All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #91 : Isee Upper Level (Grades 9 12) Quantitative Reasoning
What is the slope of a line that passes through points 

The equation for solving for the slope of a line is 
Thus, if 

Example Question #91 : Isee Upper Level (Grades 9 12) Quantitative Reasoning

Figure NOT drawn to scale
In the above figure, 



(a)
(b)
(b) is the greater quantity
(a) and (b) are equal
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(a) is the greater quantity
(a) is the greater quantity
For the sake of simplicity, let us assume that the lengths of 







If two tangents are drawn to a circle, the measure of the angle they form is half the difference of the measures of the arcs they intercept, so
This is greater than 
Example Question #1 : How To Find A Ray
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The length of the line segment connecting 
(b) The length of the line segment connecting 
(a) is greater.
(a) and (b) are equal.
(b) is greater.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
(a) and (b) are equal.
(a) The length of the line segment connecting 


(b) The length of the line segment connecting 


The segments have equal length.
Example Question #1 : Hexagons
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The area of a regular hexagon with sidelength 1
(b) The area of an equilateral triangle with sidelength 2
(a) and (b) are equal
(b) is greater
It is impossible to tell from the information given
(a) is greater
(a) is greater
A regular hexagon with sidelength 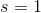


Example Question #2 : Hexagons
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The perimeter of a regular pentagon with sidelength 1 foot
(b) The perimeter of a regular hexagon with sidelength 10 inches
(a) and (b) are equal.
(b) is greater.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
(a) is greater.
(a) and (b) are equal.
The sides of a regular polygon are congruent, so in each case, multiply the sidelength by the number of sides to get the perimeter.
(a) Since one foot equals twelve inches, 
(b) Multiply: 
The two polygons have the same perimeter.
Example Question #3 : Hexagons
A hexagon has six angles with measures
Which quantity is greater?
(a)
(b) 240
(a) is greater
(b) is greater
It is impossible to tell from the information given
(a) and (b) are equal
(a) and (b) are equal
The angles of a hexagon measure a total of 
The quantities are equal.
Example Question #94 : Isee Upper Level (Grades 9 12) Quantitative Reasoning
A hexagon has six angles with measures
Which quantity is greater?
(a)
(b)
(b) is greater.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
(a) is greater.
(a) and (b) are equal.
(b) is greater.
The angles of a hexagon measure a total of 
This makes (b) greater.
Example Question #95 : Isee Upper Level (Grades 9 12) Quantitative Reasoning
The angles of Hexagon A measure
The angles of Octagon B measure
Which is the greater quantity?
(A)
(B)
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(A) is greater
(B) is greater
(A) and (B) are equal
(B) is greater
The sum of the measures of a hexagon is 
The sum of the measures of an octagon is 

Example Question #4 : Hexagons
The angles of Pentagon A measure
The angles of Hexagon B measure
Which is the greater quantity?
(A)
(B)
(A) and (B) are equal
(B) is greater
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(A) is greater
(A) is greater
The sum of the measures of the angles of a pentagon is 
The sum of the measures of a hexagon is 

Example Question #98 : Geometry

A regular hexagon has the same perimeter as the above right triangle. What is the length of one side of the hexagon?
The length cannot be determined from the information given.
By the Pythagorean Theorem, the hypotenuse of the right triangle is


The regular hexagon, which has six sides of equal length, has the same perimeter, so each side measures

Certified Tutor
All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources
























































