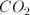All MCAT Physical Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Kinetic Molecular Theory
At room temperature which of the following equimolar gases has the fastest effusion rate?
According to Graham's law, the rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the mass: 
The gas with the lowest molecular weight will effuse the fastest. 

Example Question #2 : Kinetic Molecular Theory
Consider a helium atom and a molecule of carbon monoxide both at a temperature of 
Since both molecules are at the same temperature, the value of the temperature is irrelevant. The difference in velocity between the two molecules depends on the difference in their molar masses. The molar mass of a helium atom is 

Graham's Law describes the relationship between gas particle mass and velocity:
Using the molar masses of the particles in question, we can determine their relationship.
Example Question #52 : Fluids And Gases
Phase diagrams are used to depict changes in the properties of a solution at different temperatures and pressures. Below is a phase diagram of a polar solution.

In section 3, as the temperature increases, the velocity of the molecules __________ in a(n) __________ manner.
increases . . . indirectly proportional
decreases . . . indirectly proportional
decreases . . . indirectly proportional
increases . . . directly proportional
increases . . . indirectly proportional
This question asks you how the velocity of the molecules changes with increasing temperature. From molecular kinteics, we know that temperature is proportional to kinetic energy.
We can see that as temperature rises, the kinetic energy rises, however, the question asks us how the velocity changes. Now, we need to know how kinetic energy and velocity are related. We can pull this relationship from Newtonian mechanics.
If we simplify, we can see that 
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Physical Resources