Regulation Mechanisms and Epigenetics Practice Test
•4 QuestionsHuman chromosomes are divided into two arms, a long q arm and a short p arm. A karyotype is the organization of a human cell’s total genetic complement. A typical karyotype is generated by ordering chromosome 1 to chromosome 23 in order of decreasing size.
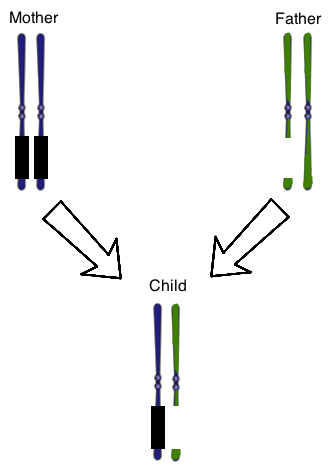
When viewing a karyotype, it can often become apparent that changes in chromosome number, arrangement, or structure are present. Among the most common genetic changes are Robertsonian translocations, involving transposition of chromosomal material between long arms of certain chromosomes to form one derivative chromosome. Chromosomes 14 and 21, for example, often undergo a Robertsonian translocation, as below.

A karyotype of this individual for chromosomes 14 and 21 would thus appear as follows:

Though an individual with aberrations such as a Robertsonian translocation may be phenotypically normal, they can generate gametes through meiosis that have atypical organizations of chromosomes, resulting in recurrent fetal abnormalities or miscarriages.
In the DNA component of a chromosome, changes such as methylation result in alterations in how DNA is processed without changing its sequence. This is known as .
Human chromosomes are divided into two arms, a long q arm and a short p arm. A karyotype is the organization of a human cell’s total genetic complement. A typical karyotype is generated by ordering chromosome 1 to chromosome 23 in order of decreasing size.
When viewing a karyotype, it can often become apparent that changes in chromosome number, arrangement, or structure are present. Among the most common genetic changes are Robertsonian translocations, involving transposition of chromosomal material between long arms of certain chromosomes to form one derivative chromosome. Chromosomes 14 and 21, for example, often undergo a Robertsonian translocation, as below.

A karyotype of this individual for chromosomes 14 and 21 would thus appear as follows:

Though an individual with aberrations such as a Robertsonian translocation may be phenotypically normal, they can generate gametes through meiosis that have atypical organizations of chromosomes, resulting in recurrent fetal abnormalities or miscarriages.
In the DNA component of a chromosome, changes such as methylation result in alterations in how DNA is processed without changing its sequence. This is known as .