All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #3 : How To Find The Area Of A Square
A square is inscribed in a circle. The diameter of the circle is 10 feet. What is the area of the square?
It cannot be determined from the information provided.
Since the diameter of the circle is 10, we know the radius of the circle is 5 feet. We can then draw radii that go from the center to two consecutive corners of the square. These radii are both 5 feet, and form a 90 degree angle (since they are diagonals of a square). Thus, with the enclosed side of the square they form a 45-45-90 triangle. Thus, the side of the square must be 
Example Question #171 : Plane Geometry

In the figure above, a square is inscribed in a circle with a diameter of 5 cm.
What is the area of the square?
The diameter of the circle and the sides of the square form a 45-45-90 triangle. Since the hypotenuse is 5 cm, then a leg of the triangle (a side of the square) is 
The area of the square is then 
Example Question #4 : How To Find The Area Of A Square
Square 





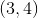
Quantity A: The area of square
Quantity B: 24
Quantity B is greater
The information cannot be determined based on the information provided
Quantity A is greater
The two quantities are equal
Quantity A is greater
If you draw points 

Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Diagonal Of A Square
If a square has a side length of 4, how long is the diagonal of the square?
4
4√2
8√2
16
2√2
4√2
A diagonal divides a square into two 45-45-90 triangles, which have lengths adhering to the ratio of x: x: x√2. Therefore, 4√2 is the correct answer as the diagonal represents the hypotenuse of the triangle. the Pythagorean theorem can also be used: 42+ 42 = c2.
Example Question #1372 : Gre Quantitative Reasoning
If a square has a side length of √2, how long is the diagonal of the square?
4-√2
4
4√2
2√2
2
2
A diagonal divides a square into two 45-45-90 triangles, which have lengths adhering to the ratio of x: x: x√2. Therefore, 2 is the correct answer as the diagonal represents the hypotenuse of the triangle. the Pythagorean theorem can also be used: √22+ √22 = c2.
Example Question #181 : Plane Geometry
A square has a side of length 5. What is the length of its diagonal?
10√3
10
5√3
5
5√2
5√2
The diagonal separates the square into two 45-45-90 right triangles. The problem can be solved by using the Pythagorean Theorem, a2 + b2 = c2. It can also be solved by recognizing the 45-45-90 special triangles, which have side ratios of x : x : x√2.
Example Question #182 : Plane Geometry
A square with width of 
We know that each side of the square is 6, so use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for the diagonal of the square. The diagonal of the square is also the diameter of the circle.
Therefore the radius must be
Now let's find the area inside the circle using the radius.

Example Question #183 : Plane Geometry
Quantity A:
The diagonal of a square with a side-length of 
Quantity B:
The side-length of a square with a diagonal of 
Quantity B is greater.
Quantity A is greater.
Both quantities are equal.
The relationship between the two quantities cannot be determined from the information given.
Both quantities are equal.
Quantity A: The diagonal of a square with a side-length of 7.
Quantity B: The side-length of a square with a diagonal of 14.
Both quantities can be determined, so can the relationship.
Quantity A:
To determine the diagonal of a square, it's important to remember that a diagonal directly bisects a square from corner to corner. In other words, it bisects the corners, creating two triangles with 45:45:90 proportions, with the diagonal serving as the hypotenuses . If you remember your special triangles, then the side-side-hypotenuse measurements have a ratio of 
In Quantity A, the side-length is 7. Following the proportion:
The diagonal equals 
Quantity B:
We can use the same ratio to figure out quantity B by substituting x for the unknown side-length quantity, which looks like this:
To find x in this ratio, just isolate x in the hypotenuse:
Divide by
Now, how does Quantity A and Quantity B match up?
On the surface, it looks like the two quanties are equal. But how do we prove it? Well, we know that 
Divide both sides by
Therefore, both quantities are equal.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Square
Quantity A:
The side-length of a square with a perimeter of 
Quantity B:
The side-length of a square with an area of 
Both quantities are equal
Quantity A is greater
Quantity B is greater
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given
Quantity A is greater
The first step to a quantitative comparison is to determine whether it can be solved at all with the given knowledge. Since all you need to find the side-length of a square is the perimeter, the area, OR the diagonal and we have one of each for these two quantities, this relationship can be determined. Thus, "the relationship cannot be determined" is out.
Now, to solve both quantities. Quantity A can be solved by translating the perimeter into side lengths: the formula for the perimeter of a square is 

Thus, quantity A is 
Quantity B can be solved by translating the area into side lengths: the formula for the area of a square is 


Thus, quantity B is roughly 
Therefore quantity A is greater.
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Square

Circle 

If the area of Circle 


If the area of Circle 



Simplifying, we get:
We know that 





Notice that the diameter is the same length as a side of the square. Thus, 

All GRE Math Resources


















































