All Biochemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #301 : Biochemistry
Which of the following is the correct structure of a disaccharide?
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Lactose = galactose + fructose
Lactose = galactose + galactose
Sucrose = glucose + glucose
Maltose = sucrose + fructose
Maltose = glucose + glucose
The correct structures of the disaccharides are:
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Sucrose = glucose + fructose
Lactose = glucose + galactose
Example Question #301 : Biochemistry
Which amino acid does this structure represent?

Glutamate
Glutamine
Arginine
Aspartate
Asparagine
Glutamate
The amino acid's R group is composed of an ethyl group, followed by a carboxylate group, and therefore represents glutamate.
Example Question #91 : Identifying Biochemical Molecules
Which amino acid does this structure represent?

Y
A
T
S
M
M
The amino acid's chiral carbon is connected to two methyl groups followed, by a sulfur, and finally another methyl group. Therefore, the amino acid is methionine (M).
Example Question #302 : Biochemistry
The amino acid phenylalanine is pictured. If a hydroxyl group was added to the carbon in the red box, which amino acid would the new molecule most closely resemble?

Arginine
Alanine
Glysine
Lysine
Tyrosine
Tyrosine
The structure would most closely resembe tyrosine (pictured).

Example Question #1 : Identifying Specific Protein Structures
If the phenyl group in the pictured molecule were removed, what amino acid would the new structure most closely resemble?

Glycine
Phenylalanine
Alanine
Valine
Tyrosine
Alanine
Alanine is the amino acid that would be formed by removing the phenyl group from phenylalanine (the pictured molecule).
Example Question #303 : Biochemistry
If the amide group of glutamine (pictured here) was removed and a hydroxyl group was added to the carbon bound to the alpha carbon of the resulting structure, what amino acid would be formed?

Valine
Threonine
Methionine
Tyrosine
Cysteine
Threonine
Threonine (pictured here) would be formed.

Example Question #4 : Identifying Specific Protein Structures
Which of the following structures is methionine?


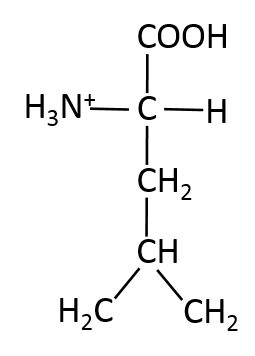

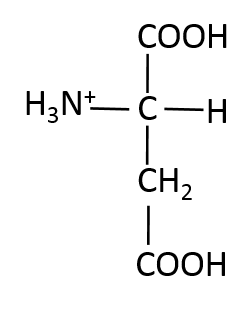

Methionine is a non-polar amino acid. It is one of two amino acids that contain sulfur, the other is cysteine.
Example Question #302 : Biochemistry
Name the given structure.

Lysine
Leucine
Alanine
Isoleucine
Valine
Leucine
Leucine is a non-polar amino acid with a 
Example Question #5 : Identifying Specific Protein Structures
Which of the following is a polar amino acid?






The polarity of an amino acid is determined by the R-group. The electronegativity difference between oxygen and carbon creates a dipole with the partial positive being on carbon and the partial negative being on oxygen. The dipole makes the molecule polar.
Example Question #9 : Identifying Specific Protein Structures
Which of the following is a basic amino acid?






Bases, according to the Bronsted-Lowry definition, are substances that accept

All Biochemistry Resources





