All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of An Equilateral Triangle

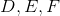


Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The area of
(b) Twice the area of
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
(a) and (b) are equal.
(a) is greater.
(b) is greater.
(a) is greater.
If segments are constructed in which the endpoints form the midpoints of the sides of a triangle, then four triangles, congruent to each other and similar to the larger triangle, are formed. Therefore, one of these triangles - specifically, 
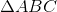


Note that the fact that the triangle is equilateral is irrelevant.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of An Equilateral Triangle
Which of the following could be the three sidelengths of an equilateral triangle?
By definition, an equilateral triangle has three sides of equal length. We can identify the equilateral triangle by converting the given sidelengths to the same units and comparing them.
We can eliminate the following by showing that at least two sidelengths differ.
2 yards = 
Two sides have lengths 6 feet and 7 feet, so we can eliminate this choice.
4 feet = 
Two sides have lengths 48 inches and 50 inches, so we can eliminate this choice.
5 feet = 
Two sides have lengths 48 inches and 60 inches, so we can eliminate this choice.


Two sides have lengths 4 feet and 5 feet, so we can eliminate this choice.



All three sides have the same length, making this the triangle equilateral. This choice is correct.
Example Question #32 : Isee Upper Level (Grades 9 12) Quantitative Reasoning
What is the hypotenuse of a right triangle with sides 5 and 8?
√89
5√4
15
12
√89
Because this is a right triangle, we can use the Pythagorean Theorem which says a2 + b2 = c2, or the squares of the two sides of a right triangle must equal the square of the hypotenuse. Here we have a = 5 and b = 8.
a2 + b2 = c2
52 + 82 = c2
25 + 64 = c2
89 = c2
c = √89
Example Question #33 : Isee Upper Level (Grades 9 12) Quantitative Reasoning
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The hypotenuse of a 
(b) The hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs of length 19 and 21
It is impossible to tell from the information given
(b) is greater
(a) is greater
(a) and (b) are equal
(b) is greater
The hypotenuses of the triangles measure as follows:
(a)
(b)


Example Question #3 : How To Find The Length Of The Hypotenuse Of A Right Triangle : Pythagorean Theorem
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs 

(b) The hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs 

(a) is greater.
(a) and (b) are equal.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
(b) is greater.
(a) is greater.
The hypotenuses of the triangles measure as follows:
(a)
(b)


Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Hypotenuse Of A Right Triangle : Pythagorean Theorem
A right triangle has a leg 

(a) The length of the second leg of the triangle
(b) 60 inches
(b) is greater.
(a) is greater.
(a) and (b) are equal.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
(a) is greater.
The length of the second leg can be calculated using the Pythagorean Theorem. Set 
The second leg therefore measures 
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Hypotenuse Of A Right Triangle : Pythagorean Theorem
What is the hypotenuse of a right triangle with sides 9 inches and 12 inches?
Since we're dealing with right triangles, we can use the Pythagorean Theorem (


Example Question #6 : Right Triangles

The perimeter of a regular pentagon is 75% of that of the triangle in the above diagram. Which is the greater quantity?
(A) The length of one side of the pentagon
(B) One and one-half feet
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(A) is greater
(A) and (B) are equal
(B) is greater
(B) is greater
By the Pythagorean Theorem, the hypotenuse of the right triangle is


The pentagon in question has sides of length 75% of 112, or

Since a pentagon has five sides of equal length, each side will have measure

One and a half feet are equivalent to 
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Hypotenuse Of A Right Triangle : Pythagorean Theorem

The track at Gauss High School is unusual in that it is shaped like a right triangle, as shown above.
Cary decides to get some exercise by running from point A to point B, then running half of the distance from point B to point C.
Which is the greater quantity?
(A) The distance Cary runs
(B) One-fourth of a mile
(A) and (B) are equal
(B) is greater
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(A) is greater
(B) is greater
By the Pythagorean Theorem, the distance from B to C is

Cary runs

Since 5,280 feet make a mile, one-fourth of a mile is equal to

(B) is greater
Example Question #8 : Right Triangles

Give the length of the hypotenuse of the above right triangle in terms of 
If we let 
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources









































