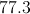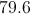All Common Core: 6th Grade Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Understand The Shape Of A Data Set: Ccss.Math.Content.6.Sp.B.5d
Which of the following is the best measure of center for the data set in the provided table?

Mode
Mean
Either mode or median
Median
Mean
In order to answer this question correctly, we need to solve for the mean, median, and mode of this data set.
To begin, let's sort the data from least to greatest:
Now that our data is ordered from least to greatest, we can solve for the median:
Remember, the median is the middle most number when a data set is ordered from least to greatest.
The median for this data set is
Next, we can look at our data set to determine the mode:
There is no mode for this set because each value only appears once.
Remember, the mode is the number in a set that appears most often.
Finally, we can solve for the mean:

Remember, the mean of a data set is the average of the numbers in a data set.
The mean for this data set is
Now that we've done our calculation we should have:
Median:
Mode: None
Mean:
We are looking for the value that is representative of the center of the data; thus the mean would be the best measure because of how varied the set is. Normally, when a data set is varied the mean is normally the best measure of center.
Example Question #2 : Understand The Shape Of A Data Set: Ccss.Math.Content.6.Sp.B.5d
Which of the following is the best measure of variability for the data in the provided table?

Neither range nor interquartile range
Either range or interquartile range
Range
Interquartile range
Interquartile range
In order to answer this question correctly, we need to solve for the range and the interquartile range.
To begin, let's sort the data from least to greatest:
Next, we can solve for the range. Remember, the range of a data set is the difference between the highest value and the lowest value in the set.
The range for this data set is
Now, we can solve for the interquartile range. Remember, the interquartile range is the difference between the upper quartile median and the lower quartile median. This means that we need to first calculate these two values. In order to do this, we need to split the data set into quartiles.
First, we will find the median:
We will then use the median to split the data in half. Next, we must find the median of the first half—or lower quartile—and then the median of the second half—or upper quartile:
Now we can solve for the difference between the upper quartile median and the lower quartile median:
Now that we have completed these operations, we should have calculated the following values:
Range:
Interquartile range:
As you can see, solving for the interquartile range requires more steps because it takes into account more of the data points; thus, given our options, interquartile range is best to use when solving for variability.
Example Question #3 : Understand The Shape Of A Data Set: Ccss.Math.Content.6.Sp.B.5d
Which of the following is the best measure of center for the data set in the provided table?

Median
Mean
Mode
Either the median or the mode
Mean
In order to answer this question correctly, we need to solve for the mean, median, and mode of this data set.
To begin, let's sort the data from least to greatest:
Now that our data is ordered from least to greatest, we can solve for the median:
Remember, the median is the middle most number when a data set is ordered from least to greatest.
The median for this data set is
Next, we can look at our data set to determine the mode:
The mode for this set is
Remember, the mode is the number in a set that appears most often.
Finally, we can solve for the mean:

Remember, the mean of a data set is the average of the numbers in a data set.
The mean for this data set is
Now that we've done our calculation we should have:
Median:
Mode:
Mean:
We are looking for the value that is representative of the center of the data; thus the mean would be the best measure because of how varied the set is. Normally, when a data set is varied the mean is normally the best measure of center.
Example Question #4 : Understand The Shape Of A Data Set: Ccss.Math.Content.6.Sp.B.5d
Which of the following is the best measure of center for the data set in the provided table?

Mean
Either median or mode
Mode
Median
Median
In order to answer this question correctly, we need to solve for the mean, median, and mode of this data set.
To begin, let's sort the data from least to greatest:
Now that our data is ordered from least to greatest, we can solve for the median:
Remember, the median is the middle most number when a data set is ordered from least to greatest.
The median for this data set is
Next, we can look at our data set to determine the mode:
The mode for this set is
Remember, the mode is the number in a set that appears most often.
Finally, we can solve for the mean:

Remember, the mean of a data set is the average of the numbers in a data set.
The mean for this data set is
Now that we've done our calculation we should have:
Median:
Mode:
Mean:
We are looking for the value that is representative of the center of the data. In this data set we have an outlier, which means the mean is not going to be the best measure of center. Also, the mode is the lowest value in our set; thus, the median is the best measure of center.
Example Question #5 : Understand The Shape Of A Data Set: Ccss.Math.Content.6.Sp.B.5d
Which of the following is the best measure of variability for the data in the provided table?

