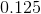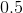All GRE Subject Test: Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #12 : Permutations

NOTE: No two people can shake hands more than once.
Step 1: Determine how many people are there..
There are 
Step 2: Determine how many people shake hands in a handshake...
Step 3: Determine how many handshakes can be made...
We have a restriction here, so we need to use permutation..
So, there will be 

Example Question #13 : Permutations
In how many ways can I rearrange the letters in the word "ANACONDA"?
Step 1: Count how many letters are in the word ANACONDA...
There are 8 letters.
Step 2: Count how many repeats of any letters (if any)..
There are 

Step 3: Find how many ways I can rearrange...
Example Question #14 : Permutations
How many ways can I arrange the letters in the word 
Step 1: Count how many numbers are in the word...
There are 
Step 2: Count the number of repeated letters...
There are 
There are 
There are 
Step 3: To find how many ways I can arrange the letters, take the factorial of the total number of letters and divide it by the factorial of how many times a certain letter repeats...
So,
Example Question #1 : Discrete Distributions
X is a continuously and uniformly distributed on the interval (0,50). Find the Expected Value (E[x]) and Variance (Var(x)) of X.
Because x is a continuous uniform random variable the expected value and variance can be found with the following formulas:
X is uniform on (a,b). In this case a is 0 and b is 50. Plugging the values of a and b into the given formulas will give the answers:
Example Question #2 : Discrete Distributions
A fair coin is tossed 15 times. What is the probability of observing less than 3 heads?
This problem uses the Binomial Distribution:
For this problem n is the number of trials, or 15. Because the problem stated that the coin was a fair coin the probability of heads is one half, or .5.
The binomial distribution is a discrete distribution so the expression x<3 has to be broken down.
Adding the probabilities will give the final answer.
Example Question #1 : How To Find Z Scores For A Data Set
The average score on the statistics final exam was 85 and the standard deviation was 

The first step in this problem is calculating the z-score.
The next step is to look up 4 in the z-table. The value from the table is 
Example Question #1 : How To Find Z Scores For A Data Set
What is the 
A 



Example Question #2 : Basic Statistics
A population of values has a mean of 43 and a standard deviation of 12. One of the values in the population is 49. What is the Z-score for that value?
A Z-score indicates whether a particular value is typical for a population or data set. The closer the Z-score is to 0, the closer the value is to the mean of the population and the more typical it is. The Z-score is calculated by subtracting the mean of a population from the particular value in question, then dividing the result by the population's standard deviation.
Example Question #2 : Data Sets And Z Scores
The z-score is also known as the standard score.
The average temperature for all the days preceding the last for the month of February was 55 degrees Farhenheit, with a standard deviation of 5 degrees.
On the last day, the temperature was 73 degrees F. What is the z-score for the temperature on the last day?
To find the z-score, follow the formula
or
Example Question #2 : How To Find Z Scores For A Data Set
A population has a standard deviation of 


A z score is unique to each value within a population.
To find a z score, subtract the mean of a population from the particular value in question, then divide the result by the population's standard deviation.
All GRE Subject Test: Math Resources
















![E[x]=25](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/725404/gif.latex)

![E[x]=25](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/725398/gif.latex)

![E[x]=4.167](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/725400/gif.latex)

![E[x]=4.167](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/725402/gif.latex)

![E[x]=25](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/725396/gif.latex)

![E[x]=\frac{a+b}{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/725406/gif.latex)

![E[x]=\frac{a+b}{2}=\frac{0+50}{2}=25](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/725408/gif.latex)