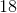All GED Science Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Elements And Compounds
On the periodic table, carbon is atomic number 

The standard sub-atomic particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, while electrons move freely around the nucleus. This question is specifically asking about the number of protons and neutrons in an atom of carbon.
Each proton and each neutron has a mass of approximately 

The atomic number refers to the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. Since the atomic number of carbon is six, there are six protons in the nucleus. For this question, however, we need the total of both the protons and neutrons (not just the protons).
Example Question #11 : Ged Science
A student is asked to make 

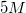
Convert liters to mL:
This is the TOTAL volume of the solution. Next, determine how much NaCl to add.
Therefore, 
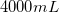
Example Question #1 : Solutions
6g of sugar is dissolved in 250mL of water. What is the percent concentration of sugar in mass per unit volume?
Concentration can be measured in a variety of ways. To find the percent mass per unit volume, we must divide the mass of solute by the volume of solvent and multiply by 100%.
We know our mass is 6g and our volume is 250mL. Use these values in the equation to find the concentration.
Example Question #1 : Biology And Life Sciences
Which of the following statements about bacteria is correct?
All bacteria require a host organism to infect
Bacteria are considered by scientists to be alive
Bacteria are neither alive nor dead
Bacteria lack the necessary organelles to be considered alive
Bacteria cells have the same general structures and organelles as animal cells
Bacteria are considered by scientists to be alive
Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms and are considered alive. Bacteria can survive and reproduce independent of a host (consider a colony of bacteria cells growing in a Petri dish). Though they do not have membrane-bound organelles, like a nucleus or mitochondria, bacterial cells do have DNA and are still able to produce cellular energy.
This question confuses many properties of viruses with those of bacteria. Viruses are not generally considered alive and require a host cell in order to replicate.
Example Question #2 : Biology And Life Sciences
The pigments in chloroplasts absorb red light and reflect green light. During photosynthesis, the absorbed light is used as energy to convert carbohydrates to ATP for the plant to use.
Under what color light would a plant grow the slowest?
Red
Purple
Yellow
Blue
Green
Green
The plant is only able to use absorbed light during photosynthesis; reflected light cannot be used as energy, as it is simply returned back into the surroundings. Red light will make a plant grow the fastest because it is absorbed. Since green light is reflected, growing a plant in green light will result in very slow growth. The light will effectively bounce off the plant, rather than being absorbed.
Example Question #3 : Biology And Life Sciences
What polysaccharide is used to construct the cell walls of fungi?
Peptidoglycan
Cellulose
Amylose
Chitin
Chitin
Fungal cell walls can be differentiated from plant and bacterial cell walls in that they are made of the polysaccharide chitin. Plant cell walls use cellulose, and bacteria use peptidoglycan. Amylose is a component of starch.
Example Question #1 : Biology And Life Sciences
What is one of the primary reasons that viruses are not considered living organisms?
They do not have nucleic acids
They do not use proteins in their structures
They do not make their own proteins
They are capable of causing disease
They do not make their own proteins
Viruses are considered non-living organisms for a variety of reasons. One of the main reasons is that viruses are incapable of creating their own proteins and must hijack host cell ribosomes in order to make them.
Virus structures contain both proteins and nucleic acids, but are unable to replicate their genetic material unless they infect a host cell.
Example Question #1 : Cells And Life
Which phase of mitosis involves the separation of sister chromatids?
Prophase
Anaphase
Telophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Mitosis is composed of four primary phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
During prophase the chromosomes condense, the nuclear membrane dissolves, and spindle fibers begin to form. Metaphase marks the time when the chromosomes align at the center of the cell and the spindle fibers attach to the centers of the chromosomes. During anaphase, the spindle fibers contract, separating the sister chromatids and pulling them toward opposite poles of the cell. Telophase marks the beginning of cytokinesis, when the cell fully divides, and the nuclear membrane reappears.
The correct answer is anaphase.
Example Question #4 : Biology And Life Sciences
Place the steps of mitosis in the correct order.
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Interphase, metaphase, prophase, anaphase, telophase
Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Metaphase, prophase, anaphase, telophase
Prophase, interphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Mitosis is the process of cell replication and division for most eukaryotic cells (with the exception of gametes, which undergo meiosis). Mitosis has four main stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Interphase is the portion of the cell cycle during which cell growth and DNA replication take place; it is not considered a stage of mitosis.
During prophase, the chromosomes form and the nuclear membrane dissolves. During metaphase, the chromosomes migrate to the center of the cell and align. During anaphase, spindle fibers pull the chromatids apart, separating sister chromatids to separate sides of the cell. During telophase, the nuclear membrane re-forms around the chromatids and the cytoplasm beings to divide to create two new daughter cells.
Example Question #3 : Biology And Life Sciences
The interphase of a cell's life cycle can be divided into which of the following phases?
Mitosis and meiosis
Replication, rest, division
Mitosis and cytokinesis
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase
G0, G1, S, and G2
G0, G1, S, and G2
Somatic cells spend the majority of their functional lives in interphase. In preparation for division, interphase can be divided into the G1, S and G2 phases. An interphase cell can also be in G0 phase, in this phase the cell is not preparing for mitosis but is performing all other normal cell functions.
All GED Science Resources