Chemical Equilibrium - AP Chemistry
Card 0 of 854
According to Le Chatelier's principle, which of the following occurs when you compress a system containing at least one gas species?
According to Le Chatelier's principle, which of the following occurs when you compress a system containing at least one gas species?
According to Le Chatelier's principle, when you compress a system, its volume decreases, so partial pressure of the all the gases in the system increases. The system will act to try to decrease the pressure by decreasing the moles of gas.
According to Le Chatelier's principle, when you compress a system, its volume decreases, so partial pressure of the all the gases in the system increases. The system will act to try to decrease the pressure by decreasing the moles of gas.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Consider formation of Nitrogen monoxide:  with
with  . If the initial concentration of N2 was 0.085M and O2 was 0.038 M, what is the concentration of nitrogen monoxide at equilibrium?
. If the initial concentration of N2 was 0.085M and O2 was 0.038 M, what is the concentration of nitrogen monoxide at equilibrium?
Consider formation of Nitrogen monoxide: 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Given the ICE table below, what are the signs on the terms that would appear in the “Change” row?


Given the ICE table below, what are the signs on the terms that would appear in the “Change” row?
Based on the balanced equation, one would use -x, -2x, and +x.
Based on the balanced equation, one would use -x, -2x, and +x.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Find the equilibrium concentrations for C in the following chemical reaction: A + B -> 2C

K = 9.0 x 10-8
Find the equilibrium concentrations for C in the following chemical reaction: A + B -> 2C
K = 9.0 x 10-8
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the equilibrium concentration for A- in the following reaction if the starting concentration of HA is 0.60 M?


What is the equilibrium concentration for A- in the following reaction if the starting concentration of HA is 0.60 M?

Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the equilibrium concentration for A- in the following reaction if the starting concentration of HA is 0.30 M?


What is the equilibrium concentration for A- in the following reaction if the starting concentration of HA is 0.30 M?

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Consider the following gasesous, reversible, exothermic reaction:

What could be done to increase the equilibrium concentration of species C?
Consider the following gasesous, reversible, exothermic reaction:
What could be done to increase the equilibrium concentration of species C?
According to Le Chatelier's principle, any changes in concentration or pressure to a system at equilibrium will cause the system to readjust to a new equilbrium. The addition of a reactant will cause the reaction to shift to the right, increasing the equilibirum concentration of the products. Thus, adding additional reactant A would increase the equlibrium concentration of product C.
Removing species A or adding species E will drive the reaction to the left, reducing the amount of species C. Since the reaction is exothermic, heat can be considered a product. Thus, increasing the temperature will also shift the reaction to the left.
According to Le Chatelier's principle, any changes in concentration or pressure to a system at equilibrium will cause the system to readjust to a new equilbrium. The addition of a reactant will cause the reaction to shift to the right, increasing the equilibirum concentration of the products. Thus, adding additional reactant A would increase the equlibrium concentration of product C.
Removing species A or adding species E will drive the reaction to the left, reducing the amount of species C. Since the reaction is exothermic, heat can be considered a product. Thus, increasing the temperature will also shift the reaction to the left.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The reaction  is at equilibrium. You have measured the concentration of
is at equilibrium. You have measured the concentration of  and
and  to be
to be
![[A]=1.2:M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/342321/gif.latex)
![[C]=0.5:M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/342322/gif.latex)
What is the equilibrium constant,  ?
?
The reaction 


What is the equilibrium constant, 
Recall that the rate constant for the equilibrium reaction

is ![K = $$\frac{[C]^{c}$$$[D]^{d}$$}{[A]^{a}$$[B]^{b}$}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/339568/gif.latex) , always remembering that it is products over reactants.
, always remembering that it is products over reactants.
Since we are at equilibrium, for every mol of  we have, we have 3 mols of
we have, we have 3 mols of  . Therefore,
. Therefore,
![[B]=3.6 :M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/342325/gif.latex)
Likewise, for every 2 mols of  we have, we have 2 mols of
we have, we have 2 mols of  . Therefore,
. Therefore,
![[C]=0.5:M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/342328/gif.latex)
Plugging all of this into the above equation we get
![K = $$\frac{[0.5M]^{2}$$$[0.5M]^{2}$$}{[1.2M]^{1}$$[3.6M]^{3}$$}=1.116*10^{-3}$](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/339571/gif.latex)
Recall that the rate constant for the equilibrium reaction
is ![K = $$\frac{[C]^{c}$$$[D]^{d}$$}{[A]^{a}$$[B]^{b}$}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/339568/gif.latex)
Since we are at equilibrium, for every mol of 

Likewise, for every 2 mols of 

Plugging all of this into the above equation we get
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Consider the following chemical reaction.

