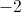All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Functions And Graphs
What is the domain of the function?
The domain of a function is the set of possible values for the 

The value inside of a square root must be greater than or equal to zero in order to have a real solution.
Now we can solve for 
Square roots have positive and negative roots, so we need to set up two results. Remember to switch the direction fo the inequality for the negative solution.
These solutions can be combined to give our final answer.
Any values of 
Example Question #2 : Functions And Graphs
Which of the following does NOT belong to the domain of the function 
1
1/2
-1/2
-1
0
0
The domain of a function includes all of the values of x for which f(x) is real and defined. In other words, if we put a value of x into the function, and we get a result that isn't real or is undefined, then that value won't be in the domain.
If we let x = 0, then we will be forced to evaluate 
The answer is 0.
Example Question #3 : Functions And Graphs
What is the domain of the function:
All real numbers except
All integers.
All real numbers except
All positive numbers.
All real numbers.
All real numbers except
The domain of a function consists of all of the possible values for x. In this case, we want to make sure that we are not dividing by 



Example Question #4 : Functions And Graphs
What is the range of 
All real numbers
The range of a function is all of the possible 

Since 



Example Question #1 : Functions And Graphs
Find the domain of the following function.
All real numbers except 
All real numbers such that 
All real numbers except 
All real numbers such that 
Domain represents all possible values for 


Example Question #361 : Algebra Ii
What is the range of 
All real numbers except -1
All real numbers greater than or equal to 0
All rational numbers
All real numbers
All real numbers greater than 0
All real numbers greater than or equal to 0
The range of a function is defined as the possible values for 

Example Question #4 : Functions And Graphs
Domain: All real numbers
Range:
Domain: All real numbers
Range:
Domain: All real numbers
Range:
The domain includes the values that go into a function (the x-values) and the range are the values that come out (the 


Example Question #1 : Introduction To Functions
If 

Using 



Therefore 

All High School Math Resources





















 is a sine curve. What are the domain and range of this function?
is a sine curve. What are the domain and range of this function?