All AP Human Geography Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #691 : Ap Human Geography
In the concentric zone model, what is the outermost zone?
transitional zone
residential zone
central business district
working class zone
commuter zone
commuter zone
The outermost zone of the concentric zone model is the commuter zone, which includes the suburbs. These are the people who live furthest away from the central business district and therefore have to commute the greatest distance to work.
Example Question #691 : Ap Human Geography
In Hoyt's Sector Model, where is the factory/industry zone located?
surrounded by the low class residential zone, and touching the central business district
between the low class residential zone and the middle class residential zone
right outside of the transitional zone
completely surrounding the central business district
between the central business district and the high class residential zone
surrounded by the low class residential zone, and touching the central business district
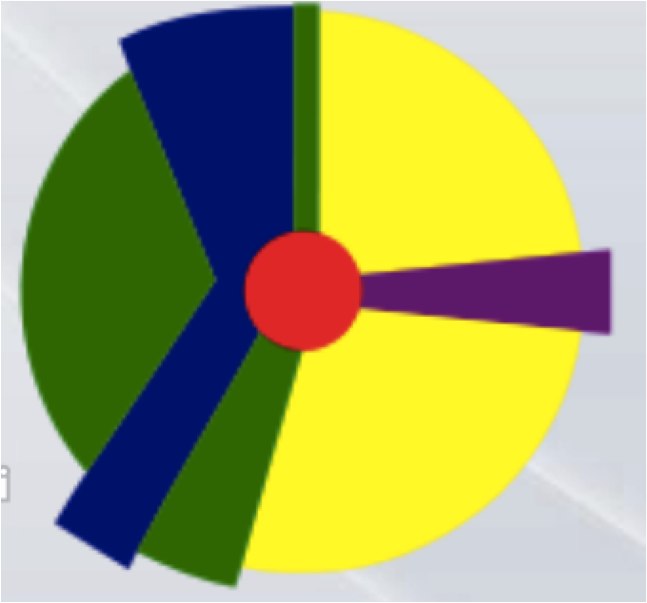
The factory/industry zone is the blue on the left, and it is located surrounded by the low class residential zone (green) and touching the central business district (red).
Example Question #691 : Ap Human Geography
A city that is divided up into several distinct neighborhoods and that lacks a centralized downtown area is best described as a __________ city.
Postmodernist
Sector Model
Modernist
Concentric Zone Model
Multiple-Nuclei Model
Multiple-Nuclei Model
A city that lacks a centralized business district or downtown area and that has several distinct neighborhoods that all act as regional centers within one larger city is best captured using the “Multiple-Nuclei Model.”
Example Question #1 : Harris & Ullman Multiple Nuclei Model
__________ is a prototypical example of a Multiple-Nuclei Model city.
Austin
San Francisco
Los Angeles
Philadelphia
Boston
Los Angeles
A Multiple-Nuclei Model city is a city that does not have one central area, but instead has several nodes that act as regional centers for economic or residential activity within one larger city. Los Angeles, with its many distinct neighborhoods, is a prototypical example of this type of city.
Example Question #1 : Models Of International Cities
__________ is the most populous city in Africa.
Lagos
Durban
Cape Town
Dakar
Nairobi
Lagos
Lagos is the capital city of Nigeria and is by far the most populous city in Africa. More than ten million people live within the city of Lagos, and an additional ten million live within the metropolitan area of Lagos. The next most populous cities in Africa are Cairo, in Egypt, and Kinshasa, in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Example Question #692 : Ap Human Geography
Which of these best defines gateway cities?
Cities that serve as economic facilitators to a large region
Cities that have advanced research facilitators and well-regarded educational institutions
None of these answers are accurate.
Cities that act as ports of entrance for migrants
Cities that have a disproportionate cultural impact on their surrounding region
Cities that act as ports of entrance for migrants
A “gateway city” is a city that serves as a port of entrance for migrants arriving in a country or a large geographic region. Cities like New York City, San Francisco, and Rio de Janeiro are classic examples of gateway cities.
Example Question #2 : Models Of International Cities
Which of these is an example of a gateway city?
Birmingham
San Francisco
Atlanta
Ottawa
Madrid
San Francisco
In human geography the term “gateway city” refers to a city that acts as a port of entry into a country or a large geographic region. San Francisco with its natural harbor and immigrant population, often referred to as the “gateway to the west,” is a classic example of a gateway city.
Example Question #693 : Ap Human Geography
Which of these is a classic example of an Islamic city?
Barcelona
Sofia
Tblisi
Venice
Medina
Medina
Medina is a prominent city in Saudi Arabia and, with its mosques, open-air markets, and prominent courtyards. As such, Medina is a classic example of an “Islamic city” from religious, cultural, and aesthetic perspectives. Sofia is in Bulgaria; Venice is in Italy; Barcelona is in Spain; Tblisi is in Georgia.
Example Question #11 : Models Of City Structure & Urban Development
All of the following are second-tier world cities except __________.
Moscow
Mumbai
London
Brussels
Los Angeles
London
London, Tokyo, and New York City are the only cities in the world that are considered to be first-tier world cities. This means they are global centers of culture, economics, and politics that have a disproportionately massive influence on the global population. Capital cities and economic centers like Moscow, Brussels, Mumbai, Los Angeles, and many others are considered to be “second-tier world cities.”
Example Question #11 : Models Of City Structure & Urban Development
Which of these is a prominent feature of a Medieval City?
None of these are features of Medieval cities.
All of these are features of Medieval cities.
Narrow streets and buildings
Cathedrals and ostentatious churches
High, defensive walls
All of these are features of Medieval cities.
Many cities first began to take shape in the late Medieval period. These cities, common throughout Europe and parts of the rest of the world, are characterized by their narrow, winding streets and looming, intimate buildings. They generally have some defensive fortifications and cathedrals and ostentatious churches dotting the landscape.
Certified Tutor
All AP Human Geography Resources