This reaction is allowed to equilibrate at some volume and pressure.
Which of the following actions will not shift the equilibrium toward the products?
Consider the following chemical reaction.
This reaction is allowed to equilibrate at some volume and pressure.
Which of the following actions will not shift the equilibrium toward the products?
Adding an inert gas will not shift the equilibrium toward the products, but neither will it shift the equilibrium toward the reactants. It has no effect because the partial pressure of each species,  ,
,  , and
, and  , will still remain constant. Since the partial pressures are constant, we know from the ideal gas law that the concentration of each species remains constant. For example, for
, will still remain constant. Since the partial pressures are constant, we know from the ideal gas law that the concentration of each species remains constant. For example, for  ,
,

Adding an inert gas will not shift the equilibrium toward the products, but neither will it shift the equilibrium toward the reactants. It has no effect because the partial pressure of each species, 



Compare your answer with the correct one above
If heat is added to an endothermic reaction, in which direction will the equilibrium shift according to Le Chatelier's principle?
If heat is added to an endothermic reaction, in which direction will the equilibrium shift according to Le Chatelier's principle?
In an endothermic reaction, heat can be treated as a reactant. Thus, if you add more reactant (heat), the system will shift to get rid of the extra reactant and shift to the right to form more products.
In an endothermic reaction, heat can be treated as a reactant. Thus, if you add more reactant (heat), the system will shift to get rid of the extra reactant and shift to the right to form more products.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
If heat is added to an exothermic reaction, in which direction will the equilibrium shift according to Le Chatelier's principle?
If heat is added to an exothermic reaction, in which direction will the equilibrium shift according to Le Chatelier's principle?
In an exothermic reaction, heat can be treated as a product. Thus, if you add more product (heat), the reaction will shift to the left to form more reactants.
In an exothermic reaction, heat can be treated as a product. Thus, if you add more product (heat), the reaction will shift to the left to form more reactants.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A reaction at equilibrium releases 25 Joules of heat energy at  . What is the entropy change for this same reaction?
. What is the entropy change for this same reaction?
A reaction at equilibrium releases 25 Joules of heat energy at 
To solve this problem, we must make use of the following equation:

At equilibrium, the value of  is 0. Therefore, we can simplify the equation.
is 0. Therefore, we can simplify the equation.



We must also convert temperature from degress Celsius into Kelvin.


To solve this problem, we must make use of the following equation:
At equilibrium, the value of 
We must also convert temperature from degress Celsius into Kelvin.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
If formate is added to a solution of formic acid in water, which of the following changes would occur?
If formate is added to a solution of formic acid in water, which of the following changes would occur?
Because formic acid is a weak acid, it will exist in equilibrium with its conjugate base, formate, while in water according to the following reaction:

If formate is added to this solution, then according to Le Chatlier's principle, the reaction will shift towards the left. Thus, the ![[H_${3}O^{+}$]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/356045/gif.latex) in solution will decrease and the pH will consequently increase. Furthermore, the addition of formate has no effect on the pKa.
in solution will decrease and the pH will consequently increase. Furthermore, the addition of formate has no effect on the pKa.
Because formic acid is a weak acid, it will exist in equilibrium with its conjugate base, formate, while in water according to the following reaction:
If formate is added to this solution, then according to Le Chatlier's principle, the reaction will shift towards the left. Thus, the ![[H_${3}O^{+}$]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/356045/gif.latex)
Compare your answer with the correct one above
For a given chemical reaction,  . What is the
. What is the  for this reaction at
for this reaction at  ?
?
For a given chemical reaction, 


To answer this question, it is necessary to use following equation:

We can solve for  by rearranging the equation to the following:
by rearranging the equation to the following:

To answer this question, it is necessary to use following equation:
We can solve for 
Compare your answer with the correct one above

Which of the following is the correct equilibrium expression for the given reaction?
Which of the following is the correct equilibrium expression for the given reaction?
For this question, we're asked to determine the correct equilibrium expression for a given reaction that is in equilibrium.
To begin with, we need to remember that pure solids and liquids are omitted from the equilibrium expression. Only gases and aqueous components of a reaction are included. The reason for this is because in a reaction at equilibrium, a pure solid or liquid will not have any appreciable change in concentration. Because their concentrations remain essentially unchanged, their value gets incorporated into the constant.
Also remember that an equilibrium expression is represented by the products divided by the reactants, each of which is raised to its stoichiometric coefficient.
In the case of the reaction given, we can see that it is already balanced. This means we are ready to set up the expression.

