All MCAT Biology Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #361 : Systems Biology And Tissue Types
Which of the following cells is responsible for producing platelets?
T-cells
Megakaryocytes
Macrophages
B-cells
Megakaryocytes
Megakaryocytes are responsible for producing platelets, the remnants of cells that help form clots.
B-cells and T-cells are responsible for humoral and cell-mediated immunity. Macrophages ingest bacteria and viruses and present them to B- and T-cells to initiate an immune reaction.
Example Question #362 : Systems Biology And Tissue Types
Which of the following cells secretes antibodies after being stimulated by helper T-cells?
Memory B-cell
Macrophage
Natural killer cell
Plasma cell
Plasma cell
Plasma cells are differentiated B-cells that serve to secrete antibodies after being stimulated by a helper T-cell.
Natural killer cells are also stimulated by helper T-cells and secrete perforin to kill invading pathogens. Memory B-cells are differentiated B-cells that are specialized to detect a re-infection by the same pathogen, allowing for a quick immune response. Macrophages ingest infecting agents.
Example Question #25 : Types Of Immune System Cells
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when body tissues are affected by an abnormal immune reaction. The result is damage to normal tissues and clinical illness. A peanut allergy is an example of a hypersensitivity reaction, but there are three additional broad classes.
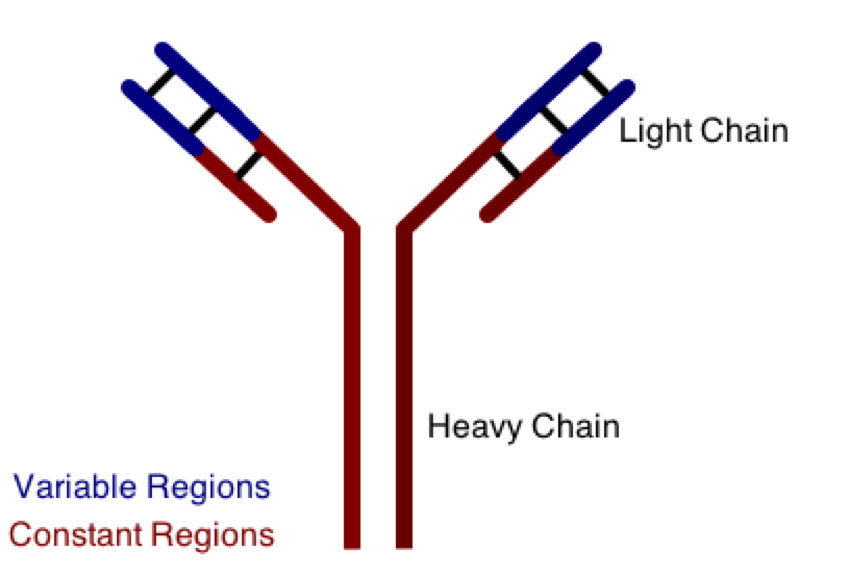
One class involves the abnormal production or deposition of antibodies. Antibodies are B-cell derived molecules that normally adhere to pathogens, rendering them unable to continue an infection. When antibodies are produced against normal tissues, however, disease can result. Figure 1 depicts a schematic structure of an antibody.
Antibodies can be divided into two peptide chains: heavy and light. Heavy chains form the backbone of the antibody, and are attached to light chains via covalent bonding. Each heavy and light chain is then further divided into constant and variable regions. Variable regions exhibit molecular variety, generating a unique chemical identity for each antibody. These unique patterns help guarantee that the body can produce antibodies to recognize many possible molecular patterns on invading pathogens.
One of the functions of antibodies is to facilitate the phagocytosis of pathogens by macrophages or other professional phagocytes. Which of the following organelles is likely to be found in abundance in professional phagocytes, relative to most other cell types?
Golgi apparatus
Endosomes
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosomes
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Endosomes
Endosomes function to shuttle phagocytosed material to the lysosome, where cellular digestion can take place. This means that professional phagocytes, such as macrophages, can be expected to have a larger number of endosomes than other cells that are less specialized for this process.
Example Question #363 : Systems Biology And Tissue Types
Which type of infection would a plasma cell be most effective in clearing from the human body?
