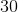All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #71 : Fractions
In terms of 



The arithmetic mean of a set is defined as the sum of terms in the set divided by the number of terms of a set. Therefore, the mean for this problem can be found as:
Example Question #72 : Fractions
Harold is drawing numbered slips of paper from a hat that are labeled 

There are 


The probability of one being drawn is 



For this sequence of events to happen, the probability is the product of the three separate probabilities:
Example Question #73 : Fractions
Happy Harold's Creamery offers specials during the week on particular sundaes. Monday they offer the Triple Trouble, in which three different scoops may be chosen from the full thirty-one that HHC offers. Tuesday features, for the same price, the Fearsome Four, which is a sundae of four scoops; however, only twenty-one flavors may be chosen from.
Quantity A: The amount of sundae options available for the Triple Trouble.
Quantity B: The amount of sundae options available for the Fearsome Four.
The relationship between the two cannot be determined.
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity A is greater.
Quantity B is greater.
Quantity B is greater.
Both of these sundae options are dealing with combinations, i.e. the order the scoops are chosen does not matter, and so the amount of possible combos is given by the formula:
Where 

For the Triple Trouble, the total amount of possible sundaes is:
And for the Fearsome Four:

Example Question #74 : Fractions
A shelf has 
Quantity A: The total number of possible combinations of shirts if 
Quantity B: The total number of possible combinations of shirts if 
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity B is greater.
Quantity A is greater.
The relationship cannot be determined.
The two quantities are equal.
It is important to realize that this problem deals with combinations, rather than permutations; the order the shirts are drawn does not matter. That being said, the formula for a combination is given as:
Where 

Quantity A:
Quantity B:
Example Question #75 : Fractions
On a trip to his friend Leslie's house, Ron drives 



To solve this problem, you may find the total distance traveled and divide that by the total time taken. The distance traveled in miles is:
Since the trip took 
Example Question #76 : Fractions
Quantity A: The average of the numbers above.
Quantity B: The median of the numbers above
Quantity A is greater.
The two quantities are equal.
The relationship between the two cannot be determined.
Quantity B is greater.
Quantity A is greater.
The average, or arithmetic mean, of a set can be found by dividing the sum of the set by the amount of values in the set:
The median for a set depends on if there's an even or odd number of values in the set.
For an odd number of values in a set that is arranged in numerical order, 

For an even number of values in a set that is again arranged in numerical order, 
Rearranging the set into numerical order gives 
All GRE Math Resources