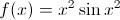All AP Calculus AB Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #24 : Functions, Graphs, And Limits
Is the following piecewise function continuous for all 
No. The function is not continuous at both 

No. The function is not continuous at 
No. There are sharp turns at 

Yes. The function is continuous at all 
No. The function is not continuous at 
Yes. The function is continuous at all 
To check if the piecewise function is continuous, all we need to do is check that the values at 3 and 5 line up.
At 



Plugging 3 into both, we see that both of them are 12 at 
Next, for 


As all three equations are polynomials, we know they will be continuous everywhere else, and they meet up smoothly at the piecewise bounds, thus ensuring that the function is continuous everywhere.
Note, there are sharp turns at 

Example Question #21 : Functions, Graphs, And Limits
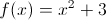


At 
neither differentiable or continuous
undefined
differentiable but not continuous
continuous but not differentiable
both continuous and diffentiable
both continuous and diffentiable
The answer is both.
If graphed the student will see that the two graphs are continuous at 
Example Question #471 : Derivatives
Which of the following functions contains a removeable discontinuity?
A removeable discontinuity occurs whenever there is a hole in a graph that could be fixed (or "removed") by filling in a single point. Put another way, if there is a removeable discontinuity at 



For example, the function 




Thus, we could say that 
As we can see, the limit of 


What this means is that 




The functions

have discontinuities, but these discontinuities occur as vertical asymptotes, not holes, and thus are not considered removeable.
The functions



The answer is

Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All AP Calculus AB Resources