Equilateral Triangles - Math
Card 0 of 504
 is an equilateral triangle. Points
is an equilateral triangle. Points 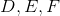 are the midpoints of
are the midpoints of  , respectively.
, respectively.  is constructed.
is constructed.
Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The area of 
(b) Twice the area of 

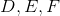


Which is the greater quantity?
(a) The area of
(b) Twice the area of
Tap to see back →
If segments are constructed in which the endpoints form the midpoints of the sides of a triangle, then four triangles, congruent to each other and similar to the larger triangle, are formed. Therefore, one of these triangles - specifically,  - would have one-fourth the area of
- would have one-fourth the area of 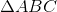 . This means
. This means  has more than twice the area of
has more than twice the area of  .
.
Note that the fact that the triangle is equilateral is irrelevant.
If segments are constructed in which the endpoints form the midpoints of the sides of a triangle, then four triangles, congruent to each other and similar to the larger triangle, are formed. Therefore, one of these triangles - specifically, 
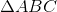


Note that the fact that the triangle is equilateral is irrelevant.
Which of the following could be the three sidelengths of an equilateral triangle?
Which of the following could be the three sidelengths of an equilateral triangle?
Tap to see back →
By definition, an equilateral triangle has three sides of equal length. We can identify the equilateral triangle by converting the given sidelengths to the same units and comparing them.
We can eliminate the following by showing that at least two sidelengths differ.

2 yards =  feet.
feet.
Two sides have lengths 6 feet and 7 feet, so we can eliminate this choice.

4 feet =  inches
inches
Two sides have lengths 48 inches and 50 inches, so we can eliminate this choice.

5 feet =  inches
inches
Two sides have lengths 48 inches and 60 inches, so we can eliminate this choice.

 yards =
yards =  feet
feet
Two sides have lengths 4 feet and 5 feet, so we can eliminate this choice.

 yards =
yards =  feet =
feet =  inches
inches
All three sides have the same length, making this the triangle equilateral. This choice is correct.
By definition, an equilateral triangle has three sides of equal length. We can identify the equilateral triangle by converting the given sidelengths to the same units and comparing them.
We can eliminate the following by showing that at least two sidelengths differ.
2 yards = 
Two sides have lengths 6 feet and 7 feet, so we can eliminate this choice.
4 feet = 
Two sides have lengths 48 inches and 50 inches, so we can eliminate this choice.
5 feet = 
Two sides have lengths 48 inches and 60 inches, so we can eliminate this choice.


Two sides have lengths 4 feet and 5 feet, so we can eliminate this choice.



All three sides have the same length, making this the triangle equilateral. This choice is correct.

If  , what is the area of this equilateral triangle?
, what is the area of this equilateral triangle?
If 
Tap to see back →
Given that the sides of our equilateral triangle are each  long, we can just plug the value in to the formula for the area of an equilateral triangle and solve for the area of the triangle:
long, we can just plug the value in to the formula for the area of an equilateral triangle and solve for the area of the triangle:
 if
if  is a side of the triangle.
is a side of the triangle.

