All SAT II Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Ionic Bonds
How many of the following compounds are ionic?
All five
Zero
One
Three
Two
Two
Ionic compounds are chemical compounds made of charged ions held together by forces called ionic bonding. Ionic bonds are formed by transfers of valance electrons, which create charged atoms (ions) which are attracted to each other because they have opposite charges. This is not be confused with covalent bonding, in which atoms form an attraction by sharing electrons.


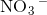



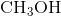




Example Question #1 : Bonding And Forces
Which of the following does not exhibit hydrogen bonding as an intermolecular force?
Hydrogen bonding occurs between hydrogen and a very electronegative atom, which is usually fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen. Thus, hydrogen bonding does not occur in 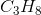
Example Question #2 : Bonding And Forces
In a solution, a weak electrolyte exists predominately as which of the following?
Molecules
Polyatomic ions
Ions
Isotopes
Electrons
Molecules
An electrolyte is a substance that when dissolved in a solution breaks up into ions. More specifically, an electrolyte breaks up into cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions). While strong electrolytes break up 100% into anions and cations, weak electrolytes break apart significantly less. Less than 10% of a weak electrolyte ionizes at all in solution. That means the 90%–99% of the weak electrolyte's molecules do not ionize. This is because the intermolecular forces that form between the solution and the weak electrolyte's molecules are not stronger than the intramolecular forces holding the molecule together. While solutions containing weak electrolytes contain both ions formed from the weak electrolyte ions and molecules of the weak electrolyte, they contain mostly molecules of the weak electrolyte.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All SAT II Chemistry Resources














