All AP Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #3 : Entropy



What is the change in entropy for the following reaction?
The change in entropy is calculated by:
When 



It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in entropy of a reaction.
Example Question #2 : Entropy
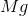

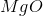
What is the change in entropy for the following reaction?
The change in entropy is calculated by:
When 
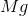

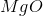
It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in entropy of a reaction.
Example Question #3 : Entropy




What is the change in entropy for the following equation?
The change in entropy is calculated by:
When 




It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in entropy of a reaction.
Example Question #44 : Thermodynamics




What is the entropy for the following reaction?
The change in entropy is calculated by:
When 




It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in entropy of a reaction.
Example Question #3 : Entropy
Which reaction will result in a negative entropy?
A reaction will have a positive change in entropy when the disorder of the system is increasing. This can happen when a liquid transitions to a gas, or more gas molecules are formed in the reaction.
Since two molecules of gaseous nitrogen dioxide can combine to form one molecule of dinitrogen tetroxide, the amount of gaseous molecules is halved. This increases order, which decreases the entropy of the system.
Example Question #43 : Thermodynamics
A reaction will reach equilibrium when the system's entropy __________.
is zero
is at a minimum
is at a maximum
entropy does not influence equilibrium at all
is at a maximum
Equilibrium is the basis of entropy, which can essentially be thought of as the distribution of energy in the system. For a reaction at a given temperature, the system's entropy will be at a maximum when it reaches equilbrium because this is the ideal energy state, and the forward and reverse reactions are occurring at a steady rate.
Example Question #42 : Thermodynamics
Consider the following reaction:
Below is a list of the standard entropy of formation for the compounds in the reaction:
What is the entropy of the reaction when one mole of ammonia is formed?
Since we have the entropies of formation, we can find the entropy of the reaction using the following equation:
We will need to use the coefficients from the balanced equation to calculate the entropy.
Since this is the entropy for the reaction when two moles of ammonia are formed, we must divide this entropy by two in order to solve for the entropy of one mole.
Example Question #81 : Thermochemistry And Kinetics
Suppose that a rxn has ∆H = -28 kJ and ∆S= -60 J/K. At what temperature will it
change from spontaneous to non-spontaneous?
500 K
46.7 K
50
467 K
467 K
Approximately 467 K. ∆G=∆H-T∆S and a rxn proceeds spontaneously when ∆G < 0
and is non-spontaneous when ∆G > 0. So if we set ∆G=0 and solve the equation for T, we will see that the crossover from spontaneous to non-spontaneous occurs when T=467K.
Example Question #81 : Thermochemistry And Kinetics
If the reaction quotient (Q) is greater than the equilibrium constant (K), what is true about the Gibbs free energy?
More information is needed to determine the gibbs free energy.
It is less than zero.
It is equal to zero.
It is greater than zero.
It is greater than zero.
If Q is greater than K, the reaction has exceeded the equilibrium state. It will proceed nonspontaneously (since equilibrium has already been reached), and this must mean that the ΔG (gibbs free energy) must be positive, or greater than zero.
Example Question #3 : Gibbs Free Energy And Spontaneity
The entropy and enthalpy of a reaction are both negative. Is the reaction spontaneous?
The reaction is not spontaneous
The reaction will be spontaneous if and only if the magnitude of the enthalpy is greater than the magnitude of the entropy times the temperature
The reaction will be spontaneous if and only if the magnitude of the entropy is greater than the magnitude of the enthalpy times the temperature
The reaction will be spontaneous if and only if the magnitude of the enthalpy is greater than the magnitude of the entropy
The reaction is spontaneous
The reaction will be spontaneous if and only if the magnitude of the enthalpy is greater than the magnitude of the entropy times the temperature
A reaction is spontaneous if the Gibb's Free Energy of the reaction is negative.
If 

Certified Tutor
All AP Chemistry Resources











































































