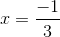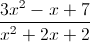All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Rational Expressions
Solve:
If 





The formula for a direct variation is:
Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #2 : Rational Expressions
If two boxes have the same depth and capacity, the length is inversely proportional to the width. One box is 


The formula for an indirect variation is:
Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #1 : Solving Rational Expressions
Simplify
This is a more complicated form of
Find the least common denominator (LCD) and convert each fraction to the LCD, then add the numerators. Simplify as needed.
which is equivalent to
Simplify to get
Example Question #1 : Simplifying Rational Expressions
Divide and simplify the following rational expression:
Multiply by the reciprocal of the second expression:
Factor the expressions:
Remove common terms:
Example Question #1 : Rational Expressions
Add and simplify the following rational expression:
Begin by multiplying the left term by 
Simplify:
Example Question #3 : Simplifying Rational Expressions
Simplify the following rational expression:
Begin by combining the terms in the denominator:
Multiply by the reciprocal of the denominator:
Remove like terms:
Example Question #3 : Rational Expressions
Simplify the following rational expression:
Create a common denominator of 
Multiply by the reciprocal of the denominator:
Simplify:
Remove common terms:
Example Question #4 : Simplifying Rational Expressions
Multiply and simplify the following rational expression:
Factor the expression:
Remove like terms:
Example Question #5 : Simplifying Rational Expressions
Divide and simplify the following rational expression:
Multiply by the inverse of the denominator:
Factor:
Remove like terms:
Example Question #351 : Algebra Ii
Solve the following rational expression:
Multiply the equation by 
All High School Math Resources