All MCAT Biology Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #2 : Lipids And Metabolism
Which of the following describes a beta oxidation reaction?
Protein is converted to alpha-keto acid
Glycogen is converted to glucose
Glucose is converted to glycogen
Fatty acid is converted to acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA is converted to fatty acid
Fatty acid is converted to acetyl-CoA
Beta oxidation is the process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the mitochondria to produce acetyl-coA, which can then enter the citric acid (Krebs) cycle. The correct transition from reactant to product for beta oxidation is fatty acid to acetyl-CoA.
Example Question #1 : Lipids And Metabolism
Fatty acids and cholesterol are stored in tissues as __________ and __________, respectively.
triacylglycerols . . . high-density lipoprotein (HDL)
triacylglycerols . . . cholesteryl esters
cholesteryl esters . . . ketone bodies
eicosanoids . . . triacylglycerols
sphingolipids . . . cholesteryl esters
triacylglycerols . . . cholesteryl esters
Fatty acids are stored as triacylglycerols in adipose tissue, while cholesterol is stored as cholesteryl esters in a number of different tissues. Both fatty acids and cholesterol are hydrophobic molecules, which is why they are stored as lipid droplets within their respective tissues.
Example Question #54 : Biochemistry And Metabolism
The cellular membrane is a very important structure. The lipid bilayer is both hydrophilic and hydrophobic. The hydrophilic layer faces the extracellular fluid and the cytosol of the cell. The hydrophobic portion of the lipid bilayer stays in between the hydrophobic regions like a sandwich. This bilayer separation allows for communication, protection, and homeostasis.
One of the most utilized signaling transduction pathways is the G protein-coupled receptor pathway. The hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of the cellular membrane allows for the peptide and other hydrophilic hormones to bind to the receptor on the cellular surface but to not enter the cell. This regulation allows for activation despite the hormone’s short half-life. On the other hand, hydrophobic hormones must have longer half-lives to allow for these ligands to cross the lipid bilayer, travel through the cell’s cytosol and eventually reach the nucleus.
Cholesterol allows the lipid bilayer to maintain its fluidity despite the fluctuation in the body’s temperature due to events such as increasing metabolism. Cholesterol binds to the hydrophobic tails of the lipid bilayer. When the temperature is low, the cholesterol molecules prevent the hydrophobic tails from compacting and solidifying. When the temperature is high, the hydrophobic tails will be excited and will move excessively. This excess movement will bring instability to the bilayer. Cholesterol will prevent excessive movement.
Which of the following hormones utilizes cholesterol as a precursor?
I. Cortisol
II. Aldosterone
III. Mineralocorticoid
III only
None of these
I only
II only
I, II and III
I, II and III
Both cortisol and aldosterone are synthesized in the adrenal cortex with cholesterol as the precursor. Mineralocorticoid refers aldosterone, which is also secreted by the adrenal cortex. All of these hormones are steroidal, which means they are derived from cholesterol. Other steroid hormones are the sex hormones.
Example Question #1 : Other Metabolic Pathways
The body attempts to maintain a steady concentration of glucose in the blood, promoting consistent brain function and red blood cell survival. When glucose levels fall, however, the body breaks down glycogen to replenish stores for a short period of time before new glucose molecules are made through the process of gluconeogenesis.
In which organ does gluconeogenesis occur?
Brain
Heart
Skeletal muscle
Liver
Liver
Gluconeogenesis, the process of creating new glucose from precursors, occurs in the liver and to a very small extent in the cortex of the kidney. The largest stores of glycogen are also located in the liver, but become quickly depleted in situations of low blood glucose.
Example Question #1 : Other Metabolic Pathways
The process of glycolysis is used by all cells of the body to turn glucose into ATP for cellular energy. When stores of glucose are low, however, the body can break down a form of stored glucose in the liver to increase glucose reserves.
What molecule is broken down by a phosphorylase in the liver to yield glucose-1-phosphate?
Glycogen
Triacylglycerol
Glycosylated protein
RNA
Glycogen
Glycogen is the polymer form of glucose, stored in the liver and other tissues when glucose is abundant. When glucose levels are high, glucose-1-phosphate is assembled into branching chains of glycogen. When glucose levels fall, glycogen is broken down by glycogen phosphorylase back into glucose-1-phosphate units. These monomers can be used in glycolysis and cellular respiration. Glycogen is the first source of energy that is used when glucose stores are low.
Example Question #1 : Other Metabolic Pathways
Which of the following cannot be directly converted to acetyl-CoA?
All of these answers can be directly converted to acetyl-CoA
Pyruvate
Alpha-keto acid
Glucose
Fatty acids
Glucose
Pyruvate can be converted to acetyl-CoA by decarboxylation. Beta oxidation can convert fatty acids to acetyl-CoA. Transaminases can be used to make alpha-keto acids, which can be converted to acetyl-coA. Glucose cannot be directly converted to acetyl-CoA; it must be transformed into pyruvate first.
Example Question #341 : Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry, And Metabolism
Which of the following is not an adequate alternative energy source for humans?
Glycogen
Triglycerides
Fatty acids
Cellulose
Alpha-keto acids
Cellulose
Carbohydrates can be stored as glycogen in the liver, fats can be stored as triglycerides or fatty acids in adipose tissue, and proteins can be made into alpha-keto acids. Hence, all of these are forms of energy storage that can be used as alternative energy sources.
Cellulose is a polysaccharide that is found in plants. Humans cannot digest cellulose due to its beta-glycosidic linkages.
Example Question #1 : Other Metabolic Pathways
When the body is unable to renew its glucose stores through glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, it makes ketone bodies derived from beta-oxidation of free fatty acids. Which of the following is not a ketone body utilized by the brain during periods of starvation?
Acetone
Aldehyde
Beta-hydroxybutyrate
Acetoacetate
Aldehyde
The three ketone bodies utilized by the body are acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone. These are produced from acetyl-CoA during beta-oxidation. Acetyl-CoA undergoes conversion reactions to the three ketone bodies in the liver.
Even if you did not know the names of the ketone bodies, you should know that aldehyde is not a ketone because its carbonyl moiety does not have carbons connected from both sides to the carbonyl carbon.
Example Question #1731 : Mcat Biological Sciences
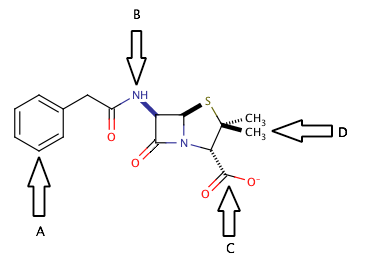
Shown above is the chemical structure for penicillin. Which of the arrows is pointing to an amide group?
B
D
C
A
B
The correct answer is arrow B. An amide group is a carbonyl group with a nitrogen that is in the alpha position (directly attached to the carbonyl carbon). Penicillin has two different amide groups in its chemical structure, but only one has an arrow pointing to it in the diagram. Arrow B points to a primary secondary amide, bond to one hydrogen and two carbons. The other amide in the molecule is a tertiary amide, bond to three carbons and no hydrogens.
Example Question #1732 : Mcat Biological Sciences
Which of the following statements about amide bonds is NOT true?
Amide bonds are polar
Amides are mildly acidic, with primary amides having a pKa of approximately fifteen
A secondary amide has the following structure.

Amides are formed by the combination of a carboxylic acid and an amine, resulting in the loss of water
The nitrogen is 

The nitrogen is 

Amides have a structure of a ketone group adjacent to an amine group.
In an amide bond, all of the atoms (the nitrogen, the carbonyl oxygen, and carbonyl carbon) are 
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Biology Resources