All MCAT Biology Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #25 : Kidney And Nephron Physiology
The interaction between blood pressure and kidney function in humans requires coordination by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). This system involves the dynamic interplay of the kidneys, lungs, and blood vessels to carefully regulate sodium and water balance.
A normal human kidney has cells adjacent to the glomerulus called juxtaglomerular cells. These cells sense sodium content in urine of the distal convoluted tubule, releasing renin in response to a low level. Renin is an enzyme that converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I (AI). AI is converted to angiotensin II (AII) by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) in the lung.
AII stimulates aldosterone secretion in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal gland. Aldosterone then acts to upregulate the sodium-potassium pump on the basolateral side of distal tubule epithelial cells to increase sodium reabsorption from the urine, as well as increasing potassium excretion.
Aldosterone functions by increasing the rate at which the sodium-potassium pump functions in the basolateral surface of distal tubule epithelial cells of the nephron. Which of the following is true of the sodium-potassium pump?
It is electrogenic
It pumps three sodium ions into the cytosol and two potassium ions out of the cytosol
It pumps two sodium ions into the cytosol and three potassium ions out of the cytosol
It pumps two sodium ions out of the cytosol and three potassium ions into the cytosol
It pumps three sodium ions into the cytosol and three potassium ions out of the cytosol
It is electrogenic
The sodium-potassium pump pumps three sodium ions out of the cytosol, and two potassium ions into the cytosol. It is electrogenic because each sodium and potassium ion have a charge of positive one, and the two ions are pumped in unequal quantities. The pump generates an electric gradient and current due to the directional flow of positive charge out of the cell.
When aldosterone is released, it increases the action of the sodium-potassium pump, causing excess sodium to be removed from the filtrate in the distal tubule, thus conserving sodium and drawing water out of the filtrate.
Example Question #26 : Kidney And Nephron Physiology
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when body tissues are affected by an abnormal immune reaction. The result is damage to normal tissues and clinical illness. A peanut allergy is an example of a hypersensitivity reaction, but there are three additional broad classes.
One class involves the abnormal production or deposition of antibodies. Antibodies are B-cell derived molecules that normally adhere to pathogens, rendering them unable to continue an infection. When antibodies are produced against normal tissues, however, disease can result. Figure 1 depicts a schematic structure of an antibody.
Antibodies can be divided into two peptide chains: heavy and light. Heavy chains form the backbone of the antibody, and are attached to light chains via covalent bonding. Each heavy and light chain is then further divided into constant and variable regions. Variable regions exhibit molecular variety, generating a unique chemical identity for each antibody. These unique patterns help guarantee that the body can produce antibodies to recognize many possible molecular patterns on invading pathogens.
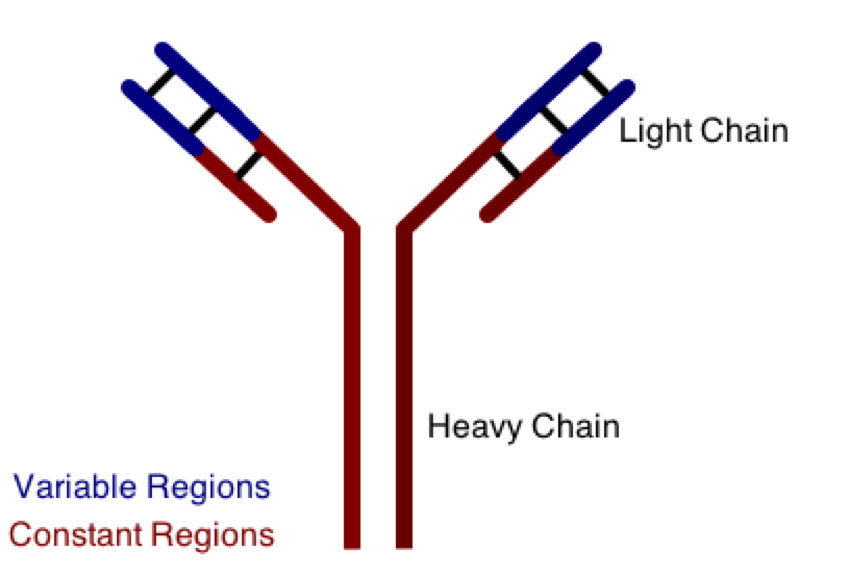
In hypersensitivity reactions, antibodies can complex with antigens and fall out of solution from the blood. These immune complexes then deposit in body tissues inappropriately, and cause disease. This situation is especially noticeable in body tissues that have a direct filtering function. Which of the following structures would most likely be affected by a disease caused by immune complex deposition?
