Earth and Space Science - 5th Grade Science
Card 0 of 456
Select the planet that comes before Earth.
Select the planet that comes before Earth.
To answer this question correctly, we need to recall the order of the planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
We can use a mnemonic device to help us remember this order. A common mnemonic device is: My Very Excellent Mom Just Served Us Noodles. The first letter of each word matches the first letter of each planet. You can come up with your own mnemonic device to help you remember the order of the planets!
The diagram provided shows the order of the planets. We can see that Venus comes before Earth; thus, Venus is the correct answer.
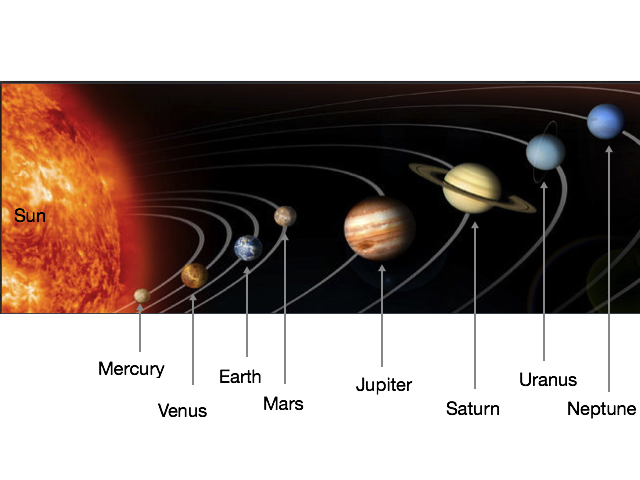
Image adapted from public domain NASA image at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/images/ppj\_hp\_pluto.jpg.
To answer this question correctly, we need to recall the order of the planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
We can use a mnemonic device to help us remember this order. A common mnemonic device is: My Very Excellent Mom Just Served Us Noodles. The first letter of each word matches the first letter of each planet. You can come up with your own mnemonic device to help you remember the order of the planets!
The diagram provided shows the order of the planets. We can see that Venus comes before Earth; thus, Venus is the correct answer.

Image adapted from public domain NASA image at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/images/ppj\_hp\_pluto.jpg.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Select the planet that is closest to the sun.
Select the planet that is closest to the sun.
To answer this question correctly, we need to recall the order of the planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
We can use a mnemonic device to help us remember this order. A common mnemonic device is: My Very Excellent Mom Just Served Us Noodles. The first letter of each word matches the first letter of each planet. You can come up with your own mnemonic device to help you remember the order of the planets!
The diagram provided shows the order of the planets. We can see that Mercury is the closest planet from the sun; thus, Mercury is the correct answer.

Image adapted from public domain NASA image at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/images/ppj\_hp\_pluto.jpg.
To answer this question correctly, we need to recall the order of the planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
We can use a mnemonic device to help us remember this order. A common mnemonic device is: My Very Excellent Mom Just Served Us Noodles. The first letter of each word matches the first letter of each planet. You can come up with your own mnemonic device to help you remember the order of the planets!
The diagram provided shows the order of the planets. We can see that Mercury is the closest planet from the sun; thus, Mercury is the correct answer.

Image adapted from public domain NASA image at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/images/ppj\_hp\_pluto.jpg.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Select the planet that comes after Earth.
Select the planet that comes after Earth.
To answer this question correctly, we need to recall the order of the planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
We can use a mnemonic device to help us remember this order. A common mnemonic device is: My Very Excellent Mom Just Served Us Noodles. The first letter of each word matches the first letter of each planet. You can come up with your own mnemonic device to help you remember the order of the planets!
The diagram provided shows the order of the planets. We can see that Mars is comes after Earth; thus, Mars is the correct answer.

Image adapted from public domain NASA image at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/images/ppj\_hp\_pluto.jpg.
To answer this question correctly, we need to recall the order of the planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
We can use a mnemonic device to help us remember this order. A common mnemonic device is: My Very Excellent Mom Just Served Us Noodles. The first letter of each word matches the first letter of each planet. You can come up with your own mnemonic device to help you remember the order of the planets!
The diagram provided shows the order of the planets. We can see that Mars is comes after Earth; thus, Mars is the correct answer.

Image adapted from public domain NASA image at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/images/ppj\_hp\_pluto.jpg.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Select the planet that is furthest away from the sun.
Select the planet that is furthest away from the sun.
To answer this question correctly, we need to recall the order of the planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
We can use a mnemonic device to help us remember this order. A common mnemonic device is: My Very Excellent Mom Just Served Us Noodles. The first letter of each word matches the first letter of each planet. You can come up with your own mnemonic device to help you remember the order of the planets!
The diagram provided shows the order of the planets. We can see that Neptune is the furthest away planet from the sun; thus, Neptune is the correct answer.

Image adapted from public domain NASA image at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/images/ppj\_hp\_pluto.jpg.
To answer this question correctly, we need to recall the order of the planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
We can use a mnemonic device to help us remember this order. A common mnemonic device is: My Very Excellent Mom Just Served Us Noodles. The first letter of each word matches the first letter of each planet. You can come up with your own mnemonic device to help you remember the order of the planets!
The diagram provided shows the order of the planets. We can see that Neptune is the furthest away planet from the sun; thus, Neptune is the correct answer.

Image adapted from public domain NASA image at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/images/ppj\_hp\_pluto.jpg.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
From the Environmental Protection Agency, "Land cover represents the actual or physical presence of vegetation (or other materials where vegetation is nonexistent) on the land surface. Land cover is also often described as what can be seen on land viewed from above. It is one means to describe landscape patterns and characteristics that are critical in understanding aspects of the environment."
Based on the EPA's graph below which type of land cover needs the most protection?

From the Environmental Protection Agency, "Land cover represents the actual or physical presence of vegetation (or other materials where vegetation is nonexistent) on the land surface. Land cover is also often described as what can be seen on land viewed from above. It is one means to describe landscape patterns and characteristics that are critical in understanding aspects of the environment."
Based on the EPA's graph below which type of land cover needs the most protection?

The land cover that appears to need the most protection is the forests. There was a significant reduction in the amount of area covered by forests. There was an increase in developed land, so there may be a connection, but further research would be needed to verify or support this inference. Humans are responsible for the protection of our land and Earth, so to stop this downward trend, we must step in.
The land cover that appears to need the most protection is the forests. There was a significant reduction in the amount of area covered by forests. There was an increase in developed land, so there may be a connection, but further research would be needed to verify or support this inference. Humans are responsible for the protection of our land and Earth, so to stop this downward trend, we must step in.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
From the Environmental Protection Agency, “Land cover represents the actual or physical presence of vegetation (or other materials where vegetation is nonexistent) on the land surface. Land cover is also often described as what can be seen on land viewed from above. It is one means to describe landscape patterns and characteristics that are critical in understanding aspects of the environment.”
The graph below shows the decrease in forests over the decade. Which answer choice(s) is a way that everyday people can help protect forests?

From the Environmental Protection Agency, “Land cover represents the actual or physical presence of vegetation (or other materials where vegetation is nonexistent) on the land surface. Land cover is also often described as what can be seen on land viewed from above. It is one means to describe landscape patterns and characteristics that are critical in understanding aspects of the environment.”
The graph below shows the decrease in forests over the decade. Which answer choice(s) is a way that everyday people can help protect forests?

The land cover that appears to need the most protection is the forests. There was a significant reduction in the amount of area covered by forests. There was an increase in developed land, so there may be a connection, but further research would be needed to verify or support this inference. Humans are responsible for the protection of our land and Earth, so to stop this downward trend, we must step in. Three simple ways that everyday citizens around the country can help forests are to go paperless, buy recycled items and then recycle them again, and to plant a tree! These are all easy changes to be made that can make a big difference.
The land cover that appears to need the most protection is the forests. There was a significant reduction in the amount of area covered by forests. There was an increase in developed land, so there may be a connection, but further research would be needed to verify or support this inference. Humans are responsible for the protection of our land and Earth, so to stop this downward trend, we must step in. Three simple ways that everyday citizens around the country can help forests are to go paperless, buy recycled items and then recycle them again, and to plant a tree! These are all easy changes to be made that can make a big difference.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The Environmental Protection Agency issues reports on many factors that impact the Earth's environment. The following graph highlights the area of growth in the United States and our emissions. The EPA explains the graph's data, "Between 1970 and 2018, the combined emissions of the six common pollutants (PM2.5 and PM10, SO2, NOx, VOCs, CO, and Pb) dropped by 74 percent. This progress occurred while the U.S. economy continued to grow, Americans drove more miles, and population and energy use increased."

What is a reasonable idea for a way citizens can help protect our air?
The Environmental Protection Agency issues reports on many factors that impact the Earth's environment. The following graph highlights the area of growth in the United States and our emissions. The EPA explains the graph's data, "Between 1970 and 2018, the combined emissions of the six common pollutants (PM2.5 and PM10, SO2, NOx, VOCs, CO, and Pb) dropped by 74 percent. This progress occurred while the U.S. economy continued to grow, Americans drove more miles, and population and energy use increased."

What is a reasonable idea for a way citizens can help protect our air?
Clean air is essential for all citizens of the United States, and according to the EPA, many of our emissions have decreased in recent years, but there is still room for improvement. "Vehicle miles traveled" was one of the six areas where our growth has increased as well as the production of harmful pollutants. If each person used public transportation methods more often than driving individual vehicles, there could be a reduction in the vehicle-related emissions that are created. This is a reasonable change that citizens can make.
Clean air is essential for all citizens of the United States, and according to the EPA, many of our emissions have decreased in recent years, but there is still room for improvement. "Vehicle miles traveled" was one of the six areas where our growth has increased as well as the production of harmful pollutants. If each person used public transportation methods more often than driving individual vehicles, there could be a reduction in the vehicle-related emissions that are created. This is a reasonable change that citizens can make.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Lakeland, Ohio has seen an increase in hazardous waste materials building up in the water. The city thinks it is because of people using harmful pesticides, herbicides, and chemicals in their yards. The city council wants to make posters to hang around town and distribute with tips for residents to decrease the hazardous waste flowing into the sewer system. Which suggestion should the city council NOT include?
Lakeland, Ohio has seen an increase in hazardous waste materials building up in the water. The city thinks it is because of people using harmful pesticides, herbicides, and chemicals in their yards. The city council wants to make posters to hang around town and distribute with tips for residents to decrease the hazardous waste flowing into the sewer system. Which suggestion should the city council NOT include?
Hazardous waste entering the water system can be dangerous! The dangerous materials that seep into the groundwater, enter the sewer systems, and run-off into local lakes and rivers can be harmful to humans, animals, and plants. Three of the tips suggested would be beneficial for the town council to post on the handouts, and one would increase the problem the city is facing. "Apply fertilizers when desired, and at the amount, you see fit." is a piece of advice that could cause residents to use too much fertilizer too often. If they wanted to change this to a tip that would benefit their cause, it should read, "Apply fertilizers only when necessary and at the recommended amount."
Hazardous waste entering the water system can be dangerous! The dangerous materials that seep into the groundwater, enter the sewer systems, and run-off into local lakes and rivers can be harmful to humans, animals, and plants. Three of the tips suggested would be beneficial for the town council to post on the handouts, and one would increase the problem the city is facing. "Apply fertilizers when desired, and at the amount, you see fit." is a piece of advice that could cause residents to use too much fertilizer too often. If they wanted to change this to a tip that would benefit their cause, it should read, "Apply fertilizers only when necessary and at the recommended amount."
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Diana has been reading about deforestation in school and learned that the use of paper goods could lead to the need to cut down forests. She wants to encourage her friends, family, and schoolmates to use fewer paper goods to help protect the environment. Which tip(s) should she share?
Diana has been reading about deforestation in school and learned that the use of paper goods could lead to the need to cut down forests. She wants to encourage her friends, family, and schoolmates to use fewer paper goods to help protect the environment. Which tip(s) should she share?
Diana should share all of the tips with her friends, family, and schoolmates. Reusing and recycling paper products is an easy way to reduce the waste in landfills and the number of trees cut down to create new products. The EPA reported that in 2017 Americans recycled 66% of the paper that they purchased. This is an excellent start to reducing our impact on the environment.
Diana should share all of the tips with her friends, family, and schoolmates. Reusing and recycling paper products is an easy way to reduce the waste in landfills and the number of trees cut down to create new products. The EPA reported that in 2017 Americans recycled 66% of the paper that they purchased. This is an excellent start to reducing our impact on the environment.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

The chart above lists the time it takes for different household objects to decompose. One way to help the environment is to repurpose items instead of throwing them away. Which of the following is an example of this strategy?

The chart above lists the time it takes for different household objects to decompose. One way to help the environment is to repurpose items instead of throwing them away. Which of the following is an example of this strategy?
Repurposing items that would typically be thrown away helps the environment. An example of repurposing an object is painting a glass bottle and using it for decoration in your home! Repurposing items reduces the amount of trash being taken to landfills, and the does not require machines like recycling at a recycling center. An example of repurposing an object is painting a glass bottle and using it for decoration in your home!
Repurposing items that would typically be thrown away helps the environment. An example of repurposing an object is painting a glass bottle and using it for decoration in your home! Repurposing items reduces the amount of trash being taken to landfills, and the does not require machines like recycling at a recycling center. An example of repurposing an object is painting a glass bottle and using it for decoration in your home!
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Consuming and producing non-renewable resources for human consumption can harm the environment. Which of the following could people do to reduce the use of non-renewable resources?
Consuming and producing non-renewable resources for human consumption can harm the environment. Which of the following could people do to reduce the use of non-renewable resources?
Gasoline is made of oil, which is a non-renewable resource. Consuming and producing gasoline can harm the environment. One way that people can reduce the use of non-renewable resources is to use less gasoline. This can be done by carpooling or riding a bike instead of driving to work individually each day.
Gasoline is made of oil, which is a non-renewable resource. Consuming and producing gasoline can harm the environment. One way that people can reduce the use of non-renewable resources is to use less gasoline. This can be done by carpooling or riding a bike instead of driving to work individually each day.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of these items should NOT be flushed down the toilet or washed into the sewer system to protect our natural water sources?
Which of these items should NOT be flushed down the toilet or washed into the sewer system to protect our natural water sources?
Flushing non-biodegradable items down the toilet can pollute the local water supply. Things like bandages, cotton balls, cleaning products, and oil should not be flushed as they do not dissolve and can contaminate water sources.
Flushing non-biodegradable items down the toilet can pollute the local water supply. Things like bandages, cotton balls, cleaning products, and oil should not be flushed as they do not dissolve and can contaminate water sources.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Brian's auto shop has several spare tires that need to be disposed of before the next shipment of tires arrives. Which of the following is the most environmentally friendly option for disposal of the tires?
Brian's auto shop has several spare tires that need to be disposed of before the next shipment of tires arrives. Which of the following is the most environmentally friendly option for disposal of the tires?
Repurposing the tires is an environmentally friendly option. By reusing the tires, less trash is littering the neighborhood and local landfills. Burning the tires would create air pollution, so it is not environmentally friendly.
Repurposing the tires is an environmentally friendly option. By reusing the tires, less trash is littering the neighborhood and local landfills. Burning the tires would create air pollution, so it is not environmentally friendly.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Billions of bees are dying off, and their hives are collapsing. The main reason for the decrease in bumblebees is the use of insecticides and pesticides. Which of the following examples is a way that a community could help stop the killing of bees?
Billions of bees are dying off, and their hives are collapsing. The main reason for the decrease in bumblebees is the use of insecticides and pesticides. Which of the following examples is a way that a community could help stop the killing of bees?
The community can help stop the killing of bees is by using safer pesticides and insecticides. Using fewer or safer pesticides can save bees and allow the food chain to stay intact.
