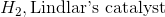All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #21 : Reactions By Reactant

What is the major product of the reaction given?





Alkenes react with NBS (N-bromosuccinimide) in the presence of light to giving products in the position next to the double called the allylic position. Below is the mechanism for this reaction:

Example Question #19 : Help With Alkene Reactions

What is the major product of the reaction given?





Alkenes react with NBS (N-bromosuccinimide) in the presence of light to giving products in the position next to the double called the allylic position. Below is the mechanism for this reaction:

Example Question #11 : Help With Alkene Reactions

What is the product of the chemical reaction given?





Hydroxylation of alkene compounds is called a hydration reaction. The reaction occurs in the presence of a strong acid catalyst to protonate the organic compound similar to Markovnikov's addition forming a carbocation as an intermediate. A water molecule nucleophilicly bonds to the carbocation intermediate. A proton is lost from the positively charged oxygen to a chloride ion yielding the alcohol product and regenerating the acid.

Example Question #21 : Reactions By Reactant

What is the product of the chemical reaction given?





Hydroxylation of alkene compounds is called a hydration reaction. The reaction occurs in the presence of a strong acid catalyst to protonate the organic compound similar to Markovnikov's addition forming a carbocation as an intermediate. A water molecule nucleophilicly bonds to the carbocation intermediate. A proton is lost from the positively charged oxygen to a chloride ion yielding the alcohol product and regenerating the acid.

Example Question #22 : Reactions By Reactant

What is the product of the chemical reaction given?





Hydroxylation of alkene compounds is called a hydration reaction. The reaction occurs in the presence of a strong acid catalyst to protonate the organic compound similar to Markovnikov's addition forming a carbocation as an intermediate. A water molecule nucleophilicly bonds to the carbocation intermediate. A proton is lost from the positively charged oxygen to a chloride ion yielding the alcohol product and regenerating the acid.

Example Question #23 : Reactions By Reactant

What is the product of the chemical reaction given?





Hydroxylation of alkene compounds is called a hydration reaction. The reaction occurs in the presence of a strong acid catalyst to protonate the organic compound similar to Markovnikov's addition forming a carbocation as an intermediate. A water molecule nucleophilicly bonds to the carbocation intermediate. A proton is lost from the positively charged oxygen to a chloride ion yielding the alcohol product and regenerating the acid.

Example Question #24 : Reactions By Reactant

What is the product of the chemical reaction given?





Hydroxylation of alkene compounds is called a hydration reaction. The reaction occurs in the presence of a strong acid catalyst to protonate the organic compound similar to Markovnikov's addition forming a carbocation as an intermediate. A water molecule nucleophilicly bonds to the carbocation intermediate. A proton is lost from the positively charged oxygen to a chloride ion yielding the alcohol product and regenerating the acid.

Example Question #25 : Reactions By Reactant

What is the product of the chemical reaction given?





Hydroxylation of alkene compounds is called a hydration reaction. The reaction occurs in the presence of a strong acid catalyst to protonate the organic compound similar to Markovnikov's addition forming a carbocation as an intermediate. A water molecule nucleophilicly bonds to the carbocation intermediate. A proton is lost from the positively charged oxygen to a chloride ion yielding the alcohol product and regenerating the acid.

Example Question #21 : Help With Alkene Reactions
What is the product of the reaction shown?
The reaction is a catalytic hydrogenation of an alkene using a palladium (Pd) catalyst. This reaction can be used to add a hydrogen atom to each carbon involved in a pi bond. The resulting molecule will be a an alkane.
Example Question #1 : Alkyne Chemistry
Starting with an alkyne, synthesis of a cis alkene is driven upon addition of which of the following reagents?
Reduction of an alkyne with hydrogen and Lindlar's catalyst will result in a cis alkene. While 
Certified Tutor
All Organic Chemistry Resources