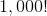All Finite Mathematics Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #41 : Logic, Sets, And Counting
Consider the logical proposition:
"William Shakespeare is dead."
True or false: The proposition "William Shakespeare is alive" is the negation of that statement.
True
False
True
The negation of a proposition 


The negation of "William Shakespeare is dead" is "It is not true that William Shakespeare is dead," or, simply, "William Shakespeare is alive."
Example Question #82 : Finite Mathematics
In order to win the grand prize in a lottery, the six numbers that come up must match the six numbers you chose; the order in which they come up need not be the same as the order on your ticket.
Is this is an example of a permutation or a combination?
Combination
Permutation
Combination
A combination is defined as an unordered subset of a set; a permutation is an ordered subset. The key to answering this question is the phrase " the order...need not be the same." This is an indication that this is a combination.
Example Question #83 : Finite Mathematics
Try without a calculator:
Which of the following is equal to 
For any whole numbers 

Setting 

Example Question #42 : Logic, Sets, And Counting
Consider the conditional statement
"If 
Give the truth value of this statement.
The statement has no truth value.
True
False
True
This conditional statement has a false antecedent 
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All Finite Mathematics Resources