membrane breakdown, formation of mitotic spindle, and disappearance of nucleolus. Recall that nucleolus is the site of ribosome synthesis; therefore, cell A is in prophase. The question states that the nuclear contents are spilling out in Cell B. Nuclear membrane holds the contents of nucleus in place. During prophase, this nuclear membrane breaks down, causing the contents of the nucleus (like chromosomes) to spill out into the cytoplasm.
Metaphase involves the alignment of the chromosomes (with sister chromatids) along the equatorial line of the cell. In anaphase, the aligned chromosomes are pulled towards the opposite ends of the cell, causing the sister chromatids to separate. Finally, in telophase two distinct cell start appearing with chromosomes that have no sister chromatids; therefore, cell C must be in telophase.
Mitosis is immediately followed by cytokinesis, during which the cytoplasm is divided equally between the two daughter cells.
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Biology Resources




