All 5th Grade Science Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #7 : Reveal Patterns In Length And Direction Of Shadows
A moon phase is one of the shapes the moon seems to have as it orbits Earth. When Earth is between the moon and the sun, you see a Full Moon. When the moon is between Earth and the sun, you can’t see the moon at all. What is this phase called?
Third Quarter
New Moon
First Quarter
Full Moon
New Moon
The shadow pattern that is depicted in the photo is the moon phases. The picture demonstrates where the Moon is located in regard to the Earth and how the Moon appears to us.
NASA explains more about this cycle, “If you have looked into the night sky, you may have noticed the Moon appears to change shape each night. Some nights, the Moon might look like a narrow crescent. Other nights, the Moon might look like a bright circle. And on other nights, you might not be able to see the Moon at all. The different shapes of the Moon that we see at different times of the month are called the Moon’s phases. The Moon does not produce its own light. There is only one source of light in our solar system, and that is the Sun. Without the Sun, our Moon would be completely dark. What you may have heard referred to as “moonlight” is actually just sunlight reflecting off of the Moon’s surface. The Sun’s light comes from one direction, and it always illuminates, or lights up, one half of the Moon – the side of the Moon that is facing the Sun. The other side of the Moon is dark.”
Source: https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/moon-phases/en/
Example Question #1 : Reveal Patterns In Length And Direction Of Shadows
If there was a full moon last night over Atlanta, Georgia, when would the next full moon occur over Atlanta?
In about 1 week
In about 1 month
In about 1 day
In about 1 year
In about 1 month
The shadow pattern that is depicted in the photo is the moon phases. The picture demonstrates where the Moon is located in regard to the Earth and how the Moon appears to us.
NASA explains more about this cycle, “If you have looked into the night sky, you may have noticed the Moon appears to change shape each night. Some nights, the Moon might look like a narrow crescent. Other nights, the Moon might look like a bright circle. And on other nights, you might not be able to see the Moon at all. The different shapes of the Moon that we see at different times of the month are called the Moon’s phases. The Moon does not produce its own light. There is only one source of light in our solar system, and that is the Sun. Without the Sun, our Moon would be completely dark. What you may have heard referred to as “moonlight” is actually just sunlight reflecting off of the Moon’s surface. The Sun’s light comes from one direction, and it always illuminates, or lights up, one half of the Moon – the side of the Moon that is facing the Sun. The other side of the Moon is dark.”
Source: https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/moon-phases/en/
Example Question #61 : Earth And Space Science
When the Sun shines on the telephone pole, a shadow of the telephone pole is cast. At different times of the day _________ .
the shadow remains in the same place and has the same length
the shadow will be at a different place
the shadow will have a different length
the shadow will be at a different place and have a different length
the shadow will be at a different place and have a different length
Patterns within shadows can be seen by measuring the length and direction and comparing them daily. The Earth's rotation causes the shadows to change throughout the day. The rotation of the Earth also causes day and night. The Earth's revolution causes slight changes in the length of these things because of its location in orbit. The correct answer is "the shadow will be at a different place and have a different length" because of the movement of the Earth.
Example Question #10 : Reveal Patterns In Length And Direction Of Shadows
The rotation of the _______ on its axis causes the position and length of the shadow to change.
Sun
Moon
Earth
Earth
Patterns within shadows can be seen by measuring the length and direction and comparing them daily. The Earth's rotation causes the shadows to change throughout the day. The rotation of the Earth also causes day and night. The Earth's revolution causes slight changes in the length of these things because of its location in orbit.
Example Question #1 : Reveal Patterns In Length Of Day And Night
Antwon researched the lengths of day and night in different parts of the world on the same day. He created a data table to display the number of daylight hours a specific latitude received on the same day (November 8th). What pattern(s) does the data table reveal about the length of day and night?

The more Southern the latitude, the more nighttime hours there are on November 8th.
The more Northern the latitude, the more daylight hours there are on November 8th.
The more Northern the latitude, the fewer daylight hours there are on November 8th.
The more Southern the latitude, the fewer daylight hours there are on November 8th.
The more Northern the latitude, the fewer daylight hours there are on November 8th.
Antwon using a data table to present the information is a clear and organized way to help others understand what his research revealed. Based on the data, it can be seen that as the number of daylight hours increases, the number of nighttime hours decreases the further south traveled. At a latitude of 90o South, there are 24 hours of sunlight and 0 minutes/hours of daylight compared to a latitude of 90o North where there is absolutely no daylight. Analyzing data can reveal patterns that help us understand the natural world and make predictions about future events.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this change takes place, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
Example Question #1 : Reveal Patterns In Length Of Day And Night
An Earth day is 24 hours because the Earth spins on its axis once every 24 hours.
False
True
True
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
The Earth rotating on its axis is the cause for day and night. When it is daytime for half of Earth, it is nighttime for the other half.
Example Question #3 : Reveal Patterns In Length Of Day And Night
Why is half of the Earth dark and the other half white in this diagram?
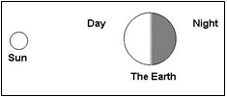
Source of diagram: The Victoria State Education and Training department
Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun.
Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis and its revolution around the Sun.
Day and night are due to the Earth revolving around the Sun, not its rotation on its axis.
Day and night are due to the Earth revolving on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun.
Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why half of the Earth is in nighttime and the other daytime, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
At any one time, half of the Earth's sphere is in sunlight while the other half is in darkness. The Earth's rotation causes this change to take place every day. It is a predictable pattern that we can count on.
Example Question #4 : Reveal Patterns In Length Of Day And Night
Mr. Green's class is studying the Solar System and Milky Way Galaxy. Today they are doing an investigation in the lab. Asia and Chele are partners for today's activity. They are given a ping pong ball with a sticker on one side, a flashlight, and their lab journals with a pencil for recording observations or data. Mr. Green turns off the lights. Asia holds the ping pong ball that represents Earth at a slight angle (like its axis) while Chele shines a flashlight on the center of the ball. Asia slowly rotates the Earth counterclockwise, and they observe where the light shines and where it doesn't. They take notice of the sticker and whether the sun shines on it or it is in darkness while the Earth rotates. Their observations are below.

