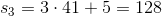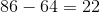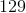All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #22 : Integers
The prime factorization of 60 is?
2 * 3 * 5
2 * 3 * 3 * 5
2 * 3 * 10
2 * 2 * 3 * 5
2 * 2 * 3 * 5
Prime numbers are numbers that can only divided by one and themselves. Breaking 60 into its prime factors yields:

Example Question #1 : Arithmetic Sequences
What is the sum of the odd integers 
None of the other answers
Do NOT try to add all of these. It is key that you notice the pattern. Begin by looking at the first and the last elements: 1 and 99. They add up to 100. Now, consider 3 and 97. Just as 1 + 99 = 100, 3 + 97 = 100. This holds true for the entire list. Therefore, it is crucial that we find the number of such pairings.
1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 are paired with 99, 97, 95, 93, and 91, respectively. Therefore, for each 10s digit, there are 5 pairings, or a total of 500. To get all the way through our numbers, you will have to repeat this process for the 10s, 20s, 30s, and 40s (all the way to 49 + 51 = 100).
Therefore, there are 500 (per pairing) * 5 pairings = 2500.
Example Question #2 : Sequences
A sequence is defined by the following formula:
What is the 4th element of this sequence?
With series, you can always "walk through" the values to find your answer. Based on our equation, we can rewrite 
You then continue for the third and the fourth element:
Example Question #1 : Arithmetic Sequences
What is the sum of the 40th and the 70th elements of the series defined as:
When you are asked to find elements in a series that are far into its iteration, you need to find the pattern. You absolutely cannot waste your time trying to calculate all of the values between 


For the third, you have:
Therefore, for the 40th and 70th elements, you will have:
The sum of these two elements is:
Example Question #2 : Arithmetic Sequences
The first term in a sequence of integers is 2 and the second term is 10. All subsequent terms are the arithmetic mean of all of the preceding terms. What is the 39th term?
1200
5
600
300
6
6
The first term and second term average out to 6. So the third term is 6. Now add 6 to the preceding two terms and divide by 3 to get the average of the first three terms, which is the value of the 4th term. This, too, is 6 (18/3)—all terms after the 2nd are 6, including the 39th. Thus, the answer is 6.
Example Question #2 : Sequences
Consider the following sequence of integers:
5, 11, 23, 47
What is the 6th element in this sequence?
93
191
95
None of the other answers
189
191
First, consider the change in each element. Notice that in each case, a given element is twice the preceding one plus one:
11 = 2 * 5 + 1
23 = 11 * 2 + 1
47 = 23 * 2 + 1
To find the 6th element, continue following this:
The 5th: 47 * 2 + 1 = 95
The 6th: 95 * 2 + 1 = 191
Example Question #2 : Arithmetic Sequences
The sequence 




What is the value of the 
The first term of the sequence is 

Plugging these values into the given expression for the nth term gives us our answer.

Example Question #1 : Sequences
In a sequence of numbers, the first two values are 1 and 2. Each successive integer is calculated by adding the previous two and mutliplying that result by 3. What is fifth value in this sequence?
None of the other answers
Our sequence begins as 1, 2.
Element 3: (Element 1 + Element 2) * 3 = (1 + 2) * 3 = 3 * 3 = 9
Element 4: (Element 2 + Element 3) * 3 = (2 + 9) * 3 = 11 * 3 = 33
Element 5: (Element 3 + Element 4) * 3 = (9 + 33) * 3 = 42 * 3 = 126
Example Question #1 : Arithmetic Sequences
Let Z represent a sequence of numbers 

Let us first write the value of a consecutive term in a numerical format:
Consequently,
Using the first equation, we can define 

This allows us to rewrite
as
Rearrangement of terms allows us to solve for 
Now, using our second equation, we can find 
Example Question #2 : Arithmetic Sequences
The sequence 
What is 
Begin by interpreting the general definition:
This means that every number in the sequence is five greater than the element preceding it. For instance:
It is easiest to count upwards:
All GRE Math Resources