All GMAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #31 : Triangles
A right triangle has a height of 

In order for two triangles to be congruent, they must be identical. That is, the lengths of the corresponding sides of two congruent triangles must be equal. This means that in order for a triangle to be congruent to one with a height of 

Example Question #32 : Triangles
A given right triangle has a base of 

None of the above.
In order for two right triangles to be congruent, the bases and heights must have identical lengths. Since we have a given right triangle with a base of 

Example Question #3 : Calculating Whether Right Triangles Are Congruent
A given right triangle has a height of 

None of the above.
In order for two right triangles to be congruent, the hypotenuses and acute angles must be identical. Since we have a given right triangle with an acute angle of 

Example Question #4 : Calculating Whether Right Triangles Are Congruent
A given right triangle has a base of 

None of the above.
In order for two right triangles to be congruent, the bases and heights must have identical lengths. Since we have a given right triangle with a base of 

Example Question #1 : Calculating The Height Of A Right Triangle
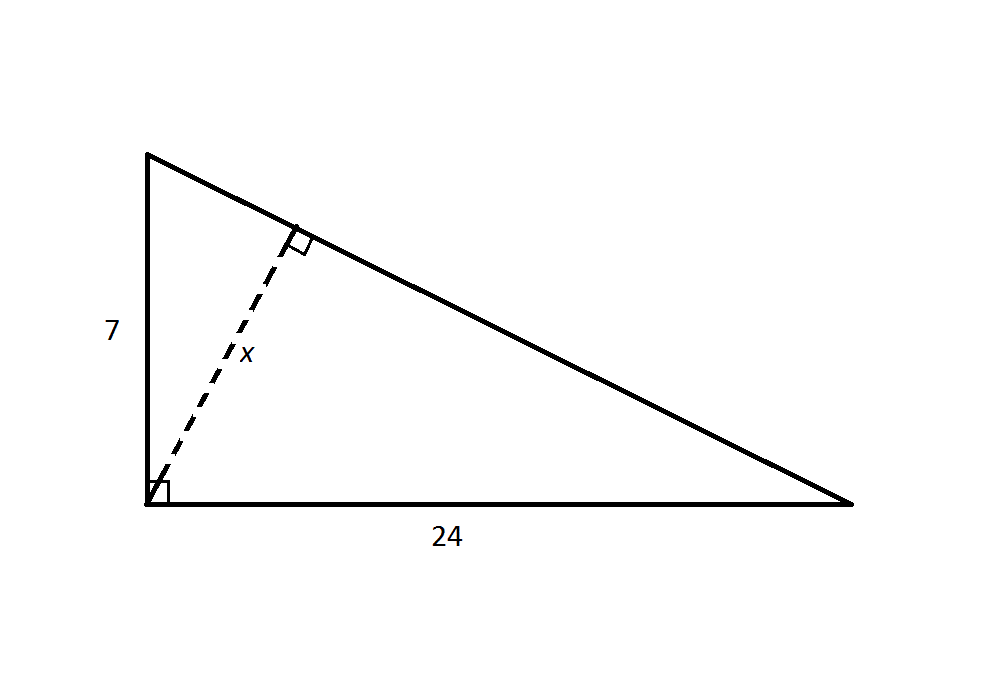
Note: Figure NOT drawn to scale
Refer to the above diagram.
Calculate
Insufficient information is given to calculate 
The hypotenuse of the large right triangle is
The area of the large right triangle is half the product of its base and its height. The base can be any side of the triangle; the height would be the length of the altitude, which is the perpendicular segment from the opposite vertex to that base.
Therefore, the area of the triangle can be calculated as half the product of the legs:
Or half the product of the hypotenuse and the length 
To calculate 
Example Question #1 : Calculating The Height Of A Right Triangle
A right triangle has a base of 8 and an area of 24. What is the height of the triangle?
Using the formula for the area of a right triangle, we can plug in the given values and solve for the height of the triangle:
Example Question #1 : Calculating The Height Of A Right Triangle

Triangle 


The height AE, divides the triangle ABC, in two triangles AEC and AEB with same proportions as the original triangle ABC, this property holds true for any right triangle.
In other words, 
Therefore, we can calculate, the length of AE:

Example Question #4 : Calculating The Height Of A Right Triangle

Triangle 


As we have previously seen, the height of a right triangle divides a it into two similar triangles with sides of same proportion.
Therefore, we can set up the following equality: 

By plugging in the numbers, we get, 

Example Question #5 : Calculating The Height Of A Right Triangle





Since here ABC is a isosceles right triangle, its height is half the size of the hypotenuse.
We just need to apply the Pythagorean Theorem to get the length of BC, and divide this length by two.


Therefore, 

Example Question #1 : Calculating An Angle In A Right Triangle
Of the two acute angles of a right triangle, one measures fifteen degrees less than twice the other. What is the measure of the smaller of the two angles?
Let one of the angles measure 


The acute angles measure 

All GMAT Math Resources





































































