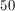All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #12 : Exponents
Which of the following is equal to 




Example Question #1 : How To Multiply Exponents
Which of the following is equal to 
First, multiply inside the parentheses: 
Then raise to the 7th power: 
Example Question #22 : Exponents
Simplify:
Remember, we add exponents when their bases are multiplied, and multiply exponents when one is raised to the power of another. Negative exponents flip to the denominator (presuming they originally appear in the numerator).
Example Question #471 : Algebra


Quantity A:
Quantity B:
Quantity A is greater.
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity B is greater.
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
(y2)(y4) = y2+4 = y6
Plug in two different values for y.
Plug in y = 1: y8 = y6
Plug in y = 2: y8 > y6
Since the results differ, the relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
Example Question #23 : Exponents
Evaluate:
Can be simplified to:
Example Question #1574 : Gre Quantitative Reasoning
Simplify the following expression.
To solve this problem, we must first understand some of the basic concepts of exponents. When multiplying exponents with the same base, one would simply add the powers together with the same base to obtain the result. For example, 
When raising exponents to a certain power, one would simply multiply the power the exponent is being raised to with the exponent itself to obtain the new exponent. The base also gets raised to the same power as it normally would and the new exponent gets put on afterward. For example 
Now that we have covered the basic concepts of exponent manipulation, we can now solve the problem. The top part of the expression give to us is 

The new expression becomes 
Solving for the denominator of the equation, we previously stated that when multiplying exponents together with the same base, we simply add the exponents together and keep the same base. Therefore 
The new expression becomes 


Example Question #3 : How To Solve For A Variable As Part Of A Fraction
Find x.
None
Cross multiply:
Example Question #71 : Algebraic Fractions
The numerator of a fraction is the sum of 4 and 5 times the denominator. If you divide the fraction by 2, the numerator is 3 times the denominator. Find the simplified version of the fraction.
Let numerator = N and denominator = D.
According to the first statement,
N = (D x 5) + 4.
According to the second statement, N / 2 = 3 * D.
Let's multiply the second equation by –2 and add itthe first equation:
–N = –6D
+[N = (D x 5) + 4]
=
–6D + (D x 5) + 4 = 0
–1D + 4 = 0
D = 4
Thus, N = 24.
Therefore, N/D = 24/4 = 6.
Example Question #43 : Algebraic Fractions
If 

Start by cross multiplying to get the equation

Then simplify by subtracting 

Example Question #44 : Algebraic Fractions
If 

We start by solving for x in 

Then substituting 60 for x in,


All GRE Math Resources