All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Specific Reactions And Named Reactions
Which substrate, when subjected to ozonolysis followed by treatment with dimethyl sulfide, would give only one hydrocarbon product?
1,3-octadiene
3-octene
4-octene
2-octene
1,7-octadiene
4-octene
Ozonolysis is essentially used to cleave a compound at the location of a double bond. For the result to be a single product, the cleavage must occur at a point of symmetry.
4-octene, a symmetrical alkene, would give two equivalents of butanal upon ozonolysis. All of the other compounds are unsymmetrical and would give at least two different non-identical products.
Example Question #2 : Specific Reactions And Named Reactions
Ozonolysis of an alkyne results in the products 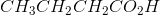

5,5-dimethyl-3-heptyne
2,2-dimethyl-3-heptyne
3,3-dimethyl-2-heptyne
None of these
2,2-dimethyl-3-octyne
2,2-dimethyl-3-heptyne
Ozonolysis of the alkyne breaks the alkyne at the triple bond. The carbons that were in the triple bond become the carbons of either a ketone or a carboxylic acid depending on if they are terminal or not.
Working backwards, one can take the products and remove their oxygens. Then, the carbons from which the oxygens were removed should be triple bonded. The initial compound has seven carbons in its longest chain. Counting from the side closest to the bond, C2 has two methyl groups bound to it. The triple bond runs across C3 and C4. Thus the answer is 2,2-dimethyl-3-heptyne.
Example Question #5 : Specific Reactions And Named Reactions
An organic chemist reacts one mole of 4-octene with excess 
Octane
Two moles of octanol
None of these
Two moles of butal
Two moles of butal
These are standard conditions for an ozonolysis reaction. For an ozonolysis reaction to take place, all we need is an alkene and ozone. The ozone essentially cuts the alkene in half and adds a carbonyl group to each half of the carbon chain.
Certified Tutor
All Organic Chemistry Resources




