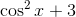All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Trigonometric Identities
What is the 

When working with basic trigonometric identities, it's easiest to remember the mnemonic: 

When one names the right triangle, the opposite side is opposite to the angle, the adjacent side is next to the angle, and the hypotenuse spans the two legs of the right angle.
Example Question #2 : Trigonometric Identities
Simplify 
Simplifying trionometric expressions or identities often involves a little trial and error, so it's hard to come up with a strategy that works every time. A lot of times you have to try multiple strategies and see which one helps.
Often, if you have any form of 






This doesn't seem to help a whole lot. However, we should recognize that 

We can cancel the 

Example Question #13 : Graphing The Sine And Cosine Functions

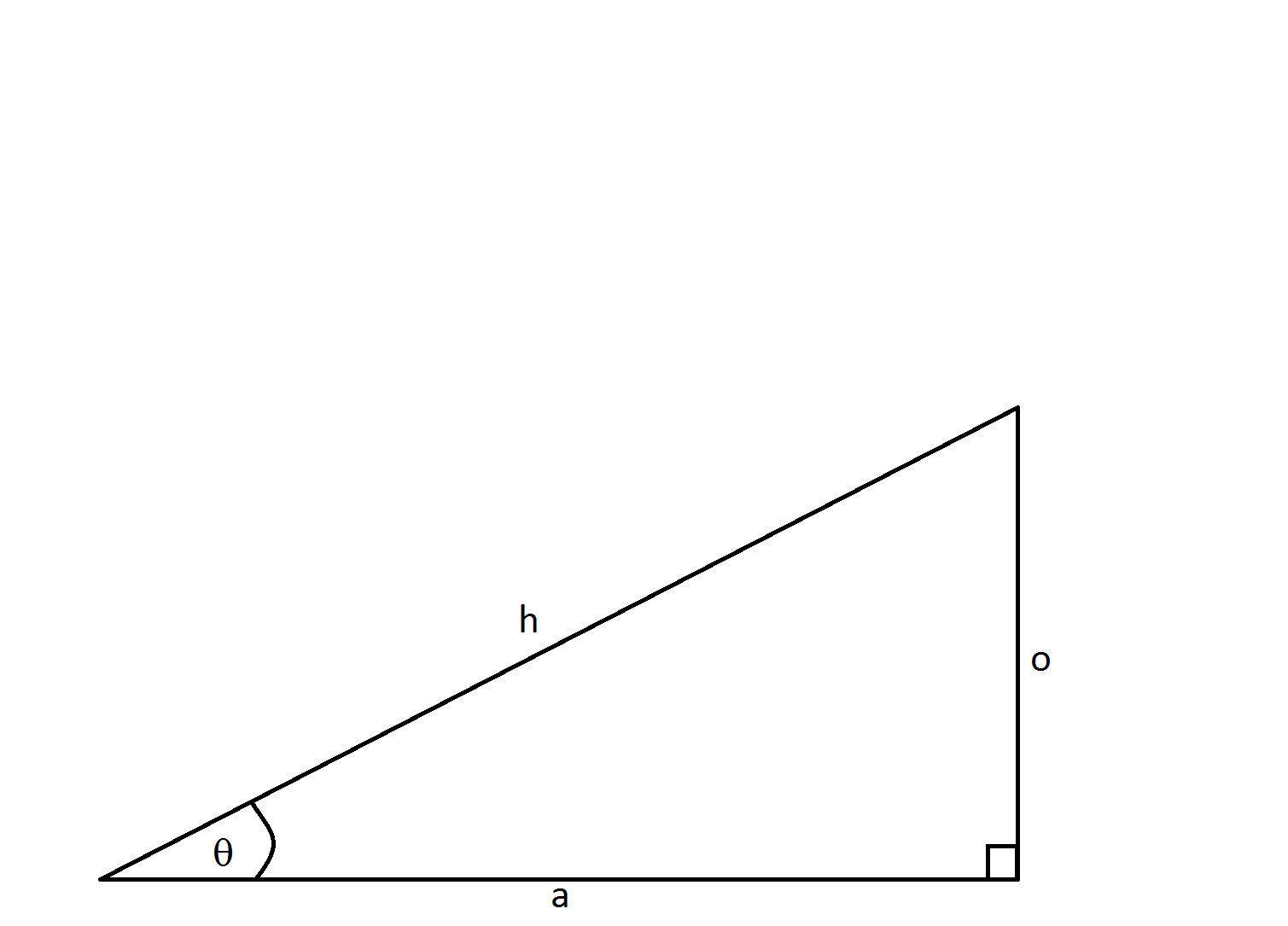
What is the 

When working with basic trigonometric identities, it's easiest to remember the mnemonic: 


When one names the right triangle, the opposite side is opposite to the angle, the adjacent side is next to the angle, and the hypotenuse spans the two legs of the right angle.
Example Question #14 : Graphing The Sine And Cosine Functions

What is the 

When working with basic trigonometric identities, it's easiest to remember the mnemonic: 


When one names the right triangle, the opposite side is opposite to the angle, the adjacent side is next to the angle, and the hypotenuse spans the two legs of the right angle.
Example Question #111 : Trigonometry
Simplify

Example Question #112 : Trigonometry
Simplify

and

Example Question #1841 : High School Math
Simplify 
Remember that 
Example Question #8 : Trigonometric Identities
Simplify:
This is the most simplified version.
Whenever you see a trigonometric function squared, start looking for a Pythagorean identity.
The two identities used in this problem are 

Substitute and solve.
Example Question #1851 : High School Math
Factor and simplify 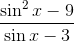
This is already it's most reduced form.
To reduce 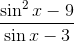
Notice that we can cancel out a 
This leaves us with 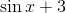
Example Question #2 : Trigonometric Identities
Simplify 
To simplify 

Notice that the opposite's cancel out, leaving 
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All High School Math Resources

































![[\cos(x)/\sin(x)]\times\sin(x)=\cos(x)](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/27160/gif.latex)