Glomerulus
Sinoatrial node
Haversian canal
Semicircular canals
Neuromuscular junction
Glomerulus
The glomerulus is the primary site of filtration in the kidney. Together, the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule for the renal corpuscle of the nephron and are responsible for collecting filtrate from the blood. Deposition and accumulation of immune complexes in the glomerulus would result in blockage of its filtering functions, impeding nephron function and preventing proper excretion of soluble wastes.
The sinoatrial node is the natural pacemaker region of the heart, located in the right atrium. Haversian canals are the central regions of osteons and often house nerves and blood vessels, facilitating cellular communication within bone. Neuromuscular junctions are the interface regions between a single neuron and the muscle fiber it innervates. The semicircular canals are located in the inner ear and function in the propagation an integration of sound vibrations. None of these structures are involved in filtration, and they would most likely be unaffected by the presence of immune complexes in the body.
Example Question #23 : Excretory System
Which of the following is true regarding the nephron?
Aldosterone acts at the collecting duct to increase membrane permeability to 
Bowman's capsule is repsonsible for preventing all proteins from entering the filtrate
The collecting duct is permeable to water and responsive to aldosterone
The renal corpuscle is made up of the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule
The distal tubule absorbs 



The renal corpuscle is made up of the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule
Together, Bowman's capsule and the glomerulus make up the renal corpuscle. Blood flows through the glomerulus, where high hydrostatic pressures force plasma through the fenestrations of the glomerular endothelium into Bowman's capsule. The substance that ends up in the capsule is called the filtrate, which then moves to the proximal tubule. Proteins, glucose, and ions are secreted from the proximal tubule back into the blood.
The collecting duct is impermeable to water and is not particularly sensitive to aldosterone. Instead, aldosterone, a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal cortex, acts primarily at the distal tubule to increase sodium reabsorption, potassium secretion, and ultimately water reabsorption to increase blood pressure. The distal tubule absorbs Na+ and Ca2+, not HCO3-.
Example Question #27 : Kidney And Nephron Physiology
A researcher is analyzing two locations in the loop of Henle. His results indicate that a sample of filtrate from location A has a much higher solute concentration than a sample of filtrate from location B. Based on his results, what might the researcher conclude about the identity of the locations?
Location B is the ascending limb of the loop of Henle because both water and sodium are reabsorbed in the ascending limb
Location A is the descending limb of the loop of Henle because only water is reabsorbed in the descending limb
Location B is the descending limb of the loop of Henle because only water is reabsorbed in the descending limb
Location A is the ascending limb of the loop of Henle because both water and sodium are reabsorbed in the ascending limb
Location A is the descending limb of the loop of Henle because only water is reabsorbed in the descending limb
The loop of Henle is a U-shaped structure found in the nephron. Its main function is to reabsorb water and essential solutes. Reabsorption is the process by which nutrients and water are transported from the filtrate back into the body.
The loop of Henle contains two parts: the descending limb and the ascending limb. The descending limb functions to reabsorb water, whereas the ascending limb functions to reabsorb sodium and chloride ions. The question states that filtrate in location A has a higher solute concentration. This means that filtrate in location A has more solutes (or less water) than filtrate in location B. Since the descending limb only reabsorbs water, the filtrate concentration is higher in the descending loop; water is removed without solute being able to follow. Location A would be the descending limp of the loop of Henle because it reabsorbs water and increases the solute concentration of the filtrate.
Concentration decreases in the ascending limb when ions are pumped out of the filtrate, removing solute.
Example Question #25 : Kidney And Nephron Physiology
Cortisol is a stress hormone that is produced in the __________, the__________ portion of adrenal gland.
adrenal medulla . . . outer
adrenal cortex . . . outer
adrenal cortex . . . inner
adrenal medulla . . . inner
adrenal cortex . . . outer
The adrenal gland is situated superior to the kidney, and is responsible for the production of several key hormones.
