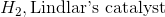All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #11 : Hydrocarbons
Starting with an alkyne, synthesis of a cis alkene is driven upon addition of which of the following reagents?
Reduction of an alkyne with hydrogen and Lindlar's catalyst will result in a cis alkene. While 
Example Question #271 : Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry, And Metabolism
Which of the following molecule is a type of terpene?





Terpenes are special classes of lipids that are derived from isoprene units. An isoprene unit’s molecular formula is 

The molecular formula 



Pentene is an alkene with the molecular formula 


Example Question #11 : Specific Reactions And Named Reactions
Acetaldehyde 

reduced . . . alcohol
reduced . . . alkane
oxidized . . . amide
oxidized . . . carboxylic acid
reduced . . . alkane
The correct answer is that the aldehyde is reduced to an alkane. In viewing the final product, we see that acetaldehyde would be reduced to ethane. The reaction of any aldehyde or ketone with hydrazine and the subsequent addition of base and heat will result in that aldehyde or ketone being reduced to an alkane, and is referred to as the Wolf-Kishner reaction. The Wolf-Kishner reagent is a commonly tested reducing agent.
Example Question #1 : Help With Grignard Reactions

What reagent(s) will successfully complete the synthesis reaction shown above?
Isopropyl-MgBr; hydronium ions
Methyl-MgCl; hydronium ions
Ethyl-MgI; hydronium ions
N-propyl-MgBr; hydronium ions
N-propyl-MgBr; hydronium ions
This is an example of a Grignard reagent reaction. Because we are adding three carbons to our chain, the Grignard reagent we need must have three carbons on it. We can therefore rule out methyl grignard and ethyl grignard.
N-propyl is the straight-chained 3-carbon alkane, while isopropyl is branched. Looking at our final product, we can see the carbon chain we have added is straight-chained, and thus N-propyl Grignard is the best option. Because Grignard reagents are relatively basic, we must add an hydronium ion workup to protonate our alcohol.
Example Question #12 : Organic Chemistry
What is the product of the reaction between 2-butanone and lithium aluminum hydride?
3-butanone
3-butanol
Butane
None of these
2-butanol
2-butanol
Lithium aluminum hydride is a reducing agent. It reduces ketones and carboxylic acids to alcohols. 2-butanone is a 4-carbon chain with a double bond between an oxygen and carbon 2. The reduction turns the double bond with oxygen into a single bond to a hydroxy group. This makes the product 2-butanol.
Example Question #1 : Ketone Chemistry

Which of the following would be a major product of the given reaction?





The reaction of a primary amine with a ketone or aldehyde produces an imine by nucleophilic addition. Below is the mechanism for the reaction given:

Example Question #2 : Carbonyls
Which of the following reactions would NOT produce a carboxylic acid?
PCC is considered a weak oxidizing agent. The reaction of a primary alcohol with PCC would only yield an aldehyde, while reaction with a secondary alcohol will yield a ketone. PCC will not be used to generate carboxylic acids.
A stronger oxidation, like 

Example Question #11 : Functional Group Reactions
Which one of the following compounds can produce a carboxylic acid only when reacted with sodium dichromate and sulfuric acid?
Pentanal
2-methylpentan-2-ol
1-pentanol
2-pentanol
2-pentanone
1-pentanol
After recognizing the reagents given, we know we need to begin with an alcohol. The alcohol choices differ only by how substituted they are.
For a carboxylic acid to form from a reaction with sodium dichromate and sulfuric acid, a primary alcohol needs to be available. Therefore, 1-pentanol is the correct answer.
Example Question #1 : Carboxylic Acid Chemistry
When 3-chloroheptane undergoes malonic ester synthesis, the final product is __________.
None of the other answers
malonic ester
a ten-carbon ketone
3-ethylheptanoic acid
nonanoic acid
3-ethylheptanoic acid
The malonic ester is deprotonated at the most acidic hydrogen, the one on the carbon between the two oxygens. The electrons from that bond to the hydrogen form a carbon-carbon double bond while electrons from the oxygen-carbon double bond go to the oxygen atom. This is the enolate form. The chlorine leaves the 3-chloroheptane and the electrons from the carbon-carbon double bond bond to the carbon that the chlorine left. At the same time, the carbonyl is reformed. After deesterfication, 3-ethylheptanoic acid is formed.
Example Question #1 : Other Carbonyl Chemistry
When butanoic acid undergoes the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky (HVZ) reaction, the final product is __________.
butanoyl bromide
2-bromobutanoic acid
None of the other answers
3-bromobutanoic acid
heptanoic acid
2-bromobutanoic acid
In the HVZ reaction of a carboxylic acid, a bromine is added to the alpha carbon. Phosphorus catalyzes the reaction and allows for the formation of an acyl halide. Acyl halides readily undergo enol-ketone tautomerization. The enol form uses electrons from the carbon-carbon double bond to bond to the bromine. In water, the two bromine molecules convert back to a carboxylic acid with one bromine on the alpha carbon.
Certified Tutor
All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources