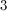All SAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #111 : Integers
If k and m are positive integers, let k # m be equal to the reaminder when k is divided by m. For example, 3 # 2 = 1. All of the following are true EXCEPT:
0 # (k + m) = 0
k # k = m # m
(k2 )# k = 0
m # m = 0
(km) # k = m
(km) # k = m
Let's look at each statement separately and see if it must be true.
First, let's consider 0 # (k + m) = 0.
This statement essentially says that if we divide 0 by the sum of k and m, the remainder should be 0. In general, when 0 is divided by an integer (other than itself), the result is zero with a remainder of zero. For example, if 0 is divided by 2, then 2 will go into zero exactly zero times with a remainder of zero. Because the sum of k and m is an integer, this means that zero divided by (k + m) will also have a remainder of zero. Thus, 0 # (k + m) = 0 is true.
Next, let's examine m # m = 0. This statement says that if we divide m by itself, we should get a remainder of zero. This is true, because any integer divided by itself is equal to 1, with a remainder of zero. Remember that the result of using the # symbol only gives us the remainder. Therefore m # m = 0, not 1.
Let's now look at k # k = m # m.
As we established previously, m # m = 0. Similarly, k # k = 0, because any integer divided by itself produces a remainder of zero. Because m # m and k # k both equal zero, they are also equal to each other. Thus, k # k = m # m is indeed true.
Next, let's consider (k2) # k = 0. This says that if we square an integer and then divide the result by the integer, we should get a remainder of zero. This is true, because an integer is always a factor of its square. In other words, the square of an integer is always divisible by the integer. And if one number is divisible by another, then the resulting quotient has a remainder of zero. For example (52) # 5 = 0, because when we divide 25 by 5, we get 5 with a remainder of zero. Again, remember that we are only concerned with the remainder.
By the process of elmination, the answer is (km) # k = m. Let's see why this statement must be false. The product of k and m has factors k and m. For example, the product of 4 and 3, which equals 12, has the factors 4 and 3. When a number is divided by one of its factor, the resulting remainder must be zero. For example (4(3)) # 4 = 12 # 4 = 0, because the remainder when 12 is divided by 4 is equal to zero. Thus (km) # k = 0, not m.
The answer is (km) # k = m.
Example Question #761 : Arithmetic
If 


5
7
3
6
4
5
We will essentially have to represent 180 as a product of prime factors, because 2, 3, 5, and 7 are all prime numbers. The easiest way to do this will be to find the prime factorization of 180.
180 = 18(10)= (9)(2)(10) = (3)(3)(2)(10)=(3)(3)(2)(2)(5) = 



In order for 

The answer is 5.
Example Question #22 : Factors / Multiples
What is the product of the distinct prime factors of 24?
The prime factorization of 24 is (2)(2)(2)(3). The distinct primes are 2 and 3, the product of which is 6.
Example Question #11 : How To Factor A Number
How many prime factors does 
Since 7 is prime, its only prime factor is itself.
Example Question #122 : Integers
What is the smallest positive multiple of 12?
Multiples of 12 are found by multiplying 12 by a whole number. Some examples include:
Clearly, the smallest positive value obtainable is 12. Do not confuse the term multiple with the term factor!
Example Question #31 : Factors / Multiples
How many prime factors of 210 are greater than 2?
one
four
five
three
two
three
Begin by identifying the prime factors of 210. This can be done easily using a factoring tree (see image).

The prime factors of 210 are 2, 3, 5 and 7. Of these factors, three of them are greater than 2.
Example Question #12 : How To Factor A Number
How many integers between 50 and 100 are divisible by 9?
8
5
7
9
6
6
The smallest multiple of 9 within the given range is 
The largest multiple of 9 within the given range is 
Counting the numbers from 6 to 11, inclusive, yields 6.
Example Question #66 : Factors / Multiples





All SAT Math Resources