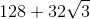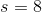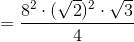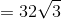All GMAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #8 : Calculating The Surface Area Of A Tetrahedron

The above diagram shows a regular right triangular pyramid. Its base 


The base is an equilateral triangle with sidelength 12, so its area can be calculated as follows:

Each of the three other faces is congruent, with base 12. The area of each is the product of its base and its height. To find the common height, we examine 




The area of 
All three lateral faces have this area.
Now add the areas of the four faces:
Example Question #21 : Tetrahedrons

The cube in the above figure has surface area 384. Give the surface area of the tetrahedron with vertices 
The surface area formula can be used to find the length of each edge of the cube:
Three faces of the tetrahedron - 
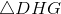


Each triangle is isosceles, so, by the 45-45-90 Theorem, each of their hypotentuses measures 


The total surface area is
Example Question #501 : Geometry
What is the surface area of a cylinder with a radius of 7 and a height of 3?
All we really need here is to remember the formula for the surface area of a cylinder.
Example Question #2 : Calculating The Surface Area Of A Cylinder
The height of a cylinder is twice the circumference of its base. The radius of the base is 9 inches. What is the surface area of the cylinder?
The radius of the base is 9 inches, so its circumference is 


Substitute 

Example Question #3 : Calculating The Surface Area Of A Cylinder
Calculate the surface area of the following cylinder.
 (Not drawn to scale.)
(Not drawn to scale.)
The equation for the surface area of a cylinder is:
we plug in our values: 
Example Question #1 : Cylinders
Calculate the surface area of the following cylinder.
 (Not drawn to scale.)
(Not drawn to scale.)
The equation for the surface area of a cylinder is
We plug in our values 
Note: we were given the diameter of the cylinder (10), in order to find the radius we had to divide the diameter by two.
Example Question #4 : Calculating The Surface Area Of A Cylinder
A cylinder has a height of 9 and a radius of 4. What is the total surface area of the cylinder?
We are given the height and the radius of the cylinder, which is all we need to calculate its surface area. The total surface area will be the area of the two circles on the bottom and top of the cylinder, added to the surface area of the shaft. If we imagine unfolding the shaft of the cylinder, we can see we will have a rectangle whose height is the same as that of the cylinder and whose width is the circumference of the cylinder. This means our formula for the total surface area of the cylinder will be the following:
Example Question #6 : Calculating The Surface Area Of A Cylinder
Grant is making a canister out of sheet metal. The canister will be a right cylinder with a height of 

This question is looking for the surface area of a cylinder with only 1 base. Our surface area of a cylinder is given by:



Example Question #502 : Geometry
Find the surface area of a cylinder whose height is 

To find the surface area of a cylinder, you must use the following equation.
Thus,
Example Question #8 : Calculating The Surface Area Of A Cylinder
A right circular cylinder has bases of radius 

The surface area of a cylinder can be calculated from its radius and height as follows:
Setting 


All GMAT Math Resources