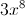All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Expressions
In April, the price of a t-shirt is 




If the original price of the T-shirt is 



If the price is then decreased by 50%, the new price 
or
The ratio of 

The 


Example Question #1521 : High School Math
Simplify 
When multiplying rational expressions, we simply have to multiply the numerators together and the denominators together. (Warning: you only need to find a lowest common denominator when adding or subtracting, but not when multiplying or dividing rational expression.)
In order to simplify this, we will need to factor 


We can easily factor out a four from both terms.

Next, notice that 






Now, we can see that
We then factor 






Be careful here. A common mistake that students make is to try to factor 

We will then put all of these pieces of information in order to simplify our rational expression.
Lastly, we cancel the factors that appear in both the numerator and the denominator. We can cancel an 


The answer is 
Example Question #1 : Simplifying Expressions
Let 



To solve this problem, plug 


Example Question #41 : Basic Single Variable Algebra
Evaluate 
When multiplying an even number of negatives, you get a positive.
When multiplying an odd number of negative, you get a negative.
Example Question #42 : Basic Single Variable Algebra
Evaluate 

When multiplying an odd number of negatives, the answer is negative.
When multiplying an even number of negatives, the answer is positive.
Example Question #1 : Simplifying Expressions
Simplify:
Example Question #2 : Expressions
Simplify:


(Like terms are terms that have the same variables with the same exponents. Only like terms can be combined together.)
Example Question #1526 : High School Math
Simplify 
Change the mixed numbers into improper fractions by multiplying the whole number by the denominator and adding the numerator:

Dividing by a fraction is the same as multiplying by the reciprocal, so the problem becomes 
Example Question #1527 : High School Math
Which of the following describes the values of x belonging to the domain of the function 
The domain of a function consists of all of the values of x for which f(x) is defined. When determining the domain of a funciton, the three most important things we want to consider are square roots, logarithms, and denominators of fractions. These tend to signal places where the function is not defined.
First, let's look at the 

Second, we need to look at the natural logarithm. The natural logarithm can only be applied to positive numbers (which don't include zero). Thus, everything within the paranethesis of the natural logarithm must be greater than zero.
There are several ways to solve this inequality. One way is to factor the left side and examine the factors. We know that 

This statement will only be true in two situations; either both factors must be positive, or both must be negative.
We can see that if 




Let's consider the interval 




Third, consider the interval 

To summarize, 

We can see now that f(x) is only defined if 

There is one more piece of information we need to consider--the denominator of f(x). Remember that a fraction is not defined if its denominator equals zero. Thus, if the denominator is equal to zero at a certain value of x, we can't include this value of x in the domain of f(x).
We can set the denominator equal to zero and solve to see if there are any values of x where the denominator would be zero.
Rewrite this as an exponential equation. In general, the equation 

If we put 
We can solve this for x.
So, let's put all of this information together. We know that f(x) is only defined if ALL of these conditions are met:
The only interval for which this is true is if x is greater than (and not equal to) zero but less than (and not equal to) 1. Thus, the domain of f(x) is 
The answer is 
All High School Math Resources




































![[x^{1/2}]^{7/3}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/181666/gif.latex)





![[x^{m}]^{n}=x^{m\times n}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/27168/gif.latex)