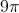All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Cylinders
This figure is a right cylinder with radius of 2 m and a height of 10 m.
What is the surface area of the right cylinder (m2)?
In order to find the surface area of a right cylinder you must find the area of both bases (the circles on either end) and add them to the lateral surface area. The area of the two circles is easy to find with 

Next find the lateral area. The lateral area if unrounded would be a rectangle with height of 10 m and length equal to the circumference of the base circles. Thus the lateral area is
Now add the lateral area to the area of the two bases:

Example Question #2 : Cylinders
Find the surface area of a cylinder given that its radius is 2 and its height is 3.2.
The standard equation to find the surface area of a cylinder is
where 

Plug in the given values for 

Example Question #3 : Cylinders
The base of a cylinder has an area of 

The standard equation for the surface area of a cylinder is
where 

We know the area is

Now that we have both 

Example Question #4 : Cylinders
Find the surface area of the following cylinder.

The formula for the surface area of a cylinder is:
where 

Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #5 : Cylinders
Find the surface area of the following cylinder.

The formula for the surface area of a cylinder is:
Where 

Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #6 : Cylinders
Find the surface area of the following partial cylinder.

The formula for the surface area of this partial cylinder is:
Where 


Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Surface Area Of A Cylinder
Find the surface area of the following partial cylinder.

The formula for the surface area of this partial cylinder is:
where 


Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #1 : Cylinders
What is the surface area of cylinder with a radius of 3 and height of 7?
The surface area of a cylinder can be determined by the following equation:
Example Question #1 : Cylinders
What is the volume of a cylinder with a radius of 2 and a length that is three times as long as its diameter?
The volume of a cylinder is the base multiplied by the height or length. The base is the area of a circle, which is 

Example Question #1 : Cylinders
A water glass has the shape of a right cylinder. The glass has an interior radius of 2 inches, and a height of 6 inches. The glass is 75% full. What is the volume of the water in the glass (in cubic inches)?
The volume of a right cylinder with radius 

Since the glass is only 75% full, only 75% of the interior volume of the glass is occupied by water. Therefore the volume of the water is:
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All High School Math Resources