Here, the  term is being squared because it has a stoichiometric coefficient of
term is being squared because it has a stoichiometric coefficient of  in the equilibrium reaction. Also notice that
in the equilibrium reaction. Also notice that  does not show up in the expression because it is a solid.
does not show up in the expression because it is a solid.
For this question, we're asked to determine the correct equilibrium expression for a given reaction that is in equilibrium.
To begin with, we need to remember that pure solids and liquids are omitted from the equilibrium expression. Only gases and aqueous components of a reaction are included. The reason for this is because in a reaction at equilibrium, a pure solid or liquid will not have any appreciable change in concentration. Because their concentrations remain essentially unchanged, their value gets incorporated into the constant.
Also remember that an equilibrium expression is represented by the products divided by the reactants, each of which is raised to its stoichiometric coefficient.
In the case of the reaction given, we can see that it is already balanced. This means we are ready to set up the expression.
Here, the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following accurately describes what occurs in reversible reactions?
Which of the following accurately describes what occurs in reversible reactions?
The definition of reversible reactions is that they are indeed reversible; in other words, they can proceed in the forward and reverse directions. Since the products can react as well to reform the reactants, these reactions usually do not proceed to completion and instead exist in a dynamic state.
The definition of reversible reactions is that they are indeed reversible; in other words, they can proceed in the forward and reverse directions. Since the products can react as well to reform the reactants, these reactions usually do not proceed to completion and instead exist in a dynamic state.
Compare your answer with the correct one above





What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
What is 
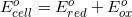
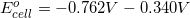

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half-reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half-reaction becomes negative.  half-reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half-reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
If delta G for a certain reaction is found to be -4955 J/mol, what is the equilibrium constant (Keq) for this reaction?
If delta G for a certain reaction is found to be -4955 J/mol, what is the equilibrium constant (Keq) for this reaction?
Given the equation delta G = -RTln(Keq), plugging in the correct values for the variables will lead us to the correct answer. Using e = 2.7, R = 8.314 J/molK, T= 298 K, and G = -4955 J, we can calculate that K = 7.4.
Given the equation delta G = -RTln(Keq), plugging in the correct values for the variables will lead us to the correct answer. Using e = 2.7, R = 8.314 J/molK, T= 298 K, and G = -4955 J, we can calculate that K = 7.4.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
If cesium metal spontaneously combusts when it comes in contact with room temperature water, which of the following must be true of the equilibrium constant of the reaction at 298 K?
If cesium metal spontaneously combusts when it comes in contact with room temperature water, which of the following must be true of the equilibrium constant of the reaction at 298 K?
When K is greater than 1, the products are favored and the reaction proceeds forward spontaneously. This must be true of the reaction, since it spontaneously occurs when the metal comes into contact with the water.
When K is greater than 1, the products are favored and the reaction proceeds forward spontaneously. This must be true of the reaction, since it spontaneously occurs when the metal comes into contact with the water.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following can always be determined based on the equation itself?
Which of the following can always be determined based on the equation itself?
According to the law of mass action, the equilibrium constant expression can always be written given the equation of the reaction itself. The equilibrium-constant expression will be written as the products over the reactants, each raised to their respectively stoichiometric coefficient. The rate law and concentrations can only be determined if there is additional data given.
According to the law of mass action, the equilibrium constant expression can always be written given the equation of the reaction itself. The equilibrium-constant expression will be written as the products over the reactants, each raised to their respectively stoichiometric coefficient. The rate law and concentrations can only be determined if there is additional data given.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

![K = $$\frac{[NO]^2$}{[N_2 ][O_2 ]}$ $=\frac{(2x)^2$}$ {(0.085-x)(0.038-x) }](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1172361/gif.latex)


![[NO] = 2x = 2(6.82 x $10^{-6}$) = 1.2 x $10^{-5}$](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1172364/gif.latex)


![K = 9 x $10^{-8}$ =\frac{ $[C]^2$}$ {[A][B]} = $$\frac{(2x)^2$$}{(0.5-x)^2$}$ \sim $$\frac{4x^2$}{(0.25) }$](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1172371/gif.latex)
![[C] = 2 (7.5 $x10^{-5}$ ) = 1.5 x $10^{-4}$](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1172372/gif.latex)


![K = $\frac{[H^+ ][A^- ]}{[HA]}$ = $$\frac{x^2$}{0.6-x}$ = 2.0 x $10^{-5}$](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1172367/gif.latex)


![[A^- ] = x = 3.5 x $10^{-3}$](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1172370/gif.latex)


![K =\frac{[H^+ ][A^- ]}{[HA]}$ $=\frac{x^2$}{0.3-x}$ = 2.0 x $10^{-5}$](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1172389/gif.latex)


![[A^- ] = x = 3.9 x $10^{-5}$](http://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1172392/gif.latex)