All Calculus 1 Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Functions
Estimate the area under the curve for the following function from 


If we are told to use 













Example Question #2 : Midpoint Riemann Sums
Find the area under 
![[0,1]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/352150/gif.latex)
The problem becomes this:

Addings these rectangles up to approximate the area under the curve is
Example Question #1 : How To Find Midpoint Riemann Sums
Approximate the area under the curve from 

We begin by finding the given change in x:
We then define our partition intervals:
We then choose the midpoint in each interval:
Then we find the value of the function at the point. This is determined through observation of the graph
Then we simply substitute these values into the formula for the Riemann Sum
Example Question #2 : How To Find Midpoint Riemann Sums
Approximate the area underneath the given curve using the Riemann Sum with eight intervals for 
We begin by defining the size of our partitions and the partitions themselves.
We then choose the midpoint in each interval:
Then we find the function value at each point.
We then substitute these values into the Riemann Sum formula.
Example Question #1031 : Calculus
Using a midpoint Reimann sum with 
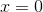

Thus, our intervals are 





The midpoints of each interval are, respectively, 


Next, we evaluate the function at each midpoint.
Finally, we calculate the estimated area using these values and
Example Question #7 : Differential Functions
The table above gives the values for a function at certain points.
Using the data from the table, find the midpoint Riemann sum of 

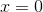

Thus, our intervals are 





The midpoints of each interval are, respectively, 


Next, use the data table to take the values the function at each midpoint.
Finally, we calculate the estimated area using these values and 
Example Question #4 : Differential Functions
Solve the integral
using the midpoint Riemann sum approximation with 
Midpoint Riemann sum approximations are solved using the formula
where 

For this problem, 
The approximate value at each midpoint is below.

The sum of all the approximate midpoints values is 
Example Question #1 : How To Find Midpoint Riemann Sums
Solve the integral
using the midpoint Riemann sum approximation with 
Midpoint Riemann sum approximations are solved using the formula
where 

For this problem, 
The approximate value at each midpoint is below.

The sum of all the approximate midpoints values is 
Example Question #10 : Differential Functions
Solve the integral
using the midpoint Riemann sum approximation with 
1
1
Midpoint Riemann sum approximations are solved using the formula
where 

For this problem, 
The approximate value at each midpoint is below.

The sum of all the approximate midpoints values is 
Example Question #1032 : Calculus
Solve the integral
using the midpoint Riemann sum approximation with 
Midpoint Riemann sum approximations are solved using the formula
where 

For this problem, 
The approximate value at each midpoint is below.

The sum of all the approximate midpoints values is 
All Calculus 1 Resources


















![A=0.2[(1-0.1^2)+(1-0.3^2)+(1-0.5^2)+(1-0.7^2)+(1-0.9^2)]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/352152/gif.latex)
![A=0.2[5-0.1^2-0.3^2-0.5^2-0.7^2-0.9^2]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/352153/gif.latex)
![A=0.2[3.35]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/352154/gif.latex)



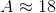


![[x_{i-1},x_i]=[0,1.6),[1.6,3.2),[3.2,4.8),[4.8,6.4),[6.4,8]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/358807/gif.latex)





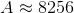



![[x_{i-1},x_i]=[-4,-2],[-2,0],[0,2],[2,4],[4,6],[6,8],[8,10],[10,12]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/359075/gif.latex)



































![\int_{a}^{b}f(x))dx\approx (\frac{b-a}{n})\left [ f({m_{1}})+f({m_{2}})+...+f({m_{n}}) \right ]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/361633/gif.latex)
![(\frac{b-a}{n})\left [ f({m_{1}})+f({m_{2}})+...+f({m_{n}}) \right ] =0.7(20.6068259)\approx14.4248](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/361635/gif.latex)






![\int_{a}^{b}f(x))dx\approx (\frac{b-a}{n})\left [ f({m_{1}})+f({m_{2}})+...+f({m_{n}}) \right ]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/361629/gif.latex)
![(\frac{b-a}{n})\left [ f({m_{1}})+f({m_{2}})+...+f({m_{n}}) \right ] =0.4(2.116738)\approx0.8467](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/361631/gif.latex)





![(\frac{b-a}{n})\left [ f({m_{1}})+f({m_{2}})+...+f({m_{n}}) \right ] =0.1571(6.37275)\approx1](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/361644/gif.latex)






![(\frac{b-a}{n})\left [ f({m_{1}})+f({m_{2}})+...+f({m_{n}}) \right ] =0.3(468.3221)\approx140.4966](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/361647/gif.latex)



