All AP Physics B Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Understanding Wavelength, Frequency, And Velocity
In the electromagnetic spectrum, __________ have the highest frequency and __________ have the greatest energy per photon.
microwaves . . . microwaves
gamma rays . . . gamma rays
infrared light . . . ultraviolet light
X-rays . . . radio waves
ultraviolet light . . . X-rays
gamma rays . . . gamma rays
The relationship between frequency and energy is determined by Planck's constant in a direct relationship. This means that as frequency increases, energy increases as well.
The electromagnetic waves with the highest frequency will have the greatest energy per photon, and vice versa.
In the electromagnetic spectrum, radio waves have the lowest frequency (largest wavelength) and gamma rays have the highest frequency (shortest wavelength). Gamma rays will thus have the highest frequency and greatest energy.
Example Question #2 : Ap Physics 2
Two in-phase waves travelling in the same direction with the same period have amplitudes of 


The amplitudes of in-phase waves add in what is called constructive interference. We can find the resultant amplitude of the first two waves by adding their individual amplitudes.
The third wave is out of phase, meaning that it will contribute destructive interference when the three waves align. We subtract the amplitude of the third wave from the total of the first two.
This is the final amplitude of the resultant wave.
Example Question #1 : Waves And Optics
An object is placed 
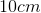






For the thin lens equation, the convention for image distance is positive on the opposite side of the lens from the object. In effectively all practical cases for a single thin lens, positive image distance corresponds to a real image, and negative to a virtual. Convex lenses effectively only produce real images for objects outside their focal distance. Based on these initial observations, certain answer choices can be eliminated.
Use the thin lens equation to choose between the remaining answer options.
In the equation, 




Since the object distance is twice the focal length, the image distance will be as well. So 
.
The ray diagram for a simple thin lens can be constructed according to three rules that apply, in their own way, either to converging or diverging lenses (convex or concave):
- A ray traveling parallel to the optical axis gets bent by the lens so as to pass, or appear to pass, through the focal point.
- A ray traveling through the center of the lens is not deviated.
- A ray passing through, or appearing to pass through, the focal point of the lens is bent parallel to the optical axis.
Following these rules, it can be seen that the convex lens brings the light rays to a real focus at the image position, and the image would fall on a screen placed at that point to create a real image.
Note: This configuration represents what is called “

Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All AP Physics B Resources