One such hormone is cortisol. Cortisol is often released when an individual is highly stressed over an extended period. It is a steroid hormone that functions to increase blood glucose levels by inducing gluconeogenesis, the process that converts glycogen stores in the liver to glucose. Cortisol is released from cells in the adrenal cortex. Recall that the adrenal cortex is the outer portion of the gland, whereas the adrenal medulla is the inner portion of the gland.
Aldosterone is another hormone that is released by cells in the adrenal cortex, and is essential for sodium reabsorption in the kidney. Epinephrine is released from the adrenal medulla in response to stimulation by the sympathetic nervous system.
Example Question #31 : Excretory System
Which of the following structures will be found in the renal medulla?
I. Glands that secrete aldosterone
II. Loop of Henle
III. Distal convoluted tubule
II only
I and III
I only
I and II
II only
Recall that the renal medulla is the inner portion of the kidney. A nephron spans both the renal cortex and the renal medulla. Structures such as the glomerulus (capillary bed), Bowman's capsule, and the proximal and distal convoluted tubules are found in the renal cortex, whereas the loop of Henle is found in the renal medulla. The collecting duct (the structure that transports urine to the renal pelvis) spans both the renal cortex and the renal medulla.
As mentioned above, distal tubules are found in the renal medulla and function to reabsorb sodium ions. Reabsorption of sodium ions inside the nephron (for example in the distal tubules) is facilitated by the hormone aldosterone. Aldosterone is a steroid hormone that is produced in glands inside the adrenal cortex (in the adrenal gland, rather than the kidney).
Example Question #32 : Excretory System
Which of the following is true regarding a nephron?
Nephrons create urine, but they cannot store urine
Nephrons are only found in the adrenal medulla
Filtration begins in nephrons’ capillary beds, called the collecting duct
A nephron is the functional unit of a neuron
Nephrons create urine, but they cannot store urine
A nephron is the functional unit of kidneys. It is the site of filtration, secretion, and reabsorption (processes essential for urine production).
Nephrons contain several structures that facilitate the proper excretion of waste through urine. A nephron contains structures that are found in both the adrenal medulla (inner region) and the adrenal cortex (outer region) of the kidneys; therefore, a single nephron spans both the adrenal medulla and the adrenal cortex. The first step in urine production occurs at the capillary beds of nephrons. Blood arrives at these capillary beds, known as the glomerulus, and initiates filtration. Filtration is the process by which potential waste products in the blood are filtered into the nephron, where they will ultimately become urine.
Remember that nephrons are the site of urine production; they do not store the urine. Once complete, urine exits the kidneys and is stored in the bladder. The bladder stores urine until it reaches the maximum capacity, causing smooth muscle around the organ to stretch. Once this maximum is reached the individual feels the urge to urinate, and the urine is excreted via the urethra.
Example Question #33 : Excretory System
In the urinary system, the ureter is most directly associated with the __________.
adrenal gland
renal pelvis
liver
renal vein
renal pelvis
The renal pelvis (hollow structure within the kidney) narrows to become the ureter, which leads to the bladder.
Example Question #471 : Systems Biology And Tissue Types
Which components of the nephron can be found in the renal medulla?
The loop of Henle and the collecting duct
The entire nephron can be found within the cortex of the kidney
The proximal and distal convoluted tubules
The loop of Henle and the glomerulus
The loop of Henle and the collecting duct
The loop of Henle descends into the medulla before ascending back into the cortex. The collecting duct, which ends the nephron, extends into the medulla.
Example Question #31 : Excretory System
Which of the following is true of a functioning kidney?
Only water can enter into Bowman's capsule by passive diffusion
Glucose, water, and ions permeate the visceral layer of Bowman's capsule to enter the blood vessels of the glomerulus
Macromolecules, such as proteins, do not enter Bowman's capsule due to the impermeability of the podocyte membrane
All blood solutes pass from the glomerulus into Bowman's capsule, adding to the volume of the filtrate
Macromolecules, such as proteins, do not enter Bowman's capsule due to the impermeability of the podocyte membrane
The visceral layer of Bowman's capsule is permeable to small blood solutes. Blood cells and most macromolecules remain in the blood stream.
One answer choice is nearly correct: "Glucose, water, and ions permeate the visceral layer of Bowman's capsule to enter the blood vessels of the glomerulus." While these solutes do in fact permeate the membrane, they exit the blood vessels of the glomerulus to enter Bowman's capsule.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Biology Resources






