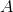Eigenvalues as Optimization - Linear Algebra
Card 0 of 8
True or False, the Constrained Extremum Theorem only applies to skew-symmetric matrices.
True or False, the Constrained Extremum Theorem only applies to skew-symmetric matrices.
Tap to see back →
It only applies to symmetric matrices, not skew-symmetric ones. The Constrained Extremum Theorem concerns the maximum and minimum values of the quadratic form 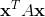 when
when  .
.
It only applies to symmetric matrices, not skew-symmetric ones. The Constrained Extremum Theorem concerns the maximum and minimum values of the quadratic form 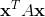

The maximum value of a quadratic form 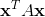 (
( is an
is an  symmetric matrix,
symmetric matrix,  ) corresponds to which eigenvalue of
) corresponds to which eigenvalue of 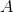 ?
?
The maximum value of a quadratic form 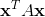



Tap to see back →
This is the statement of the Constrained Extremum Theorem. Likewise, the minimum value of the quadratic form corresponds to the smallest eigenvalue of 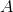 .
.
This is the statement of the Constrained Extremum Theorem. Likewise, the minimum value of the quadratic form corresponds to the smallest eigenvalue of 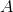
True or False, the Constrained Extremum Theorem only applies to skew-symmetric matrices.
True or False, the Constrained Extremum Theorem only applies to skew-symmetric matrices.
Tap to see back →
It only applies to symmetric matrices, not skew-symmetric ones. The Constrained Extremum Theorem concerns the maximum and minimum values of the quadratic form 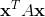 when
when  .
.
It only applies to symmetric matrices, not skew-symmetric ones. The Constrained Extremum Theorem concerns the maximum and minimum values of the quadratic form 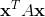

The maximum value of a quadratic form 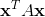 (
( is an
is an  symmetric matrix,
symmetric matrix,  ) corresponds to which eigenvalue of
) corresponds to which eigenvalue of 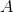 ?
?
The maximum value of a quadratic form 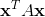



Tap to see back →
This is the statement of the Constrained Extremum Theorem. Likewise, the minimum value of the quadratic form corresponds to the smallest eigenvalue of 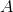 .
.
This is the statement of the Constrained Extremum Theorem. Likewise, the minimum value of the quadratic form corresponds to the smallest eigenvalue of 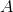
True or False, the Constrained Extremum Theorem only applies to skew-symmetric matrices.
True or False, the Constrained Extremum Theorem only applies to skew-symmetric matrices.
Tap to see back →
It only applies to symmetric matrices, not skew-symmetric ones. The Constrained Extremum Theorem concerns the maximum and minimum values of the quadratic form 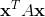 when
when  .
.
It only applies to symmetric matrices, not skew-symmetric ones. The Constrained Extremum Theorem concerns the maximum and minimum values of the quadratic form 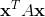

The maximum value of a quadratic form 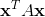 (
( is an
is an  symmetric matrix,
symmetric matrix,  ) corresponds to which eigenvalue of
) corresponds to which eigenvalue of 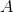 ?
?
The maximum value of a quadratic form 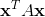



Tap to see back →
This is the statement of the Constrained Extremum Theorem. Likewise, the minimum value of the quadratic form corresponds to the smallest eigenvalue of 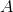 .
.
This is the statement of the Constrained Extremum Theorem. Likewise, the minimum value of the quadratic form corresponds to the smallest eigenvalue of 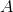
True or False, the Constrained Extremum Theorem only applies to skew-symmetric matrices.
True or False, the Constrained Extremum Theorem only applies to skew-symmetric matrices.
Tap to see back →
It only applies to symmetric matrices, not skew-symmetric ones. The Constrained Extremum Theorem concerns the maximum and minimum values of the quadratic form 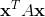 when
when  .
.
It only applies to symmetric matrices, not skew-symmetric ones. The Constrained Extremum Theorem concerns the maximum and minimum values of the quadratic form 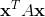

The maximum value of a quadratic form 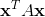 (
( is an
is an  symmetric matrix,
symmetric matrix,  ) corresponds to which eigenvalue of
) corresponds to which eigenvalue of 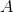 ?
?
The maximum value of a quadratic form 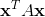



Tap to see back →
This is the statement of the Constrained Extremum Theorem. Likewise, the minimum value of the quadratic form corresponds to the smallest eigenvalue of 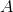 .
.
This is the statement of the Constrained Extremum Theorem. Likewise, the minimum value of the quadratic form corresponds to the smallest eigenvalue of