Based on Asia and Chele's observations, how do we know which areas of the world are experiencing daytime?
The parts of the Earth that are facing away from the Sun will experience daytime while the other half experiences night.
The parts of the Earth that are facing the Sun will experience nighttime while the other half experiences day.
The parts of the Earth that are facing the Sun will experience daytime while the other half experiences night.
Asia and Chele's investigation does not reveal any patterns or information about nighttime and daytime.
The parts of the Earth that are facing the Sun will experience daytime while the other half experiences night.
The part of Earth facing the Sun will experience day time. The opposite side will be experiencing nighttime. The Earth's rotation on its axis determines daytime and night because of its location regarding the Sun.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
Example Question #5 : Reveal Patterns In Length Of Day And Night
Mr. Green's class is studying the Solar System and Milky Way Galaxy. Today they are doing an investigation in the lab. Asia and Chele are partners for today's activity. They are given a ping pong ball with a sticker on one side, a flashlight, and their lab journals with a pencil for recording observations or data. Mr. Green turns off the lights. Asia holds the ping pong ball that represents Earth at a slight angle (like its axis) while Chele shines a flashlight on the center of the ball. Asia slowly rotates the Earth counterclockwise, and they observe where the light shines and where it doesn't. They take notice of the sticker and whether the sun shines on it or it is in darkness while the Earth rotates. Their observations are below.

How does the amount of sunlight change as the Earth rotates?
The part of the Earth that faces the Sun gets brighter as it rotates towards the light and will soon be dark and experience night. The part that was facing away from the Sun starts to get darker as it moves into the daytime and receives light.
The part of the Earth that faces the Sun gets dimmer as it rotates away from the light and will soon be dark and experience night. The part that was facing away from the Sun starts to get lighter as it moves into the daytime and receives light.
The part of the Earth that faces the Sun gets dimmer as it rotates towards from the light and will soon be dark and experience day. The part that was facing away from the Sun starts to get lighter as it moves into the daytime and receives light.
The part of the Earth that faces the Sun gets brighter as it rotates away from the light and will soon be light and experience night. The part that was facing away from the Sun starts to get dimmer as it moves into the daytime and receives light.
The part of the Earth that faces the Sun gets dimmer as it rotates away from the light and will soon be dark and experience night. The part that was facing away from the Sun starts to get lighter as it moves into the daytime and receives light.
The amount of sunlight changes at a location based on whether they are facing towards the Sun or away from the Sun. When facing directly towards the Sun, an area will experience daytime while the opposite side of Earth experiences night. The light starts to dim as the Earth rotates, and the location begins to experience nighttime. As the rotation takes place, the opposite of Earth becomes lighter as daytime begins.
Example Question #66 : Earth And Space Science
Why do the Sun and the Moon appear to move across the sky from east to west instead of remaining in one place?
The Sun and Moon appear to move across the sky because Earth revolves around the Sun.
The Sun and Moon appear to move across the sky because Earth rotates on an axis.
The Sun and Moon appear to move across the sky because the Sun rotates on an axis.
The Sun and Moon appear to move across the sky because the Sun revolves around Earth.
The Sun and Moon appear to move across the sky because Earth rotates on an axis.
The amount of sunlight changes at a location based on whether they are facing towards the Sun or away from the Sun. When facing directly towards the Sun, an area will experience daytime while the opposite side of Earth experiences night. The light starts to dim as the Earth rotates, and the location begins to experience nighttime. As the rotation takes place, the opposite of Earth becomes lighter as daytime begins.
The Victoria State Education and Training department explains why this is true, "The Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun, and the moon orbits the Earth. The Earth is essentially a sphere, and the Sun is a nearby star, which is an unimaginably large ball of gas that radiates light and heat as products of nuclear reactions. The Earth orbits the Sun once every 365 days and rotates about its axis once every 24 hours. Day and night are due to the Earth rotating on its axis, not its orbit around the Sun. The term 'one day' is determined by the time the Earth takes to rotate once on its axis and includes both day time and night time."
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All 5th Grade Science Resources




