All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #11 : Right Triangles

Refer to the above right triangle. Which of the following is equal to 
By the Pythagorean Theorem,
Example Question #47 : Plane Geometry
Given 

Which is the greater quantity?
(a)
(b)
(b) is greater.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.
(a) and (b) are equal.
(a) is greater.
(a) and (b) are equal.
The sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is , so:
This is a 


Example Question #48 : Plane Geometry

Give the length of one leg of an isosceles right triangle whose area is the same as the right triangle in the above diagram.
The area of a triangle is half the product of its height and its base; in a right triangle, the legs, being perpendicular, can serve as these quantites.
The triangle in the diagram has area

An isosceles right triangle has two legs of the same length, which we will call 

Example Question #51 : Isee Upper Level (Grades 9 12) Quantitative Reasoning
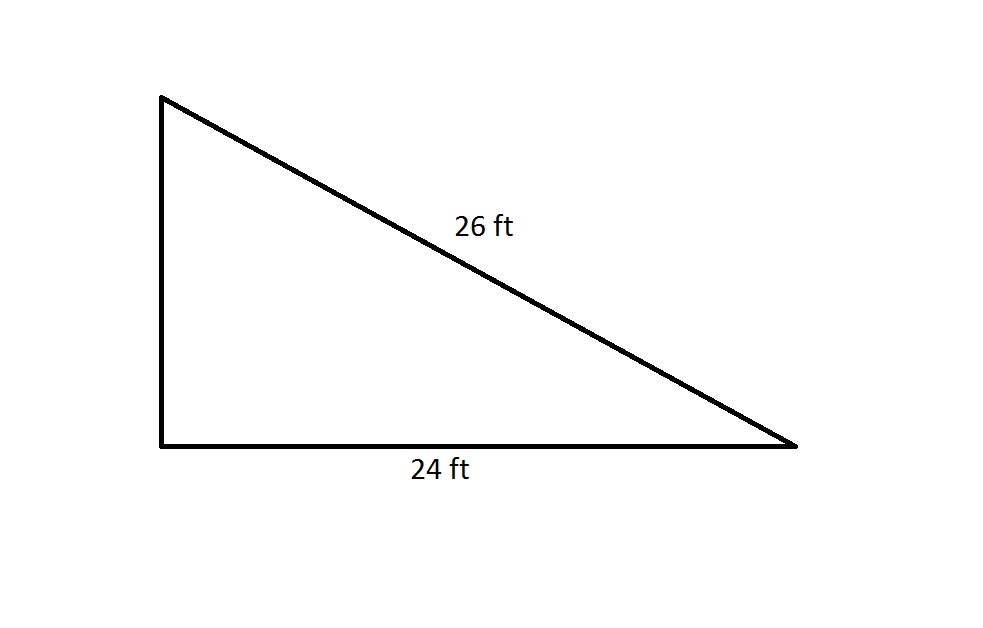
The perimeter of a regular octagon is 20% greater than that of the above right triangle. Which is the greater quantity?
(A) The length of one side of the octagon
(B) 3 yards
(A) is greater
(B) is greater
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(A) and (B) are equal
(A) and (B) are equal
By the Pythagorean Theorem, the shorter leg has length

The perimeter of the right triangle is therefore

The octagon has perimeter 20% greater than this, or

A regular octagon has eight sides of equal length, so each side of this octagon has length

Example Question #51 : Plane Geometry

The area of a square is equal to that of the above right triangle. Which is the greater quantity?
(A) The sidelength of the square
(B) 4 yards
(B) is greater
(A) and (B) are equal
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(A) is greater
(B) is greater
By the Pythagorean Theorem, the shorter leg has length

The area of a triangle is equal to half the product of its base and height; for a right triangle, the legs can serve as these. The area of the above right triangle is

The sidelength is the square root of this; 

Example Question #51 : Geometry

Figure NOT drawn to scale.
Refer to the above triangle. Which is the greater quantity?
(a)
(b) 108
(b) is the greater quantity
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(a) is the greater quantity
(a) and (b) are equal
(b) is the greater quantity
We can compare these numbers by comparing their squares.
By the Pythagorean Theorem,
Also,


Example Question #54 : Isee Upper Level (Grades 9 12) Quantitative Reasoning
Consider a triangle, 



(a) 55
(b)
It is impossible to determine which is greater from the information given
(a) and (b) are equal
(a) is the greater quantity
(b) is the greater quantity
(b) is the greater quantity
Suppose 
By the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, a triangle is right if and only if the sum of the squares of the lengths of the smallest two sides is equal to the square of the longest side. Compare the quantities 
Therefore, if




However, 

Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources









































