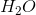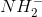All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Hydrocarbons
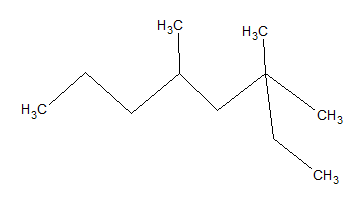
What is the IUPAC name of the given molecule?
2,2,4-trimethyloctane
None of these
4,6-dimethyl-6-ethylpentane
3,3,5-trimethylnonane
3,3,5-trimethyloctane
3,3,5-trimethyloctane
The longest carbon chain that can be formed is eight carbons. The base molecule is octane.
Using IUPAC rules, substituents should have the lowest possible numbers; thus, we start counting carbons from the right side rather than the left. If you count from the correct side, there are two methyl groups on carbon 3 and one on carbon 5. Thus, the name of the moleculue is 3,3,5-trimethyloctane.
Example Question #2 : Hydrocarbons

How could you brominate the compound?
None of these
Bromine gas
Bromine and UV light
Bromine and peroxides
Hydrobromic acid
Bromine and UV light
The given molecule is an alkane. The only way to brominate an alkane is with bromine gas and UV light. The energy from the light serves to creat two radical bromines. These radicals are capable of bonding with alkanes. If the given compound were an alkene, either hydrobromic acid or bromine and peroxides would work.
Example Question #3 : Hydrocarbons
Which of the following can reduce an alkene to an alkane?
Lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4)
H2/Pd and H2/Raney nickel
H2/Raney nickel
H2/Pd
Lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) and H2/Pd
H2/Pd and H2/Raney nickel
Neither lithium aluminum hydride, nor sodium borohydride will reduce C–C double bonds.
H2/Raney nickel and H2/Pd can each (individually) reduce an alkene to an alkane. Since both H2/Raney nickel and H2/Pd can reduce the alkene, the answer is both of those reagents. This is a catalytic hydrogenation reaction, and H2/Raney nickel not only reduces C–C double bonds, but also carbonyl compounds.
Example Question #1 : Reactions By Reactant
Identify the major organic product expected from the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-2-pentanol.
cis-3-methyl-2-pentene
2-methyl-1-pentene
None of the other answers
3-methyl-1-pentene
2-methyl-2-pentene
2-methyl-2-pentene
The initial compound is a five-carbon alkane chain with methyl and hydroxy groups on the second carbon. Dehydration involves the hydrogenation of the hydroxy group. That group then leaves, and a double bond is formed. Zaitsev's rule states that double bonds are more stable on more highly substituted carbons. The double bond forms across carbons two and three.
Example Question #2 : Hydrocarbon Products

What is the IUPAC name of the given diene?
5-chloro-3,6-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene
3-chloro-2,5-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene
3-chloro-2,5-dimethyl-2,6-heptadiene
None of these answers
5-chloro-3,5-dimethyl-1,6-heptadiene
5-chloro-3,6-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene
You must begin counting the carbons so that the first functional substituent has the lowest possible number. In this case, C1 is connected to C2 by the double bond, meaning we start counting from the left.
The longest carbon chain is seven carbons so the parent molecule is heptane. With this numbering, there are methyl groups on carbons 3 and 6 and a chlorine on carbon 5.
Substituents are named in alphabetical order and two double bonds result in a diene. Thus, the correct answer is 5-chloro-3,6-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene.
Example Question #4 : Hydrocarbons
The stereochemical pathway for the hydrogenation of an alkene with a metal catalyst, such as platinum, occurs via __________.
Markovnikov addition
formation of a bridged carbocation
syn addition
anti-Markovnikov addition
anti addition
syn addition
Hydrogenation of an alkene with a metal catalyst, such as platinum, occurs via syn addition.
It is important to note the three main types of reactions for alkenes. The first type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism in which the electrophile attacks the carbocation nucleophile. This can yield syn or anti products. The second type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism that forms a bridged carbocation as the intermediate. This can yield only anti products. The third and last type of reaction is a 1-step addition. This can only yield syn products.
An example of the third type of reaction is the addition of a hydrogen with palladium, platinum, or nickel as demonstrated in the picture.

Example Question #1 : Functional Group Reactions
What is(are) the product(s) in the Pd-catalyzed hydrogenation if 1,2-dimethylcyclopentene?
1,1-dimethylcyclopentene
A mixture of trans- and cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
Dimethylcyclopentane
Trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
Cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
Cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
The product for this hydrogenation is cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane.
It is important to note the three main types of reactions for alkenes. The first type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism in which the electrophile attacks the carbocation nucleophile. This can yield syn or anti products. The second type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism that forms a bridged carbocation as the intermediate. This can yield only anti products. The third and last type of reaction is a 1-step addition. This can only yield syn products.
The cis product alone forms because the reagents used were hydrogen and a metal catalyst palladium (other common metal catalysts are platinum and nickel). This type of reagent with an alkene will always be a 1-step addition that yields solely syn products. Cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane is the only answer that solely indicates syn products.
Example Question #171 : Gre Subject Test: Chemistry

What reagent will complete this reaction?
None of these
PBr3
SOBr2
Br2 / light
N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) / light
N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) / light
N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) brominates at allylic positions. Br2 will not complete this reaction with the presence of the double bond.
Example Question #11 : Reactions By Product
What is the best reagent for abstracting a hydrogen from ethyne?
None of these
The triple bond in ethyne makes the hydrogens slightly more acidic than those found in ethane. A very strong base, such as the conjugate base of ammonia, would be able to abstract that hydrogen. The abstraction turns the base into ammonia. It also creates a carbanion that can be used for chain extension and alkyne synthesis.
Example Question #1 : Alkyne Chemistry

What is the product of the compound when it reacts with two equivalents of base?
None of these
2-pentyne
1-pentyne
1-pentene
2-pentene
2-pentyne
For each equivalent of base, a pi bond is formed between the carbons initially bound to the bromine atoms. For each bond formed, a bromine leaving group leaves the hydrocarbon. One equivalent of base abstracts a hydrogen. The electrons from the bond to the hydrogen create a pi bond. This occurs twice, and a triple bond is formed. The result is a 5-carbon chain with a triple bond between the second and third carbons. This molecule is 2-pentyne.
Certified Tutor
All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources