Cell Potential and Free Energy - AP Chemistry
Card 0 of 13
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
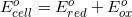
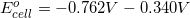

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
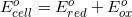
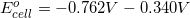

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
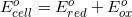
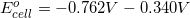

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
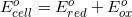
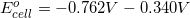

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
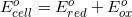
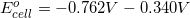

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
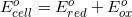
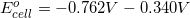

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
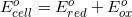
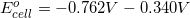

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
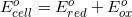
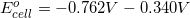

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
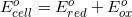
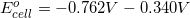

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
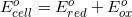
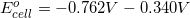

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
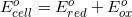
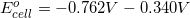

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
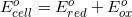
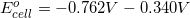

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
1. 

2. 

3. 
What is  ? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
? Is reaction 3 spontaneous?
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
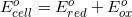
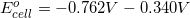

There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the  . Reaction 3 has
. Reaction 3 has  being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.
being reduced so the potential for the half reaction becomes negative.  half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
half reaction appears the same in reaction 3 so the potential is the same. Second, negative voltages indicate non-spontaneity and positive voltages are spontaneous.
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Compare your answer with the correct one above