Given that the sides of our equilateral triangle are each 


ΔABC is an equilateral triangle with side of length 8.
Find the height (to the nearest tenth).
ΔABC is an equilateral triangle with side of length 8.
Find the height (to the nearest tenth).
Tap to see back →
Equilateral triangles have sides of equal length, with angles of 60°. To find the height, we can draw an altitude to one of the sides in order to split the triangle into two equal 30-60-90 triangles.
Now, the side of the original equilateral triangle (lets call it "a") is the hypotenuse of the 30-60-90 triangle. Because the 30-60-90 triange is a special triangle, we know that the sides are x, x , and 2x, respectively.
, and 2x, respectively.
Thus, a = 2x and x = a/2.
Height of the equilateral triangle = 
Equilateral triangles have sides of equal length, with angles of 60°. To find the height, we can draw an altitude to one of the sides in order to split the triangle into two equal 30-60-90 triangles.
Now, the side of the original equilateral triangle (lets call it "a") is the hypotenuse of the 30-60-90 triangle. Because the 30-60-90 triange is a special triangle, we know that the sides are x, x
Thus, a = 2x and x = a/2.
Height of the equilateral triangle =
ΔABC is an equilateral triangle with side 12.
Find the height of ΔABC (to the nearest tenth).
ΔABC is an equilateral triangle with side 12.
Find the height of ΔABC (to the nearest tenth).
Tap to see back →
Equilateral triangles have sides of all equal length and angles of 60°. To find the height, we can draw an altitude to one of the sides in order to split the triangle into two equal 30-60-90 triangles.
Now, the side of the original equilateral triangle (lets call it "a") is the hypotenuse of the 30-60-90 triangle. Because the 30-60-90 triange is a special triangle, we know that the sides are x, x , and 2x, respectively.
, and 2x, respectively.
Thus, a = 2x and x = a/2.
Height of the equilateral triangle = 
Equilateral triangles have sides of all equal length and angles of 60°. To find the height, we can draw an altitude to one of the sides in order to split the triangle into two equal 30-60-90 triangles.
Now, the side of the original equilateral triangle (lets call it "a") is the hypotenuse of the 30-60-90 triangle. Because the 30-60-90 triange is a special triangle, we know that the sides are x, x
Thus, a = 2x and x = a/2.
Height of the equilateral triangle =
ΔABC is an equilateral triangle with side 17.
Find the area of ΔABC (to the nearest tenth).
ΔABC is an equilateral triangle with side 17.
Find the area of ΔABC (to the nearest tenth).
Tap to see back →
Equilateral triangles have sides of equal length, with angles of 60°. To find the area, we can first find the height. To find the height, we can draw an altitude to one of the sides in order to split the triangle into two equal 30-60-90 triangles.
Now, the side of the original equilateral triangle (lets call it "a") is the hypotenuse of the 30-60-90 triangle. Because the 30-60-90 triange is a special triangle, we know that the sides are x, x , and 2x, respectively.
, and 2x, respectively.
Thus, a = 2x and x = a/2.
Height of the equilateral triangle = 
Given the height, we can now find the area of the triangle using the equation:

Equilateral triangles have sides of equal length, with angles of 60°. To find the area, we can first find the height. To find the height, we can draw an altitude to one of the sides in order to split the triangle into two equal 30-60-90 triangles.
Now, the side of the original equilateral triangle (lets call it "a") is the hypotenuse of the 30-60-90 triangle. Because the 30-60-90 triange is a special triangle, we know that the sides are x, x
Thus, a = 2x and x = a/2.
Height of the equilateral triangle =
Given the height, we can now find the area of the triangle using the equation:
ΔABC is an equilateral triangle with side 6.
Find the area of ΔABC (to the nearest tenth).
ΔABC is an equilateral triangle with side 6.
Find the area of ΔABC (to the nearest tenth).
Tap to see back →
Equilateral triangles have sides of all equal length and angles of 60°. To find the area, we can first find the height. To find the height, we can draw an altitude to one of the sides in order to split the triangle into two equal 30-60-90 triangles.
Now, the side of the original equilateral triangle (lets call it "a") is the hypotenuse of the 30-60-90 triangle. Because the 30-60-90 triange is a special triangle, we know that the sides are x, x , and 2x, respectively.
, and 2x, respectively.
Thus, a = 2x and x = a/2.
Height of the equilateral triangle = 
Given the height, we can now find the area of the triangle using the equation:

Equilateral triangles have sides of all equal length and angles of 60°. To find the area, we can first find the height. To find the height, we can draw an altitude to one of the sides in order to split the triangle into two equal 30-60-90 triangles.
Now, the side of the original equilateral triangle (lets call it "a") is the hypotenuse of the 30-60-90 triangle. Because the 30-60-90 triange is a special triangle, we know that the sides are x, x
Thus, a = 2x and x = a/2.
Height of the equilateral triangle =
Given the height, we can now find the area of the triangle using the equation:
If the perimeter of an equilateral triangle is 54 inches, what is the area of the triangle in square inches?
If the perimeter of an equilateral triangle is 54 inches, what is the area of the triangle in square inches?
Tap to see back →
The answer is  .
.
To find the area you would first need to find what the length of each side is: 54 divided by 3 is 18 for each side.
Then you would need to draw in the altitude of the triangle in order to get its height. Drawing this altitude will create two 30-60-90 degree triangles as shown in the picture. The longer leg is  times the short leg. Thus the height is
times the short leg. Thus the height is  .
.
Next we plug in the base and the height into the formula to get


The answer is 
To find the area you would first need to find what the length of each side is: 54 divided by 3 is 18 for each side.
Then you would need to draw in the altitude of the triangle in order to get its height. Drawing this altitude will create two 30-60-90 degree triangles as shown in the picture. The longer leg is 

Next we plug in the base and the height into the formula to get


What is the area of this triangle if  ?
?
What is the area of this triangle if 
Tap to see back →
The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle with side length  is
is

So, since  ,
,


The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle with side length 
So, since 
If an equilateral triangle has a height of  , what would be the perimeter? Round to the nearest tenth.
, what would be the perimeter? Round to the nearest tenth.

