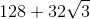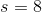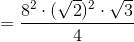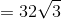All GMAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #21 : Tetrahedrons

The cube in the above figure has surface area 384. Give the surface area of the tetrahedron with vertices 
Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
The surface area formula can be used to find the length of each edge of the cube:
Three faces of the tetrahedron - 
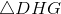


Each triangle is isosceles, so, by the 45-45-90 Theorem, each of their hypotentuses measures 


The total surface area is
All GMAT Math Resources
Popular Subjects
SAT Tutors in Seattle, Physics Tutors in Phoenix, Reading Tutors in Phoenix, Spanish Tutors in Philadelphia, SSAT Tutors in Philadelphia, Physics Tutors in Atlanta, SAT Tutors in Boston, GMAT Tutors in San Diego, Reading Tutors in Miami, Chemistry Tutors in Atlanta
Popular Courses & Classes
MCAT Courses & Classes in Boston, GMAT Courses & Classes in Philadelphia, ACT Courses & Classes in Philadelphia, GRE Courses & Classes in Philadelphia, LSAT Courses & Classes in Miami, SAT Courses & Classes in Miami, LSAT Courses & Classes in Washington DC, Spanish Courses & Classes in San Francisco-Bay Area, ISEE Courses & Classes in Denver, GRE Courses & Classes in Houston