The community can help stop the killing of bees is by using safer pesticides and insecticides. Using fewer or safer pesticides can save bees and allow the food chain to stay intact.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
How could nonrenewable resources be replaced with renewable resources?
How could nonrenewable resources be replaced with renewable resources?
Nonrenewable energy resources, like coal, nuclear, oil, and natural gas, are available in limited supplies. This is usually due to the long time it takes for them to be replenished. Renewable resources are replenished naturally and over relatively short periods. Renewable resources include biomass energy (such as ethanol), hydropower, geothermal power, wind energy, and solar energy. Creating electricity with solar energy instead of coal will reduce the dependence on fossil fuels, find a cleaner way to produce electricity, and reserve more coal.
Nonrenewable energy resources, like coal, nuclear, oil, and natural gas, are available in limited supplies. This is usually due to the long time it takes for them to be replenished. Renewable resources are replenished naturally and over relatively short periods. Renewable resources include biomass energy (such as ethanol), hydropower, geothermal power, wind energy, and solar energy. Creating electricity with solar energy instead of coal will reduce the dependence on fossil fuels, find a cleaner way to produce electricity, and reserve more coal.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Jinger was researching water sources on Earth and learned that only 3% of Earth's water is freshwater. She also read that this resource is becoming polluted in a significant way. Which answer choice(s) demonstrates a rational solution to the water pollution problem?
Jinger was researching water sources on Earth and learned that only 3% of Earth's water is freshwater. She also read that this resource is becoming polluted in a significant way. Which answer choice(s) demonstrates a rational solution to the water pollution problem?
Jinger is very proactive in thinking of ways that she can reduce her impact on our freshwater resources. With only 3% of the Earth providing necessary freshwater supplies, humans cannot afford to waste or poison the water. Keep litter, pet wastes, leaves, and debris out of street gutters and storm drains to keep sewer systems from being overwhelmed with materials that need to be sorted and cleaned. Disposing of used oil, antifreeze, paints, and other household chemicals properly are essential for lakes and ponds in nearby areas. Water run-off from hosing these materials out of driveways or flushing them down storm drains leads to absorption and spread. Applying lawn and garden chemicals sparingly and according to directions will help to reduce waste and overuse of harmful chemicals that leak into water sources.
Jinger is very proactive in thinking of ways that she can reduce her impact on our freshwater resources. With only 3% of the Earth providing necessary freshwater supplies, humans cannot afford to waste or poison the water. Keep litter, pet wastes, leaves, and debris out of street gutters and storm drains to keep sewer systems from being overwhelmed with materials that need to be sorted and cleaned. Disposing of used oil, antifreeze, paints, and other household chemicals properly are essential for lakes and ponds in nearby areas. Water run-off from hosing these materials out of driveways or flushing them down storm drains leads to absorption and spread. Applying lawn and garden chemicals sparingly and according to directions will help to reduce waste and overuse of harmful chemicals that leak into water sources.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The United States Environmental Protection Agency released a report of the different sources of energy and how much of each was consumed between 1949 and 2017. The EPA reported that:
"From 1949 to 2017, total U.S. energy use roughly tripled. Energy use has risen fairly steadily over time, with the exception of a few noticeable declines in the 1970s, 1980s, and late 2000s, which were largely associated with supply shocks (e.g., the 1973 oil embargo) or economic downturn. In 1949, the U.S. obtained 91 percent of its energy from fossil fuels. Despite the emergence of nuclear power and the growth of renewable sources, in 2017, the nation still relied on fossil fuels for 80 percent of its energy needs. For that year, the largest share (37 percent) of U.S. energy consumed was derived from petroleum (including gasoline), followed by natural gas (29 percent) and coal (14 percent). Recent years have seen increases in some sources of energy (natural gas and renewables) and decreases in others (petroleum and coal)."

Burning coal, oil, and gasoline give off sulfur, nitrogen, and carbon into the air. These emissions combine with water vapor in the clouds and make acid – sulfuric, nitric, and carbonic acid. The wind carries acidic clouds, sometimes thousands of miles. They fall to Earth as acid rain or snow. How can the effects of these emissions be decreased?
The United States Environmental Protection Agency released a report of the different sources of energy and how much of each was consumed between 1949 and 2017. The EPA reported that:
"From 1949 to 2017, total U.S. energy use roughly tripled. Energy use has risen fairly steadily over time, with the exception of a few noticeable declines in the 1970s, 1980s, and late 2000s, which were largely associated with supply shocks (e.g., the 1973 oil embargo) or economic downturn. In 1949, the U.S. obtained 91 percent of its energy from fossil fuels. Despite the emergence of nuclear power and the growth of renewable sources, in 2017, the nation still relied on fossil fuels for 80 percent of its energy needs. For that year, the largest share (37 percent) of U.S. energy consumed was derived from petroleum (including gasoline), followed by natural gas (29 percent) and coal (14 percent). Recent years have seen increases in some sources of energy (natural gas and renewables) and decreases in others (petroleum and coal)."

Burning coal, oil, and gasoline give off sulfur, nitrogen, and carbon into the air. These emissions combine with water vapor in the clouds and make acid – sulfuric, nitric, and carbonic acid. The wind carries acidic clouds, sometimes thousands of miles. They fall to Earth as acid rain or snow. How can the effects of these emissions be decreased?
Energy consumption and the sources used to feed this every growing need are a constant battle and concern in the United States. Reliance on renewable resources would limit the use of petroleum, natural gas, and coal, which are nonrenewable fossil fuels. These resources take millions of years to replenish, and our supply is slowly running out. Renewable resources like hydroelectric power, solar power, and wind power are all options that are a financial investment to start but cost less over time, have a dramatically less negative impact on the Earth, and do not run out. The idea to increase the reliance on renewable sources and decrease the dependence on nonrenewable sources is a scientifically based idea that is reasonable and may work. Using electricity derived from wind, water, or solar power will be beneficial to decreasing emissions.
Energy consumption and the sources used to feed this every growing need are a constant battle and concern in the United States. Reliance on renewable resources would limit the use of petroleum, natural gas, and coal, which are nonrenewable fossil fuels. These resources take millions of years to replenish, and our supply is slowly running out. Renewable resources like hydroelectric power, solar power, and wind power are all options that are a financial investment to start but cost less over time, have a dramatically less negative impact on the Earth, and do not run out. The idea to increase the reliance on renewable sources and decrease the dependence on nonrenewable sources is a scientifically based idea that is reasonable and may work. Using electricity derived from wind, water, or solar power will be beneficial to decreasing emissions.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Blin and Dev are brainstorming ideas to help protect Earth's resources. They know there are decreasing numbers of pollinators for fruit and vegetable plants. These resources are vital to providing us with the food we need to eat. How can Blin and Dev help protect the pollinators we have and increase their numbers?
Blin and Dev are brainstorming ideas to help protect Earth's resources. They know there are decreasing numbers of pollinators for fruit and vegetable plants. These resources are vital to providing us with the food we need to eat. How can Blin and Dev help protect the pollinators we have and increase their numbers?
Blin and Dev are highlighting a significant problem around the world - the reduction of pollinators. These are one of Earth's vital resources because they help plants reproduce and make the fruits and vegetables we consume daily. Pollinators can be birds, bats, bees, butterflies, and many other creatures. They spread pollen from one plant to another, allowing the plant to become fertilized. Planting flowers that bloom in a variety of colors will attract different pollinators to the different colored color petals. This will increase the likelihood of plants being fertilized and reproduction occurring.
Blin and Dev are highlighting a significant problem around the world - the reduction of pollinators. These are one of Earth's vital resources because they help plants reproduce and make the fruits and vegetables we consume daily. Pollinators can be birds, bats, bees, butterflies, and many other creatures. They spread pollen from one plant to another, allowing the plant to become fertilized. Planting flowers that bloom in a variety of colors will attract different pollinators to the different colored color petals. This will increase the likelihood of plants being fertilized and reproduction occurring.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The Environmental Protection Agency issues reports on many factors that impact the Earth's environment. The following graph highlights the area of growth in the United States and our emissions. The EPA explains the graph's data, "Between 1970 and 2018, the combined emissions of the six common pollutants (PM2.5 and PM10, SO2, NOx, VOCs, CO, and Pb) dropped by 74 percent. This progress occurred while the U.S. economy continued to grow, Americans drove more miles, and population and energy use increased."

CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) emissions have been on the decline according to the graph. Which answer choice(s) could be a reason for this reduction in emissions?
The Environmental Protection Agency issues reports on many factors that impact the Earth's environment. The following graph highlights the area of growth in the United States and our emissions. The EPA explains the graph's data, "Between 1970 and 2018, the combined emissions of the six common pollutants (PM2.5 and PM10, SO2, NOx, VOCs, CO, and Pb) dropped by 74 percent. This progress occurred while the U.S. economy continued to grow, Americans drove more miles, and population and energy use increased."

CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) emissions have been on the decline according to the graph. Which answer choice(s) could be a reason for this reduction in emissions?
Clean air is essential for all citizens of the United States, and according to the EPA, many of our emissions have decreased in recent years, but there is still room for improvement. Hybrid vehicles and electric vehicles have come down in price, making them more affordable for the everyday driver. This new access to an alternative full vehicle reduces the emissions produced. Many cities are improving their public transit infrastructures allowing residents to use busses, trains, and high-speed rail systems to travel. This reduces the number of individual drivers on the roads, so there are fewer emissions.
Clean air is essential for all citizens of the United States, and according to the EPA, many of our emissions have decreased in recent years, but there is still room for improvement. Hybrid vehicles and electric vehicles have come down in price, making them more affordable for the everyday driver. This new access to an alternative full vehicle reduces the emissions produced. Many cities are improving their public transit infrastructures allowing residents to use busses, trains, and high-speed rail systems to travel. This reduces the number of individual drivers on the roads, so there are fewer emissions.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Pankaj is presenting helpful tips for protecting Earth's resources to his class tomorrow. He is running through his speech and finds an error with one of the pieces of advice. Which tip is NOT a helpful way to protect Earth's resources?
Pankaj is presenting helpful tips for protecting Earth's resources to his class tomorrow. He is running through his speech and finds an error with one of the pieces of advice. Which tip is NOT a helpful way to protect Earth's resources?
Pankaj has included useful tips for his teacher and classmates, but there is one that he should not recommend that they follow, "Run the dishwasher only when empty.". This would be quite a waste of water and would not conserve resources. Pankaj should suggest that the dishwasher be run when full so water and electricity are not wasted. Water is a precious natural resource and should not be lost on just a few dirty dishes
Pankaj has included useful tips for his teacher and classmates, but there is one that he should not recommend that they follow, "Run the dishwasher only when empty.". This would be quite a waste of water and would not conserve resources. Pankaj should suggest that the dishwasher be run when full so water and electricity are not wasted. Water is a precious natural resource and should not be lost on just a few dirty dishes
Compare your answer with the correct one above