If an equilateral triangle has a height of 

Tap to see back →
Since the triangle is equilateral, all sides are the same length. Therefore, we only need to find the length of one side to determine the perimeter. We can do this by means of the Pythagorean Theorem. In the attached figure, the equilateral triangle has been divided into two right triangles, for which the Pythagorean Theorem can be performed:

With  representing the length of one side, we can solve for
representing the length of one side, we can solve for  using the Pythagorean Theorem:
using the Pythagorean Theorem:


Now that we know the length of one side, we can solve for the total perimeter by summing like sides:

Since the triangle is equilateral, all sides are the same length. Therefore, we only need to find the length of one side to determine the perimeter. We can do this by means of the Pythagorean Theorem. In the attached figure, the equilateral triangle has been divided into two right triangles, for which the Pythagorean Theorem can be performed:

With 

Now that we know the length of one side, we can solve for the total perimeter by summing like sides:

If the sides of this triangle are doubled in length, what is the triangle's new area in terms of the original length of each of its sides,  ?
?
If the sides of this triangle are doubled in length, what is the triangle's new area in terms of the original length of each of its sides, 
Tap to see back →
The formula of the area of an equilateral triangle is  if
if  is a side.
is a side.
Since the sides of our triangle have doubled, they have changed from  to
to  . We can substitute
. We can substitute  into the equation and solve for the triangle's new area in terms of
into the equation and solve for the triangle's new area in terms of  :
:

The formula of the area of an equilateral triangle is 

Since the sides of our triangle have doubled, they have changed from 




Suppose we triple the sides of this equilateral triangle to  . What is the area of the new triangle in terms of
. What is the area of the new triangle in terms of  ?
?
Suppose we triple the sides of this equilateral triangle to 

Tap to see back →
The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle is  if
if  is the length of one of the triangle's sides.
is the length of one of the triangle's sides.
In this problem, the length of one of the triangle's sides is being tripled, so we can substitute  into the equation for
into the equation for  and solve for the triangle's new area in terms of
and solve for the triangle's new area in terms of  :
:

The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle is 

In this problem, the length of one of the triangle's sides is being tripled, so we can substitute 



What is half the area of the above triangle if  ?
?
What is half the area of the above triangle if 
Tap to see back →
The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle is . For this problem's triangle,
. For this problem's triangle,  , so we can substitute
, so we can substitute  into the equation for
into the equation for  and solve for the area of the triangle:
and solve for the area of the triangle:

At this point, we need to divide by  , since the problem asks for half of the triangle's area:
, since the problem asks for half of the triangle's area:

The formula for the area of an equilateral triangle is



At this point, we need to divide by 

If  , what is the area of the triangle?
, what is the area of the triangle?
If 
Tap to see back →
We know this triangle is equilateral since each of its sides has the same length,  . The formula of the area of an equilateral triangle is
. The formula of the area of an equilateral triangle is  if
if  is the length of one of the triangle's sides.
is the length of one of the triangle's sides.
Since our side length is  , we can substitute that value into the equation for
, we can substitute that value into the equation for  and solve for the area of the triangle:
and solve for the area of the triangle:

We know this triangle is equilateral since each of its sides has the same length, 


Since our side length is 

Find the area of an equilateral triangle with a perimeter of 24cm. Leave answer in simplest radical form.
Find the area of an equilateral triangle with a perimeter of 24cm. Leave answer in simplest radical form.
Tap to see back →
To find the area of an equilateral triangle, one must find the base and the height.

All the sides of an equilateral triangle are congruent, so if the perimeter of the equilaterail triangle is 24, then each side must equal one third of that total which is 8cm.
This will produce a triangle that includes the following information below:

Dropping an altitude down the center of the equilateral triangle will result in two 30-60-90 triangles with a hypotenuse of 8.

In every 30-60-90 triangle the following formulas apply:


When we plug in the given information on the triangle we get:

Dividing both sides by 2 gives the below result.

We can now plug this into the long leg formula to get the height of the triangle:


Now that we have all of the information needed to find the area we plug these values into the area formula.



To find the area of an equilateral triangle, one must find the base and the height.
All the sides of an equilateral triangle are congruent, so if the perimeter of the equilaterail triangle is 24, then each side must equal one third of that total which is 8cm.
This will produce a triangle that includes the following information below:

Dropping an altitude down the center of the equilateral triangle will result in two 30-60-90 triangles with a hypotenuse of 8.