An extracellular bacterial infection
Dormant HIV
A Mycobacterium tuberculosis that has been endocytosed by a macrophage
An infection by a newly-evolved bacterial strain
An extracellular bacterial infection
The role of a plasma cell in the immune system is to produce antibodies. These antibodies are effective in binding to extracellular pathogens. Antibodies produced by plasma cells would not be effective in binding to intracellular pathogens, such as M. tuberculosis and intracellular HIV. Only one answer choice specifies an extracellular pathogen.
Plasma cells are developed from B-lymphocyte precursors in response to the presence of a specific antigen, and are part of the adaptive immune response. As such, they would be relatively ineffective at fighting a newly-evolved microbe to which the body has never been exposed before.
Example Question #364 : Systems Biology And Tissue Types
Where in the body do B-lymphocytes mature?
Red bone marrow
Thymus
Lymph nodes
Yellow bone marrow
Red bone marrow
Both B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes are derived from lymphoid progenitor cells, a division of hematopoietic stem cells. These progenitors are housed in red bone marrow. B-lymphocytes remain in the red bone marrow to mature, but T-lymphocytes transition to the thymus for positive selection.
The lymph nodes and spleen are secondary immune tissues, responsible for housing mature B- and T-lymphocytes in order to carry out the immune response. The lymph nodes and spleen are not responsible for immune cell development. Yellow bone marrow is primarily used for fat storage and is not involved in the lymphatic system or immune response.
Example Question #362 : Systems Biology And Tissue Types
Where in the body do T-lymphocytes mature?
Thyroid
Lymph nodes
Bone marrow
Thymus
Thymus
T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes both arise in the bone marrow from the lymphoid progenitor lineage of stem cells. B-lymphocytes remain in the bone marrow for maturation, while T-lymphocytes migrate to the thymus. In the thymus, T-lymphocytes are exposed to antigens from the body's own cells. If the T-cell reacts to the antigen, it is destroyed to prevent autoimmune disorders. This process is known as positive selection.
The thyroid is an endocrine gland, and is not a site for immune cell development. The lymph nodes are secondary immune tissues and are responsible for conducting the immune response and housing mature lymphocytes, not for immune cell development.
Example Question #51 : Immune And Lymphatic Systems
Which type of T-lymphocyte directly destroys infected cells?
Helper T-lymphocytes
Follicular helper T-lymphocytes
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes
Regulatory T-lymphocytes
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, also known as kill T-cells, directly destroy infected cells by releasing their cytotoxic granules into the cells and causing them to lyse.
Helper T-lymphocytes produce cytokines, which are involved in cell signaling and propagating the immune response. Follicular helper T-lymphocytes control B-cells in lymph nodes. Regulatory T-lymphocytes inhibit the immune response.
Example Question #365 : Systems Biology And Tissue Types
Plasma cells and memory cells are categorized under which division of the immune system?
Non-specific defense mechanisms
Humoral immunity
Innate immunity
Cell-mediated immunity
Humoral immunity
The immune system can be broken down into two main categories: innate and adaptive. Innate immunity includes nonspecific defense mechanisms, and the adaptive side is broken down into two primary sections, humoral and cell-mediated immunity. The key players in cell-mediated immunity are T-cells (including helper, suppressor, memory and cytotoxic T-cells). The humoral response occurs through B-cells, which are the precursors for plasma cells and memory cells. Once a B-cell is exposed to a matching antigen, it will begin to produce two types of daughter cells: plasma cells and memory cells. Plasma cells produce large amounts of antibodies in order to fight the infection at hand, where memory cells will remain in the lymph nodes for the rest of the organism's life. Memory cells are key in an organism's quick secondary response to a microbe that was previously encountered.
Example Question #31 : Types Of Immune System Cells
Which of the following cells would be categorized as an agranulocyte?
Monocyte
Neutrophil
Basophil
Eosinophil
Monocyte
Granulocytes are cells categorized because they have vesicles within their membrane that look similar to a granule. Basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils all present granule-like figures and are categorized as granulocytes. Although they derive from the same myeloid stem cells as the granulocytes, monocytes are categorized as agranulocytes.
Example Question #32 : Immune System
Which of the following molecules is not associated with the function of cytotoxic T-cells?
MHC I
Cytokines
MHC II
CD8
MHC II
In terms of MHC restriction, students should be familiar with the fact that cytotoxic T-cells are CD8+ and MHC I restricted. The alternative T subset, the helperT-ell, is CD4+ and MHC II restricted. Both cells rely on cytokines for growth, survival, and their effector functions.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Biology Resources




