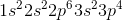All Physical Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Atoms And Elements
Which of the following electron configurations indicates an atom in an excited state?
An atom is considered to be in an excited state when one of the electrons has jumped to a higher energy level while a lower energy level is available. In the case of 
Example Question #2 : Atoms And Elements
What is the complete ground state electron configuration for the magnesium atom?
1s22s23s2
1s22s22p63s2
1s22s22p23s2
1s22s22p63s6
1s42p63s2
1s22s22p63s2
Magnesium has an atomic number of 12, so the total number of electrons in its configuration should add up to twelve. The maximum number of electrons in the s subshell is two. Of all the answer choices, only 1s22s22p63s2 fits the criteria. The sum of the exponent values is 12, matching the atomic number of magnesium, and the number of electrons in the s and p subshells matches the maximum amount possible.
Example Question #3 : Atoms And Elements
What is the complete ground state electron configuration for the iron atom?
1s42s22p63s23p24s23d6
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d4
1s22s22p63s23p63d6
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6
1s22s22p63s24s23d6
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6
Iron has an atomic number of 26, so the total number of electrons in its configuration should add up to twenty six. The maximum number of electrons in the s subshell is two. The sum of the exponent values is 26, matching the atomic number of magnesium, and the number of electrons in the s and p subshells matches the maximum amount possible.
Example Question #4 : Atoms And Elements
In an atom or molecule, why can't two electrons have the same four electronic quantum numbers?
Harmonic Reaction Orders
Kinetic energy operator
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
The first law of thermodynamics
The Pauli Exclusion Principle
The Pauli Exclusion Principle
The Pauli Exclusion Principle explains various phenomena such as the structure of atoms and how different atoms combine to share electrons. When you have two electrons that are located in the same orbital, the quantum numbers n, l and ml are the same. However, ms will be different. Two electrons cannot have the same four electronic quantum numbers because no more than two electrons may occupy an orbital, and if they do, the spin of one must cancel the spin of the other so their spins will have a zero net spin angular momentum.
Certified Tutor
All Physical Chemistry Resources