Neither range nor interquartile range
Range
Either range or interquartile range
Interquartile range
Interquartile range
In order to answer this question correctly, we need to solve for the range and the interquartile range.
To begin, let's sort the data from least to greatest:
Next, we can solve for the range. Remember, the range of a data set is the difference between the highest value and the lowest value in the set.
The range for this data set is
Now, we can solve for the interquartile range. Remember, the interquartile range is the difference between the upper quartile median and the lower quartile median. This means that we need to first calculate these two values. In order to do this, we need to split the data set into quartiles.
First, we will find the median:
We will then use the median to split the data in half. Next, we must find the median of the first half—or lower quartile—and then the median of the second half—or upper quartile:
Now we can solve for the difference between the upper quartile median and the lower quartile median:
Now that we have completed these operations, we should have calculated the following values:
Range:
Interquartile range:
As you can see, solving for the interquartile range requires more steps because it takes into account more of the data points; thus, given our options, interquartile range is best to use when solving for variability.
Example Question #81 : Statistics & Probability
Which of the following is the best measure of center for the data set in the provided table?

Median
Either mode or median
Mean
Mode
Median
In order to answer this question correctly, we need to solve for the mean, median, and mode of this data set.
To begin, let's sort the data from least to greatest:
Now that our data is ordered from least to greatest, we can solve for the median:
Remember, the median is the middle most number when a data set is ordered from least to greatest.
The median for this data set is
Next, we can look at our data set to determine the mode:
The mode for this set is
Remember, the mode is the number in a set that appears most often.
Finally, we can solve for the mean:

Remember, the mean of a data set is the average of the numbers in a data set.
The mean for this data set is
Now that we've done our calculation we should have:
Median:
Mode:
Mean:
We are looking for the value that is representative of the center of the data. In this data set we have an outlier, which means the mean is not going to be the best measure of center. Also, the mode is the lowest value in our set; thus, the median is the best measure of center.
Example Question #11 : Understand The Shape Of A Data Set: Ccss.Math.Content.6.Sp.B.5d
Which of the following is the best measure of variability for the data in the provided table?

Range
Neither range nor interquartile range
Either range or interquartile range
Interquartile range
Interquartile range
In order to answer this question correctly, we need to solve for the range and the interquartile range.
To begin, let's sort the data from least to greatest:
Next, we can solve for the range. Remember, the range of a data set is the difference between the highest value and the lowest value in the set.
The range for this data set is
Now, we can solve for the interquartile range. Remember, the interquartile range is the difference between the upper quartile median and the lower quartile median. This means that we need to first calculate these two values. In order to do this, we need to split the data set into quartiles.
First, we will find the median:
We will then use the median to split the data in half. Next, we must find the median of the first half—or lower quartile—and then the median of the second half—or upper quartile:
Now we can solve for the difference between the upper quartile median and the lower quartile median:
Now that we have completed these operations, we should have calculated the following values:
Range:
Interquartile range:
As you can see, solving for the interquartile range requires more steps because it takes into account more of the data points; thus, given our options, interquartile range is best to use when solving for variability.
Example Question #11 : How To Find Mean
In a group of 4 books, the average number of pages is is 10. Juan adds a book with 20 pages to the group. What is the new average number of pages?
If the average of 4 books was 10, then the total number of pages was 

Example Question #12 : How To Find Mean
Give the mean of the data set (nearest tenth, if applicable):
Add the six elements and divide the sum by 6:
Example Question #13 : How To Find Mean
Find the mean of this set of numbers:
54, 41, 99, 120, 66.
Firrst, add the numbers:
Then, divide by the amount of numbers in the set:
Answer: The mean is 76.
All Common Core: 6th Grade Math Resources









![\frac{\begin{array}[b]{r}50\\ -\ 20\end{array}}{ \ \ \ \space 30}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/992379/gif.latex)



![\frac{\begin{array}[b]{r}50\\ -\ 25\end{array}}{ \ \ \ \space 25}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/992383/gif.latex)





















![\frac{\begin{array}[b]{r}29\\ -\ 2\end{array}}{ \ \ \ \space 27}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/992414/gif.latex)



![\frac{\begin{array}[b]{r}7\\ -\ 2\end{array}}{ \ \ \ \space 5}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/992418/gif.latex)












![\frac{\begin{array}[b]{r}20\\ -\ 3\end{array}}{ \ \ \ \space 17}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/992351/gif.latex)



![\frac{\begin{array}[b]{r}7\\ -\ 3\end{array}}{ \ \ \ \space 4}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/992355/gif.latex)