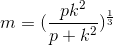All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #5 : How To Find Out When An Equation Has No Solution
Quantity A:
Quantity B: 11
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity B is greater
The relationship cannot be determined.
Quantity A is greater
Quantity B is greater
Expand 

Since 

Example Question #52 : Algebra
Quantity A:
Quantity B:
The relationship cannot be determined.
The two quantities are the same.
Quantity A is greater.
Quantity B is greater.
Quantity A is greater.
To solve this problem, expand each function described by Quantities A and B:
Quantity A:
Quantity B:
Now note that Quantities A and B only differ in that Quantity A is greater by 
Since we are told that 


Example Question #51 : Gre Quantitative Reasoning
Quantity A:
Quantity B:
Quantity A is greater.
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity B is greater.
The relationship cannot be determined.
Quantity A is greater.
Rather than manually finding common denominators and adding the fractions together, realize that
Since
Quantity A must be greater, and this can be seen without actually calculating its value.
Example Question #52 : Gre Quantitative Reasoning

Approximately, what was the percent growth of Beetleton's GDP from 2009 to 2010?
Percent growth is given as:
For Beetleton, this can be expressed as (in terms of billions of US dollars):
Example Question #53 : Gre Quantitative Reasoning
The sum of two integers is 

Let us write down what we are told in mathematical terms, designating the smaller integer as 

The sum of the two integers is 
And the larger integer is 
Writing the first equation in terms of 
Which allows us to find 
Thus, the positive difference between the two is found as
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Solution To A Rational Equation With Lcd
2
–1
0
1
–2
2
Example Question #11 : Linear / Rational / Variable Equations
–bm/(m2 + 1)
–b/(m2 – 1)
–b/(m + 1)
bm/(m2 + 1)
b/(m2 + 1)
b/(m2 + 1)
Example Question #54 : Gre Quantitative Reasoning
In the equation below, 





Example Question #1 : How To Find The Solution To A Rational Equation With Lcd
Four less than three times a certain number is equivalent to five plus four times this same number. What is three less than three times this number?
The answer cannot be determined from the information given.
The key to solving this problem is deciphering the language and translating it into a numerical representation. The first part can be written as an equaltiy as follows:
Rearranging terms allows us to solve for this mystery number:
From there we can address the problem's question:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Solution To A Rational Equation With Lcd
The arithmetic mean of 



Quantity A: 32
Quantity B: The arithmetic mean of 
The relationship between Quantity A and Quantity B cannot be determined.
Quantity B is greater.
Quantity A and Quantity B are equal.
Quantity A is greater.
Quantity A and Quantity B are equal.
The definition of an arithmetic mean of a set of values is given as the sum of all the values divided by the total count of values:
Where 


Quantity B can thus be defined as follows:
Which simplifies to:
or, simplifying:
We are told that the mean of 




and then as
Plugging this value into our definition of Quantity B, we can find its numerical value:
So
All GRE Math Resources