In every 30-60-90 triangle the following formulas apply:
When we plug in the given information on the triangle we get:
Dividing both sides by 2 gives the below result.
We can now plug this into the long leg formula to get the height of the triangle:

Now that we have all of the information needed to find the area we plug these values into the area formula.
An equilateral triangle has sides of length 6cm. If the height of the triangle is 4.5cm what is the area of the triangle?
An equilateral triangle has sides of length 6cm. If the height of the triangle is 4.5cm what is the area of the triangle?
Tap to see back →
To find the area of any triangle we can use the formula 1/2 (base x height) , that is the base times the height divided by two. It is important to remember any of the sides of an equaliateral triangle can be used as the base when the hieght is given. The area can be found by (6 x 4.5) divided by 2; which gives 13.5 square centimeters.
To find the area of any triangle we can use the formula 1/2 (base x height) , that is the base times the height divided by two. It is important to remember any of the sides of an equaliateral triangle can be used as the base when the hieght is given. The area can be found by (6 x 4.5) divided by 2; which gives 13.5 square centimeters.
A circle with a radius of  is inscribed in an equilateral triangle with side lengths of
is inscribed in an equilateral triangle with side lengths of  as shown in the figure below.
as shown in the figure below.

Find the area of the shaded region.
A circle with a radius of 


Find the area of the shaded region.
Tap to see back →
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we must first find the area of the circle and the area of the equilateral triangle.
Recall how to find the area of a circle:

Plug in the given radius to find the area of the circle.

Next, recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:

Plug in the length of the side of the triangle to find the area.

In order to find the area of the shaded region, we will need to subtract the area of the circle from the area of the triangle.


Make sure to round to  places after the decimal.
places after the decimal.
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we must first find the area of the circle and the area of the equilateral triangle.
Recall how to find the area of a circle:
Plug in the given radius to find the area of the circle.
Next, recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:
Plug in the length of the side of the triangle to find the area.
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we will need to subtract the area of the circle from the area of the triangle.
Make sure to round to 
A circle with a radius of  is inscribed in an equilateral triangle with side lengths of
is inscribed in an equilateral triangle with side lengths of  as shown in the figure below.
as shown in the figure below.

Find the area of the shaded region.
A circle with a radius of 


Find the area of the shaded region.
Tap to see back →
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we must first find the area of the circle and the area of the equilateral triangle.
Recall how to find the area of a circle:

Plug in the given radius to find the area of the circle.

Next, recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:

Plug in the length of the side of the triangle to find the area.

In order to find the area of the shaded region, we will need to subtract the area of the circle from the area of the triangle.


Make sure to round to  places after the decimal.
places after the decimal.
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we must first find the area of the circle and the area of the equilateral triangle.
Recall how to find the area of a circle:
Plug in the given radius to find the area of the circle.
Next, recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:
Plug in the length of the side of the triangle to find the area.
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we will need to subtract the area of the circle from the area of the triangle.
Make sure to round to 
Given:  ;
;  has length nine inches.
has length nine inches.
True or false: The perimeter of  is one yard.
is one yard.
Given: 

True or false: The perimeter of 
Tap to see back →
The perimeter of an equilateral triangle - one with three sides of equal length - is equal to three times the length of one side. Therefore,  has perimeter
has perimeter

One yard is equal to 36 inches, making the statement false.
The perimeter of an equilateral triangle - one with three sides of equal length - is equal to three times the length of one side. Therefore, 
One yard is equal to 36 inches, making the statement false.
A circle with a radius of  is inscribed in an equilateral triangle with side lengths of
is inscribed in an equilateral triangle with side lengths of  as shown in the figure below.
as shown in the figure below.

Find the area of the shaded region.
A circle with a radius of 


Find the area of the shaded region.
Tap to see back →
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we must first find the area of the circle and the area of the equilateral triangle.
Recall how to find the area of a circle:

Plug in the given radius to find the area of the circle.

Next, recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:

Plug in the length of the side of the triangle to find the area.

In order to find the area of the shaded region, we will need to subtract the area of the circle from the area of the triangle.


Make sure to round to  places after the decimal.
places after the decimal.
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we must first find the area of the circle and the area of the equilateral triangle.
Recall how to find the area of a circle:
Plug in the given radius to find the area of the circle.
Next, recall how to find the area of an equilateral triangle:
Plug in the length of the side of the triangle to find the area.
In order to find the area of the shaded region, we will need to subtract the area of the circle from the area of the triangle.
Make sure to round to 