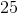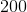All AP Environmental Science Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #361 : Ap Environmental Sciences
All of the following are potential benefits to dams EXCEPT __________.
Sedimentation buildup
Recreation opportunities from the resulting lake
Water level management
Clean electricity generation
Flood control
Sedimentation buildup
Dams can be huge boons to local economies, and are a landmark of human engineering and achievement; however, they do carry serious consequences to the natural environment. They lead to sediment buildup, which hurts the flow of nutrients downstream, ruins the natural riverscape, and can cause the area behind the dam to become more shallow.
Example Question #3 : Energy Sources And Production
All of the following are drawbacks to dams EXCEPT __________.
Habitat alteration
Local inhabitants may be forced to move
Destruction of surrounding farmland
Increased air pollution
Interruption of migration patterns among fish
Increased air pollution
Dams carry numerous drawbacks, but one benefit of dams that they do not increase air pollution. Hydroelectric power is considered to be one of the cleanest forms of energy.
Example Question #21 : Energy Production And Usage
Which of the following is NOT an adverse affect of building dams to generate hydro-electric power?
Animals that rely on fish as sustainance may begin to decline because the dam has permanently altered fish habitat.
Many fish populations (including salmon and trout) are decimated because dams restrict access to essential habitat.
Dams can contribute to flooding and resulting property damage.
The energy required to operate and maintain the dam is often equal to the energy produced by the dam.
Dams often change the current and width of a watershed, altering the riparian ecosystem.
The energy required to operate and maintain the dam is often equal to the energy produced by the dam.
The energy output from a hydro-electric dam is substantial enough to result in most of America's major rivers being damned. The more pressing issues that these damns cause are changes to the aquatic ecosystem and restriction of movement for migratory fish species.
Example Question #23 : Energy Production And Usage
Hydroelectric energy composes a significant portion of the U.S. energy grid and is a low-emission, renewable form of energy. Which of the following would be a substantial issue with expanding hydroelectric energy production?
The reported amount of electricity generated by hydroelectric dams is actually an inflated figure derived from theoretically running at full capacity and is not realistic.
The amount of energy invested in hydroelectric is about equal to the amount of energy harnessed from the process.
Most if not all rivers capable of generating substantial hydroelectric energy have already been dammed and are working at high capacity.
With the pressing issue of climate change and changes in precipitation, it is unclear how much energy current hydroelectric dams can provide in the future, let alone how much energy dams built in the future could provide.
There is currently a federal ban on the construction or development of future hydroelectric dams to protect fish populations.
Most if not all rivers capable of generating substantial hydroelectric energy have already been dammed and are working at high capacity.
While there are federal wetland conservation laws geared at protecting aquatic habitat, there is currently no federal ban on constructing hydroelectric dams, and the returned energy investment for hydroelectric is quite substantial. The dominant issue with expanding hydroelectric energy production is that in the U.S., we have dammed most if not all of the significant energy-producing water bodies. Further expansion of hydroelectric power will not yield as much energy as the current dams operating in the U.S.
Example Question #1 : Other Energy Sources
Charlie lives off-grid and gets his electricity from a 5,000 watt gasoline generator, but with the rising cost of fossil fuel, Charlie is looking to convert to solar energy. If a standard solar panel can generate 200 watts, how many panels would Charlie need to purchase if he wants to get the same energy output that he does with his gas generator?
Wattage is a measurement of electricity being generated over time. When compared to the 5,000 watt output of a conventional generator, a single solar panel generating 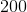
This calculation tells us that Charlie will need 25 standard solar panels to generate the same amount of electricity as one gasoline generator.
Example Question #24 : Energy Production And Usage
An important renewable energy source is solar power. Solar power works by storing sunlight in batteries using which type of cells?
Photovoltaic cells
Radiation cells
Thermal cells
Eukaryotic cells
Photovoltaic cells
The correct response is photovoltaic cells. These photovoltaic cells are the reason we can capture and use sunlight to power our homes and cars. Technological advances in photovoltaic cells have made solar energy economically viable over the past decade. Eukaryotic cells are a type of living organisms, while thermal and radiation cells are made-up terms.
Example Question #361 : Ap Environmental Sciences
Scientists agree that this option holds the most promise for an efficient, cheap, and environmentally safe source of fuel.
Proton pumps
Ethanol made from cellulosic plants
Ethanol made from corn
Biodiesel made from corn
Agricultural wastes
Ethanol made from cellulosic plants
Ethanol can be made from cellulosic—or woody—plants such as switchgrass, poplars, and willows. Cellulose, or plant tissue, sequesters a huge amount of carbon and contains a great deal more energy per unit than corn. Scientists believe that within the next two decades, research will have figured out how to quickly and efficiently break down plant tissue for fermentation into fuel.
Biodiesel made from corn is environmentally safe to burn; however, it requires a great deal of water and resources to grow and harvest.
Agricultural wastes can have a negative impact on air quality due to the pollutants they generate when burned, such as sulfur oxide, nitrogen oxide, and carbon monoxide.
Example Question #26 : Energy Production And Usage
Which of the following is NOT a drawback of utilizing hydrogen as a fuel source?
The input of energy to produce hydrogen is often greater than the energy of the resulting hydrogen.
Hydrogen has a low energy density by volume.
Existing infrastructure for manufacturing and transporting hydrogen is minimal to nonexistent.
Hydrogen is very challenging and dangerous to transport.
Hydrogen has a low energy density by weight.
Hydrogen has a low energy density by weight.
Hydrogen is very challenging to transport and it requires a large energy investment to produce it. While hydrogen has a low energy density by volume, it actually has a very high energy density by weight. This has to do with the fact that hydrogen, discussed in this context, is a gas.
Example Question #1 : Other Energy Sources
Which of the following is NOT correct about geothermal energy?
Geothermal has proven cost-effective in remote communities where importing fuel is challenging and expensive.
Iceland has been able to utilize geothermal to meet over twenty-five percent of their energy demand, in large part because of the geothermal activity of the region.
Fuel consumption of geothermal plants is insignificant when compared to that of coal and natural gas plants.
Geothermal energy can be harnessed in any region of the world and contribute substantially to the power grid.
While sustainable, geothermal plants do emit small quantities of carbon dioxide and some toxic gases, originally trapped in gas pockets deep below the surface.
Geothermal energy can be harnessed in any region of the world and contribute substantially to the power grid.
Geothermal activity has proven to be a cheap, low-cost and environmentally friendly energy source for communities located in areas with high geothermal activity, particularly where the earth's crust is rather thin (e.g. Iceland); however, this method of harvesting energy is not very economically feasible or possible in areas with little near-surface geothermal activity.
Example Question #2 : Other Energy Sources
Which of the following most accurately defines "Synfuel"?
A liquid fuel processed from a non-petroleum material such as coal or waste plastics.
A derivative of waste plastics that results in a form of kerosene
A counterfeit fuel produced by illegitimate companies that can prove harmful to industry when mixed with fuel reserves
Synthetic fuel, derived exclusively from non-organic sources as opposed to organic sources (e.g. biodiesel, ethanol, etc.)
Fuel synthesized in a laboratory as opposed to refined from crude oil
A liquid fuel processed from a non-petroleum material such as coal or waste plastics.
Synfuel is derived from waste plastic, coal, natural gas and other non-petroleum sources. It is a liquid fuel and the process of deriving synfuel can produce gasoline, diesel, and kerosene.
Certified Tutor
All AP Environmental Science Resources